PLA (Polylactic acid) and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) are two of the two most commonly used thermoplastic filament materials in 3D printing. Due to its unique performance differences, it is widely used inPrototype Manufacturing, functional components and industrial production.
PLA dominateseducational modelsand consumer packaging due to its biodegradability and low cost, while PET has become a mainstream choice for precision parts and electronic and electrical packaging due to its high strength and temperature resistance. In this paper, the physical characteristics, processing parameters and practical application scenarios of the two are systematically compared in order to provide material selection basis for3D printingpractitioners and product designers.
What is PLA?
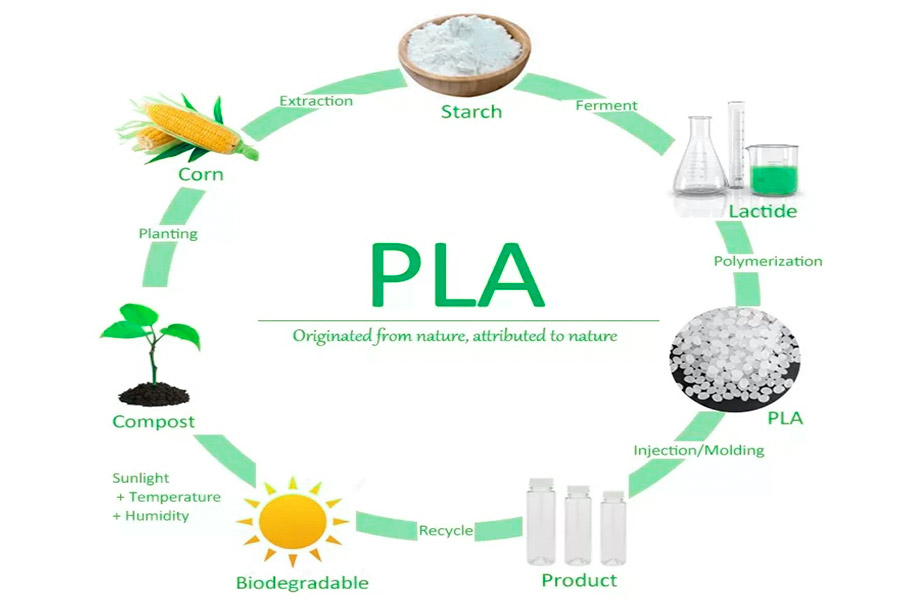
PLA (Polylactic acid)is a renewable biobased polymer synthesized from lactic acid and widely used in 3D printing, packaging, healthcare and other fields. It is fermented from corn, sugar cane and other plant starch, has a certain degree of material flexibility and temperature resistance. PLA is glassy at room temperature and has a melting point of about 150-160 ° C, but should not exceed 80 ° C in long-term use or be susceptible to softening or degradation.
Its biggest feature is completebiodegradability, which can be broken down into carbon dioxide and water in about 6 months under industrial composting conditions (55-60 ° C), and the carbon emissions its production are much lower than from conventional petroleum materials (such as PET). However, its temperature resistance and impact resistance is relatively weak and requires modification (such as adding TPU or benzene ring structure) or copolymerization with other materials to improve its performance.
What is PET filament?
PET filamentis a synthetic fiber or 3D printing consumable made from polyethylene terephthalate. It is widely used in industrial manufacturing, packaging, textile and electronic products. Through condensation reaction, rigid aromatic molecular chain is formed, which makes the material have the characteristics of high strength, chemical corrosion resistance and excellent dimensional stability.
PET filaments have a melting point of 220-260 ° C and a long-term temperature of around 120 ° C, but are prone to yellowing under UV irradiation and require antioxidants to slow aging. In 3D printing, PET are typically used to produceprecision mechanical parts, abrasionresistant tools, or components (such as battery battery separators circuit circuit board insulation that require high temperature resistance resistance due to its high modulus ((3-5 GPa) and impact resistance.
What are the characteristics of PLA and PET filament?
Characteristics of PLA filaments
1.Ability to work
- Low melting point (approx. 150-160 ° C), does not require high temperature equipment for printing, suitable for desktop printing.
- Fluidity is good, it is not easy to block the nozzlein printing process, strong interlayer adhesion, reducing the problem of edge curling and voids.
2. Chemical stability
- Strong acid and alkali resistance: stable to weak acids, base and most organic solvents, suitable for chemical packaging orelectronic componentpackaging.
- UV sensitivity: Long-term exposure can cause skin to turn yellow, and antioxidants or UV absorbers need to be added to slow aging.
3. Application flexibility
- High surface smoothness:Printed surfaceis fine and can be used for appearance parts (such as phone cases) without the need for post polishing.
