Rapid prototyping services will always be required in the context of product development, and the fact of the matter is that there would always have been complexities regarding quotations and delivery of quality. Hence, there would always have been delays regarding the development of products and the market opportunities would always have remained inaccessible.
The problem arises as a result of the opaque pricing, RRS, and the ability of the normal manufacturing companies. For the challenges to be met, the LS Manufacturing applies an efficient rapid prototyping method that entails opaque pricing, successful production, and also the control of quality for the provision of high-quality goods to the client within the shortest time possible.

Rapid Prototyping Services: Quick Reference Guide
| Section | Key Points |
| Industry Pain Points | Quoting, lead times, and quality uncertainty. Inhibit dvlpment and entry. |
| Root Causes | Cryptic Pricing, Inadequate capacity, lack of standardized fast response processes. |
| Core Solution | Standardized and transparent quotation. Fast turnaround manufacturing. In-house quality control system. |
| Key Benefits | Time-to-market is shorter, as costs are fixed and assured quality is provided with decreased risk associated with projects and effective development processes. |
| Common Technologies | 3D printing (SLA, SLS, FDM), CNC machining, vacuum casting, sheet metal rapid prototyping. |
| Material Options | Material options plastics (ABS, Nylon, Resins), Metal (Aluminum, Steel), Silicon |
| Ideal Applications | Form and fit testing, Function testing, Feedback, Model presentation, Pilot production runs. |
The rapid prototyping services are closing the gap that existed in the design and mass production phases, allowing innovation to occur at a fast pace. Rapid prototyping relates to the challenges that exist regarding time, the cost factors that must be addressed, as well as the aspects of speed and quality required for innovation to occur at a fast pace.
Why Trust This Guide? Practical Experience From LS Manufacturing Experts
Because it’s not theory. It’s from the front lines. Our shop isn’t a clean lab. It’s a living environment and we are faced with real-world problems on a daily basis. We are not just knowledge-filled in the area of rapid prototyping. We do this knowledge. It is chaos that a prototype can present when it is faced with functionality testing. It is important that the finish presented at presentation prototype is indicative of confidence and financing. It is through precise prototype that millions are produced successfully.
Over the many years, we have been capable of producing well over tens of thousands of custom rapid prototypes. Each project we tackle is something that we have learned from, whether it is optimizing prototypes for maximum strength, incorporating designs from reputable sources such as NIST Materials Data, to combining rapid prototypes with accuracy. Our process integrates industry standards and continually updated knowledge, referencing resources like Wikipedia for the latest in materials science and technologies.
Every single recommendation that has been made throughout the progression of this guide has been honed through personal trials that have been perfected through implementation. We share what we know so that we can avoid mistakes that may have been encountered by people developing an e-learning system.
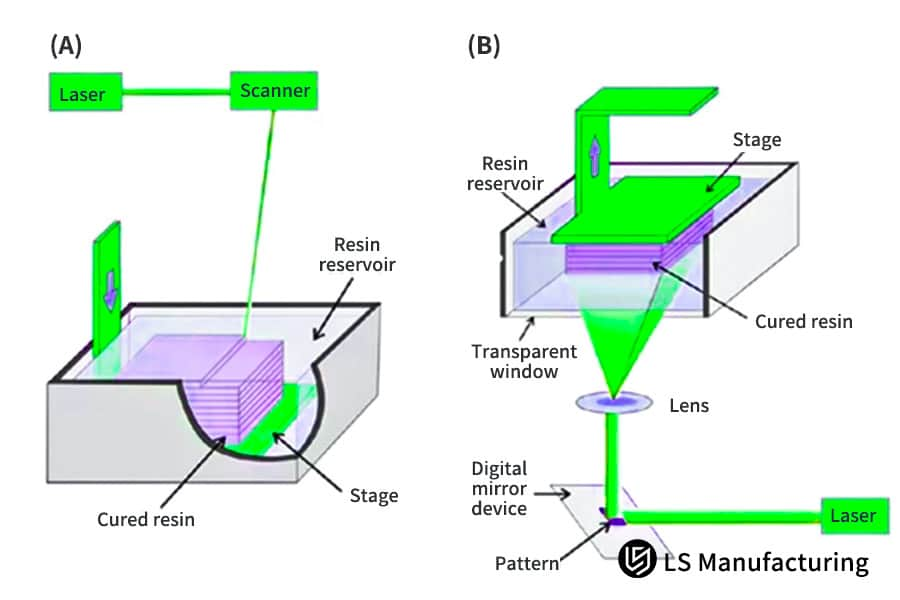
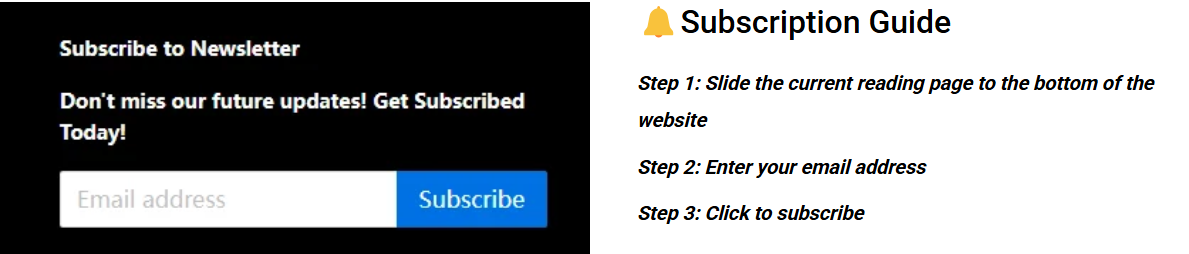
Figure 1: Laser-assisted rapid prototyping process and its working diagram by LS Manufacturing
How Can Professional Rapid Prototyping Services Help Companies Accelerate Product Development Cycles?
The process from concept to market is highly competitive. Expert rapid prototyping services are highly essential for the product development acceleration, as these help to skip the conventional long process in favor of new technology-based fast track processes that facilitate a first mover advantage against competition in the market. Certain key tools and mechanisms for this process would include:
Integrated Advanced Technology Solutions to Maximize Speed
In this way, by leveraging the power of multiple advanced technologies such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and vacuum casting, all product services ensure the usage of the most advanced technology always. It thereby enables the handling of design changeover in a real-time manner by removing bottlenecks to thereby ensure rapid iterations to accelerate the product development acceleration.
Standardized Systems for the Predictable Timeline
Predictability is the most challenging aspect of this procedure. The larger players in this industry have implemented a quote and production system. It is this that makes it possible to maintain this quick turnaround time, like 24 hour quotes and 3-5 days delivery, that is necessary to keep up with the timeline of this project.
Dedicated Capacity to Eliminate Queues
Acceleration is impossible with limited bandwidth. A robust service provider maintains a dedicated fleet of advanced equipment. This dedicated capacity ensures immediate job scheduling, by passing the typical delays of shared production lines and guaranteeing that your project receives immediate attention for a true fast turnaround.
Validation for Risk Mitigation
Velocity without confidence is nothing that should be encouraged in the context of validation. Rapid prototyping services is applicable to the validation of shape, functionality, and fitness for the early phases of the risk cycle. It would assist in the possible errors in design for the early escape of design errors and would thereby lower the design life cycle of the project.
In conclusion, professional rapid prototyping services can be termed as strategic accelerators. This is because they compact time scales through flexibility offered by technology, predictability of the process, and synchronizing resources. This integrated approach facilitates a faster, more reliable iteration loop, directly contributing to significant product development acceleration and ensuring a fast turnaround from initial idea to market-ready product.
What Are The Key Steps In The Core Technical Process Of Rapid Prototyping?
The projects accomplished by the use of rapid prototyping are anything but a machining operation. In fact, projects accomplished by the use of rapid prototyping comprise a well-choreographed series of operations. The above steps comprising the technical process comprise a series of procedures created in a way that they ensure accuracy, speed, and reliability—a converted computer-aided design file into a correct model for analysis. The above series of operations may be divided into a series of crucial steps:
| Stage | Key Activities |
| Design & File Review | Review of the design files in 3D CAD format to decide the manufacturer-ability of the design and provide feedback on the design changes. |
| Process & Material Selection | Based on the requirement, selection of the technology and the material. CNC machines, 3D printer, etc. |
| Automated Quoting & Planning | The use of AI technology to generate an instantaneous production plan as per the complexity level. |
| Digital Preparation & Setup | Preparation of machine, orientation of a part, and preparation of the support structure. |
| Production & Build | The build stage where the object shall be produced using the selected processes of additive/subtractive. |
| Post-Processing | Removing supports, sanding, polishing, painting, or assembling components to achieve the desired final finish. |
| Inspection & Delivery | Final dimensional inspection, verification against specs, and meticulous packaging for safe shipment. |
In conclusion, the rapid prototyping technical process that begins with a file and ends up with a completed product. This requires a level of knowledge that should be acquired at a particular stage, along with a smooth transition that should take place from one stage to another. More importantly, it should be noted that an entire process for quality control takes place within a prototype that is quick.
