The importance ofmetal weldingin modern manufacturing is self-evident. It is a bridge connecting the manufacturing world and one of the key technologies to achieve complex structural design and product manufacturing. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous expansion of application fields, metal welding technology will play a more important role in the future manufacturing industry. Sowhat is metal welding?Today I will take you to learn the definition, basic principles, main methods, and application areas of metal welding.
What is metal welding?
Metal welding is an operationthat joins two or more metal objects (of the same or dissimilar metals) together through heat or pressure, or both. The metal welding method can be used to join two related metals together perfectly and it is an important construction related activity that is usually used to join materials together by applying heat. Welding processes include various types and methods, such as arc welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, and rod (lead arc) welding, each with its own unique characteristics and uses.Metal welding is widely used in many fieldssuch as machinery manufacturing, shipbuilding, aerospace, automobile manufacturing, petrochemical industry, electronic technology and construction.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of metal welding?
As an important joining technology,metal welding has a series of advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Welding establishes strong, durable, and permanent joint links. | It is hazardous when performed under the safety and security guidelines. |
| It is a simple process that results in a great finish. | It is a difficult task to dismantle the joined material through welding. |
| The technique, when used with filler material, produces a stronger weld than the base material. | Requires skilled labor and electric supply. |
| It can be performed at any place. | |
| It is an economical and affordable process. | |
| It is used in various sectors like construction, automobile, and many more industries. |
What Are the Common Materials Used in Metal Welding?
There are manymaterials commonly used in metal welding. The following are some common metal materials and their applications in welding:
1 Steel:
- Mild steel:has good weldability and is often used to manufacture various structural parts and components.
Medium carbon steel: such as 45 steel, which has good comprehensive mechanical properties and is often used to manufacture high-strength moving parts, such as turbine impellers, compressor pistons, etc. - Alloy steel:such as 40Cr, which has good comprehensive mechanical properties after quenching and tempering. It is often used to manufacture medium-speed and medium-load parts, such as machine tool gears, shafts, etc. Mold steel is also a type of alloy steel and is often used to manufacture various molds.
2. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys:
Aluminum alloys are lightweight and corrosion-resistant and are widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronic equipment, and home appliances industries. Laser welding of aluminum alloys can produce welded enclosure with extremely high strength and no risk of pores or cracking.
Stainless steel includes austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel and martensitic stainless steel. Austenitic stainless steel has good welding performance, ferritic stainless steel has strong toughness, and martensitic stainless steel has unsatisfactory welding effect but low cost. Stainless steel is commonly used in the food and medical industries due to its hygienic properties.
4. Copper and Copper Alloys:
Copper and its alloys have high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and strength. Laser welding can weld copper materials quickly and efficiently and can be used to manufacture complex structural parts and electronic components. Copper and copper alloys are also commonly used in electrical and decorative applications.
5. Cast iron:
Although cast iron has poor weldability, it can still be used to repair some important cast iron parts after proper welding repair processes, such as preheating and selecting appropriate welding rods.
6. Other non-ferrous metals:
Such as titanium, nickel, tin, chromium, niobium, gold, silver and other metals and their alloys. These metals show different welding characteristics in laser welding or other welding methods, and can be selected according to specific needs.
7.Special alloy:
Such as nickel-based alloys, cobalt-based alloys, etc. These alloys have special physical and chemical properties and are often used for welding in harsh environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion.

What Are the Different Types of Metal Welding?
Metal welding is an important process for joining metals.Welding methodscan be divided into many types according to the degree of heating and process characteristics during the welding process. Here are some common types of metal welding:
1. MIG Welding (Gas Metal Arc Welding – GMAW)
An arc welding method that uses a molten electrode and an external gas as the arc medium to protect the metal droplets, welding pool and high-temperature metal in the welding zone. The protective gas usually uses inert gas (such as argon or helium), which is suitable for welding materials such as aluminum and aluminum alloys, copper and copper alloys, and stainless steel. There is almost no oxidation and burning loss during the welding process, the metallurgical process is simple, and the cost is relatively low.
2. TIG Welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding – GTAW)
A non-melting tungsten electrode is used to generate an arc under the protection of inert gas to heat and melt the workpiece. The welding quality is high and it is suitable for high-quality welding of various metal materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc. The arc is stable and the thermal efficiency is high, enabling high-speed and continuous welding.
3. Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding – SMAW)
An easy-to-operate and highly flexible welding method that can adapt to the welding needs of various steel materials, different thicknesses and various spatial locations. The quality of the weld is greatly affected by the technical level of the welder, which requires the welder to have high operating skills and experience. The equipment is simple and low-cost, and is suitable for welding small batches, multiple varieties, and complex-shaped workpieces.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
The meltable flux-cored welding wire is used as the electrode, the base material is used as the other electrode, and pure CO2 or CO2+Ar gas is used as the protective gas. The welding wire is filled with a flux mixture that creates a thin layer of liquid slag that envelops the droplets and covers the molten puddle during welding, providing additional protection. It is suitable for automatic welding, semi-automatic welding or fully automatic welding. It has high welding efficiency and is suitable for welding carbon steel, low-parameter alloy steel, stainless steel and cast iron.