- Multifunctional modification: performance boundary can be extended by copolymerization (e.g. PETG) or coating processes (e.g. conductive coatings).
4. Limitations
- Processing difficulty: high temperature is easy to produce odor, released carbon 2 gas, temperature control needs to be strictly controlled to avoid degradation of the material.
- The nozzle Easy clogging: Powdered residue can clog the nozzle and needs to be cleaned regularly.
- Environmental challenges: Traditional PET depend on fossil resources and are difficult to degrade after disposal (microplastic pollution risk).
What are the differences between PLA and PET film?
1.Physical characteristics
| performance | PLA(Polylactic acid) | PET |
| Melting temperature | 150–160°C | 220–260°C |
| Glass transition temperature | 60–65°C | 75–85°C |
| tensile strength | 20–40 MPa | 50–80 MPa |
| Bending modulus | 1.5–3 GPa | 3–5 GPa |
| thermal stability | Long term use temperature < 80 ° C | Long term use temperature < 120 ° C |
2. Chemical stability
- Polylactic acid: resistant to weak acid/base but easily degrades at high temperature (>100 ° C) and soluble in strong solvents (e.g. chloroform).
- PET: Acid-base resistant, but sensitive to ultraviolet light, easy to yellow after long-term exposure.
3.3D Printing Parameter Settings
| parameter | PLA(Polylactic acid) | PET |
| Recommended extrusion temperature | 180–220°C | 240–280°C |
| Floor height | 0.1–0.3 mm | 0.1–0.25 mm |
| Printing speed | 30–60 mm/s | 20–40 mm/s |
| Fan control | Need to be activated to reduce interlayer adhesion | Need to be closed to avoid material carbonization |
4. Finished product characteristics and applications
- PLA(Polylactic acid):PLA has good biocompatibility and biodegradation, moderate strength and heat resistance, and is suitable for 3D printing applications where material properties requirements are not particularly high.
Main uses: rapid prototyping,educational tools,medical equipment.
- PET:The finished products PET has excellent physical and chemical stability and can be adapted to 3D printing with high material performance due to its high strength and heat resistance.Compared with PLA, its biocompatibility and degradability are poor.
Main uses:consumer electronics,auto components,aerospace components.
What filament is better than PLA?
- ABS Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene):ABS has high strength and heat resistance and can withstand higher temperatures and loads. Its interlayer adhesion is generally superior to PLA, especially in enclosed printing or devices with heating beds.
- PETG (polyethylene terephthalate 1,4-cyclohexanediate):PETG combines PLA printability with ABS durability while providing better transparency and gloss. It also has lower warping tendency and warping and excellent interlayer adhesion.
- Polyamide:Nylon filament are characterized by high strength, toughness and wear resistance. It also has good moisture absorption and is stable in humid conditions.
- PC (polycarbonate):PC is highly shock resistant, heat resistance and transparent. It also protects against ultraviolet light and chemical corrosion.
What are the impacts of PLA and PET filament on environmental sustainability?
1. Sources of raw materials and resource consumption
- PLA(Polylactic acid)
Renewable:mainly from corn, sugar cane and other plant starch, fermented into lactic acid, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Carbon emissions: Production is about 30% lower than PET, but material cultivation may involve pesticide use and water resource consumption.
- PET
Fossil fuel dependence: The feedstock is petrochemicals (PTA and MEG), with high carbon emissions extraction and transport.
Non renewability: Long-term dependence on limited resources and fluctuations in crude oil prices affect cost stability.
2.Environmental impacts during production
- PLA(Polylactic acid)
Low energy consumption:Low melting point (150-160 ° C), lower processing energy consumption for printing processing than PET (220-260 ° C).
Wastewater and waste: Organic wastewater is produced fermentation process and needs to be treated rigorously to avoid contamination.
- PET
High energy consumption process: condensation reaction requires high temperature and pressure, and energy consumption is significantly higher than PLA.
Recycling: Waste silk produced during production can be recycled to reduce resource waste, but only 20-30% of PET is recycled globally.
3.Environmental impacts over the usage cycle
- PLA(Polylactic acid)
Temperature resistance and lifespan limitations: Long-term use at temperatures below 80 ° C leads to ageing and deformation, which can lead to frequent replacement (increased resource consumption).
Transport and storage requirements: Storage in a dry environment (humidity<30%) increases logistics energy consumption and packaging costs.
- PET
High strength, durability and longer service life than PLA reduce frequency of replacement and long-term resource occupation.
4.Recyclable resources
- PLA(Polylactic acid)
Biodegradability: Using industrial compost, it breaks down into CO ₂ and water (temperature and humidity conditions need to be controlled) within six months.
Incineration treatment: Incomplete combustion may produce toxic gases (e.g. dioxins).