How To Quickly Obtain An Accurate Quote For A Custom Rapid Prototyping?
In order for the custom rapid prototyping quote to be achieved properly and effectively, the initial step has an important role to play. In most instances, the biggest problem lies with ensuring that the custom rapid prototyping quote possesses the quick quotation and that it truly takes into account the complexity involved within the custom rapid prototyping task. Among the most crucial factors that will enable a rapid and accurate quote to be provided are:
- Comprehensive Project Documentation: It is essential for the purpose of pricing that it needs to be carried out with foresight. The document containing full information about the 3D CAD files, material, surface finish, and levels of tolerance does away with uncertainties. The submission of the document also enables an in-depth feasibility study to be carried out by the supplier of the services to make sure that the technology of processing being used is feasible and the calculation for pricing has been carried out on exact, and not approximate, information.
- Intelligent Automated Analysis: Manual quoting is not only time-consuming, it also entails several errors. More intelligent organizations utilize the Internet for the instantaneous analysis of file geometry by using AI technology. This automated analysis is the engine behind a reliable quick quotation, compressing what could take days into hours.
- Transparent Cost-Breakdown System: The actual custom rapid prototyping quote is not fixed in one amount. You would require a transparent cost-breakdown system so that you could bifurcate the total cost of the raw material and the machine cost and human resource cost.
- Collaborative Feedback Loop: The quotation is best accomplished through dialog. This stage of processing for the first quotation phase of design is where the service can start the early elements of the feedback loop with a view to designing the review of Design for Manufacturability (DFM). There are large components of cost savings at this early stage of proposed change that could potentially optimize the quotation.
Thus, the importance of coming up with the right, right, and correct custom rapid prototyping quote is significantly reliant on the inputs as well as the processing part related to the supplier. The inputs related to documentation, intelligence analysis, among others, are the aspects by which the accurate pricing is obtained, which is primarily important as far as the project is concerned.

Figure 2: On-demand injection molding prototyping and quick-turn online production services by LS Manufacturing
Analysis Of The Working Principle And Applicable Scenarios Of Rapid Prototyping Technology?
Understanding how rapid prototyping works is key to unlocking its full potential. Rapid prototyping is treated as the possibility of an alternate for the traditional tool and manufacture since the models are developed on the basis of the 3D idea of the dimension on either additive sub-layer processing or accuracy of subtraction machining. The following table outlines common methods and their primary application scenarios for effective process selection:
| Technology | How It Works (Simplified) | Ideal Application Scenarios |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Very detailed: UV laser solidified liquid plastic. | Very detailed models, vision protos, master models for injection mold production. |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | The laser melted a layer of nylon or a material with which a bond was formed. | Application functional prot-os assemblies require functional elements. Parts for small-scale prod-uction require more prot-os components. |
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Filament extrusion of thermoplastic material from FDM. | Modelling basing on early concepts, functional verification of full-size parts, prototyping if form factor is not a subject. |
| CNC Machining | It includes the material being cut away by using CNC machining tools from the raw material. | The process is done to produce prototypes parts while working with special metals and engineering plastics. Already finished parts which require production at very tight tolerances can be achieved. |
The general concept for the working process of rapid prototyping technology involves the concept of direct digital fabrication. The technology application for the project does not produce successful results as the concept seems to apply to other projects. The criteria for selecting the type of technology to be employed cover material, accuracy, strength, and application.
How To Obtain The Fastest Prototype Quote While Ensuring Quality?
Innovation must be encouraged but this must not generate any cost in the form of trusts being established. The fast prototyping quote gathering, the need for the two aspects of satisfaction of the clients, as well as the need for the two aspects of the quality assurance regarding the servicing entity, may very well be taken from the perspective of the servicing entity. Finally, the most fundamental key elements that have a mandatory key role regarding the issue at hand are:
- Standardized and Parametric Cost Models: The reality concerning speed shall be appreciated when there will be no guessing at all involved. Quality services shall, therefore, generate an opportunity for providing the services of the standardized and parametric cost models; these models will then set the fees according to the file that will be uploaded and the processing of that particular file.