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
The arc burns under the flux layer, and the machine automatically completes arc ignition, electrode feeding, arc movement and other actions. The welding current is large, the productivity is high, and the penetration depth is large, which can save groove processing time and welding materials. The protection effect is good, the metallurgical process is perfect, the welding parameters are stable, and the weld shape is beautiful. However, the adaptability is poor, it is only suitable for flat welding positions, and the equipment structure is complex and the investment is large.
How does welding processes affect metal selection?
1. MIG Welding (Gas Metal Arc Welding – GMAW)
- Metal type:MIG welding is suitable for stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper and other metals. Similar to TIG welding, MIG welding also uses inert gas (such as argon) or reactive gas (such as carbon dioxide or mixed gas) for protection. For welds that require higher welding speed and larger penetration depth, MIG welding is a more suitable choice.
- Limitations: MIG welding has high requirements on the welding environment, and the gas protection effect needs to be ensured to avoid weld oxidation.
2. TIG Welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding – GTAW)
- Metal type:The biggest advantage of TIG welding is that it can weld a variety of metals and alloys, including stainless steel, nickel alloys, titanium, aluminum, magnesium, copper, etc. Its arc is concentrated and the heat input is controllable, making it ideal for welding thin plates and high melting point metals. For active metals (such as aluminum, magnesium) and their alloys, TIG welding can effectively prevent oxidation due to its inert gas protection (such as argon) and ensure the quality of the weld.
- Limitations:Although TIG welding is widely applicable, it may be less efficient for high-volume production and thick plate welding.
3. Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding – SMAW)
- Metal type:Arc welding can weld carbon steel, low alloy steel, stainless steel and other metals. It protects the weld seam through the gas and slag generated by the welding rod coating and avoids contamination of the weld seam by oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere. For welds with complex structures that are difficult to mechanize or automatically weld, arc welding has good adaptability.
- Limitations:The welding efficiency of arc welding is relatively low and requires high skills of the welder.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- Metal type:Flux-cored wire arc welding combines the advantages of electrode arc welding and gas shielded welding, and is suitable for welding a variety of metal materials. The welding wire is filled with powder, which melts during the welding process and produces protective gas and slag to protect the weld. It is especially suitable for occasions where high-quality welds are required, such as the welding of pressure-bearing equipment.
- Limitations:Flux-cored arc welding has high requirements on wire quality and welding process. It is necessary to ensure that the powder powder is evenly distributed and the welding parameters are reasonable.
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
- Metal type:Submerged arc welding is widely used in the welding of heavy workpieces such as steel structures, boilers and pressure vessels due to its high efficiency, high quality and ease of automation. It is suitable for welding carbon steel, low alloy steel and other ferrous metals, but there are applicability problems when welding non-ferrous metals (such as copper, aluminum, magnesium) because its high thermal conductivity and easy oxidation may lead to poor welding quality.
- Limitations:Submerged arc welding has high requirements on the welding environment, and it is necessary to ensure uniform flux coverage and stable combustion.
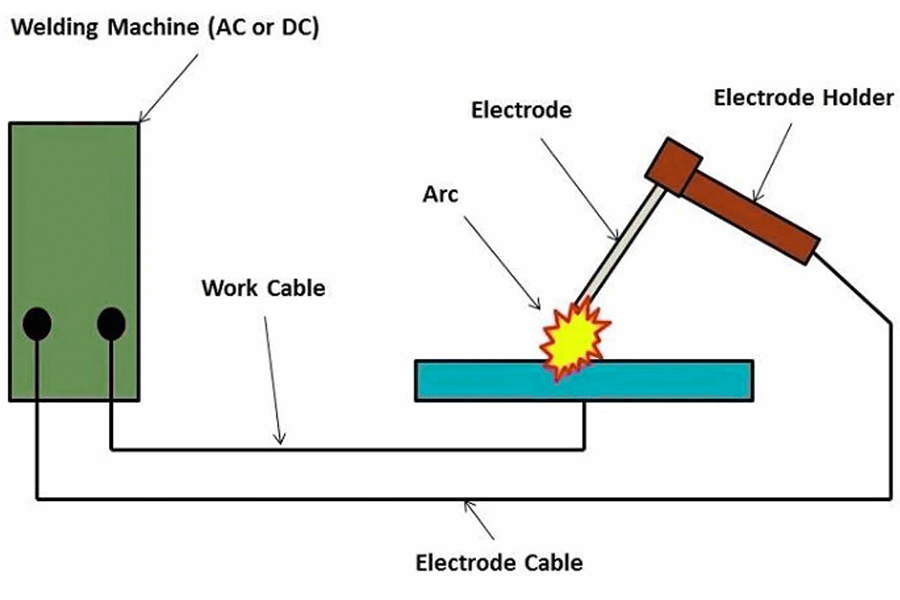
What Tools Are Essential for Metal Welding?
The tools and equipment required for metal welding mainly include welding machines, electrodes, welding clamps, filling materials, etc.