- PET
Physical recycling: Bottle to bottle recycling technology is well-established but limited by the diversity of PET products such as coloured and blended materials.
Chemical recovery: Renewable monomers (terephthalic acid) is available through alcoholysis/hydrolysis processes, but at a high technical cost.

What factors should be considered when choosing PLA or PET in 3D printing projects?
In 3D printing projects,neither PLA nor PET is absolute "best" universal solutions, but requires a balanced selection based on specific needs. Here are the key determinants of both to help you find the most appropriate solution:
| factor | Prioritize PLA | Priority should be given to PET |
| Recommended choices | Desktop printing (low temperature), beginner friendly | Industrial grade equipment (high temperature), requiring technical experience |
| Cost sensitivity | Limited budget, small-scale production | Adequate budget and pursuit of high performance |
| Printing equipment | BasicFDM printing | Need enclosed printing chamber+constant temperature plate (to reduce warping) |
| Performance requirements | General mechanical performance and flexibility requirements | High strength, temperature resistance, chemical resistance |
| Environmental requirements | Biodegradation and carbon neutrality targets | Complete recycling system and lightweight requirements |
There is no absolute 'best', only more suitable solutions:
PLA is a compromise of "fast, low-cost, and environmentallyfriendly" as a 3D-printed consumable, suitable for prototype validation and simple scenarios.
PET is a high performance, durable, industrial-grade option for complex functional requirements.
It is suggested that according to the specific requirements, budget, time frame and environmental protection target of the project, combining with the results of the pilot work, the optimal decision should be made.
LS Teamis focused on providing global customers with full-process solutions covering high-precisionCNC machining,3D printing, rapid prototyping development, and more. Whether you're a startup or an industry leader, clicking on upload design files can provide a one-stop, quick-response service from technology assessment to cost optimization to meet your specific time, cost and project needs.
What are the applicable scenarios for PLA and PET film?
PLA(Polylactic acid):
- Prototype production and Education Model:Rapid validation of design concepts with low cost and high safety (suitable for students or DIY enthusiasts).
- Packaging and containers: Disposable tableware, food boxes, storage boxes (use at low temperatures to avoid heat distortion).
- Decorative parts: Low precision ornaments, display models, jewelry pedestals (available with high-gloss or translucent variants).
- Medical and biological field:temporary models of medical devices, biodegradable implants (subject to biocompatibility standards).
PET (polyester):
- Functional parts:mechanical components, buckles, hinges (subject to certain stresses or vibrations).
- Electronics casing: Phone case, charger holder (high temperature resistance, good insulation).
- Outdoor gear: camping gear, sealants (UV protection, rain protection).
- Pipes and containers: Lightweight pipes and storage boxes (pressure-resistant and lightweight).
Summary
PLA is fermented from plant starch.Polyester fibers are characterized by biodegradation, low carbon emissions and low temperature processing, but have low melting point and limited mechanical strength. Based on petrochemical resources (PTA + EG condensation condensation), PET can melting point up to 260 ° C. and have high strength, chemical resistance and thermal stability, but are non-degradable and energy-intensive for processing.
When it comes to applications,PLA dominates the market for 3D printing, lightweight products, and single-use consumer goods, with PET focusing on industrial packaging, high-performance fiber, and engineered components.The two are not completely interchangeable: PLA is suitable for low-cost, biofriendly situations, while PET is more competitive in areas of high mechanical strength and environmental adaptability requirements.

Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1.Can PET filaments replace PLA?
PLA is a biodegradable polymer with poor thermal stability, limited heat resistance and high temperature easy deformation. By contrast, PET plastic is a thermoplastic polyester with excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance and chemical stability.
2.What is the difference between PLA and PET plastic?
PLA is a biodegradable polymer with poor thermal stability, limited heat resistance and high temperature easy deformation. By contrast, PET plastic is a thermoplastic polyester with excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance and chemical stability.
3.What are the common processing issues of PLA and PET filaments in 3D printing?
Easy edge curling and layering, high temperature deformation, stress cracking, limited printing speed (poor PET fluidity, slow printing), smell release (PET material decomposes easily at high temperatures), surface roughness.Optimizing temperature, floor height, scaffolding settings and selecting modified materials,such as PETG, can alleviate some of the problems.
4.Which is more suitable for 3D printing technology, PLA or PET film?
PLA is better for 3D printing. It has the advantages of rich color, smooth surface, convenient processing, no heating bed, less warping and solvent resistance. PET films are not specifically designed for 3D printing. The most common type of 3D printing is PETG, or PET film, which has a higher printing temperature and higher environmental requirements. Overall, PLA is better suited to 3D printing.