1. Welding machine
Thewelding machineis the core equipment for metal welding and is used to convert electrical energy into the heat energy required for welding. Common welder types include:
- Welding machine: A welding power source used to convert alternating current into low voltage and high current. It is an essential equipment in welding operations.
- Laser welding machine: Using laser beam as a heat source for welding, it has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and small heat affected zone.
- Ultrasonic welding machine: The energy generated by ultrasonic vibrations melts and joins metals together, suitable for welding some specific materials.
2. Electrode
Electrodes play the role of transmitting current, melting metal and forming welds during the welding process. Depending on the welding method, the form of the electrode is also different:
- Welding rod:In electric welding, the welding rod acts as an electrode and consists of a metal core and a coating. When the welding rod comes into contact with the weldment and is energized, the welding rod melts and forms a weld with the weldment.
- Welding gun electrodes:In gas welding or some special welding methods, the welding gun may contain electrodes for generating and maintaining an arc or flame.
- Resistance welding electrode:In resistance welding, the electrode is used to clamp the weldment and pass electric current, so that the weldment melts and joins together under the action of resistance heat. These electrodes are usually made of materials such as copper, chromium, zirconium and copper that are resistant to high temperatures and have good electrical conductivity.
3. Welding clamp
Thewelding clampis a tool used to hold the welding rod and transmit the welding current during welding operations. It not only ensures that the welder can control the electrode stably during the welding process, but also protects the welder's hands from high temperature and arc light to a certain extent. Therefore, a welding clamp can also be considered a type of safety gear.
4. Filling materials
In some welding methods, in order to increase the strength and sealing of the weld, filler materials need to be used:
- Welding wire:In welding methods such as gas shielded welding and gas tungsten arc welding, the welding wire is fed into the weld as a filler material and forms a weld together with the molten base metal.
- Solder:In low-temperature welding methods such as soldering, solder is used to fill the weld and join the metal parts. Solder is usually made of metal alloys with low melting points, such as tin-lead alloys.
FAQs
1.What is the meaning of metal welding?
Metal welding is an important metal processing method. Its significance is mainly reflected in the fact that welding can connect metal materials of different materials, shapes, and sizes together to form an overall structure, thereby improving the strength and stability of the structure. Through welding, damaged metal parts can be repaired and their service life extended, and metal parts can be processed and transformed to meet specific use needs. Welding plays an important role in the production of metal products, such as steel structures, metal pipes, railway tracks, etc., which are manufactured through welding technology.
2.What welding metal is used?
When welding metal, the welding method used mainly depends on factors such as the material, thickness, strength requirements, and production conditions of the metal. The following are some common welding methods and their applicable metal materials: Arc welding: Suitable for welding of various metal materials, including steel, aluminum, copper, etc. Common arc welding methods include manual arc welding, submerged arc welding, argon arc welding, etc. Gas welding: Using the combustion of oxygen and gas to produce high temperatures, it is suitable for welding thin metal materials and alloys with lower melting points. Laser welding: With high precision and efficiency, it is suitable for welding precision parts and thin plate materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc. Resistance welding: suitable for welding small metal parts such as thin plates and filaments, as well as metal structures that require high-strength connections.
3.What is welding and its uses?
Welding is a method of joining adjacent workpieces together by applying heat or pressure, or both, with or without filler material. Welding is used in a wide variety of applications, and metal welding plays an important role in the development of aircraft, spacecraft, and other transportation industries. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is used in aircraft and other transportation industry developments where the precision of GTAW works well with aluminum and specialty alloys for weight reduction and fuel consumption reduction. Metal welding technology is widely used in the construction industry to create structurally strong steel frames by fusing various steel components. In addition, metal welding is widely used in the manufacture of pressure vessels, bridges, building structures, aircraft and spacecraft, railway coaches and general purposes, as well as in shipbuilding, automotive, electrical, electronics and defense industries. Metal welding is also widely used in the automotive industry for a variety of purposes including vehicle repair, production of fuel tanks, pressure vessels and pipes.
4.What is the principle of welding?
Simply put, the principle of welding is to use heat to melt metal materials and form a bond between metals. The specific process mainly includes: ①Heating: When welding starts, the metal at the weld needs to be heated by a heat source to bring it to the melting temperature. ② Melting: Under the action of the heat source, the metal at the weld gradually melts to form a molten pool. The metal atoms in the molten pool lose their binding force and can move freely. ③Cooling and solidification: The molten pool will gradually solidify after cooling, forming a solid metal combination. During the solidification process, the metal atoms in the molten pool rearrange to form a crystal structure. ④Metallic bonding: Through the process of heating, melting and cooling, the metal atoms in the welding part diffuse and combine with each other, forming a strong connection.
Summary
Metal welding is a method of joining adjacent workpieces together by applying heat or pressure, or both, with or without filler material. Metal welding is a colorful technology that is not only widely used in various industries, but also provides strong support for achieving high strength, high precision, high reliability and durability. With the continuous development and innovation of welding technology, metal welding will continue to play a more important role in the future.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
This article was written by multiple LS contributors. LS is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.