- Integrated Real-Time Production Intelligence: A quote is only good as its deliver date, and this shall only be attained if the quote is accurate, which in turn shall only be attained when the possibility of the quote becomes viable. The technology will be capable of leveraging the information which is being generated by the shop floor, based on information within the line lengths.
- Automated Initial Design Analysis: Speed carries out no critical analyses at all. Once the design is loaded, the quote engine carries out an initial manufacturability check and points out potential issues that might arise. These are areas intended to hang and walls that are either too small or not thick enough. This will enhance the ability of the quality assurance department because no designs that require hanging will go to production.
- Pre-Defined Quality & Cost Parameters: There has been a degree of unity in this scenario regarding the uniformity. The cost structure for this paper, therefore, will factor in the post processing activities: the pre-defined sanding activities, basic finish activities, as well as the inspection cycles regarding that. It would, therefore, be feasible to ensure that the basic fast prototyping quote estimate regarding quality assurance could be guaranteed. Define, refine, and look for a definition precisely.
This, therefore, encompasses that a true and fast prototyping quote cost for the creation of the prototype will come from an increased process that utilizes parameter models, the numbers for production, and checks, which will assist in delivering an efficient pricing system linked to the quick turnaround cycle, thereby employing parameters that are associated with the quality assurance from the start of the initial costing value.
What Key Capabilities Should Be Considered When Selecting A Rapid Prototyping Service Provider?
The supplier selection shall be analyzed by a strategic approach that shall impact the timeline and cost of success of the respective project. The right capability assessment of a rapid prototyping service provider would then be investigated within a framework that is more than just assessing cost, and would include even the key competencies that are being developed for guaranteed execution effect or partner effect. Key areas of focus and emphasis of effective supplier selection would then include:
Technical arsenal and production capabilities
The machines will form the backbone of the supplier. It will be important for a machine to be judged based on the capabilities of the machines being utilized. The capabilities will include using multi-axis CNC machines, 3D industrial printers, among others. The different capabilities will mean the supplier will be in a position to handle the challenges posed by materials of a different nature. They will be equipped with the right tool to handle your work.
Expertise and Support to Collaborate
The machines will be operated by humans. Assess the expertise of the vendor with regard to technology. Does the vendor bring in technical capabilities through a team of technicians that could provide a meaningful contribution in the region of design for manufacture, DFM? In addition to availability, the service component should also consider support to collaborate.
Quality Systems Certified
Consistency needs to be assured. The proper rapid prototyping service provider will be written in a certified quality system such as ISO 9001. This type of system will give a series of proven processes for traceability as well as consistency. Check their inspection process. They have to inspect during manufacturing as well as measure their completed parts.
Responsiveness & Project Management
The rate at which you carry out prototyping in your project needs to go past the rate at which the machines operate. You will have to assess the responsiveness of the vendors in operations. The rate at which they quote for your questions needs to be considered, in addition to notifications of updates in projects from a single point of contact.
In reality, the process of choosing a rapid prototyping provider must involve many aspects. Through their technical capability assessment, human skills, and process abilities to judge them, it would be possibly able to choose a supplier who would assist them to accelerate the entire development process of the products and just produce them.
Figure 3: Worldwide rapid prototyping industry expansion projections segmented by region by LS Manufacturing
What Are The Standard Procedures And Required Documents For Obtaining A Prototype Quote?
Initiating a new prototyping project starts with obtaining a clear and reliable cost estimate. Understanding the standardized prototyping quotation process and preparing the correct documentation requirements are the first critical steps to ensure a smooth workflow and an accurate pricing for your project. A streamlined and efficient quotation process typically involves the following key stages:
Initial Project Submission & Data Supply
The beginning of the entire process, of course, comes from your side, namely the customer submission of the following specified documents. Finally, the most fundamental documentation requirements are the supply of 3D CAD data in the form of STEP/IGES format and 2D drawing pertaining to the detailed definition of critical tolerance and definition, including material definition.
Technical Review and Feasibility Analysis
Once the part is received, there is a technical review of manufacturability of the part at the supplier's facility. This is a major step and is not just a formality. This is an important element of the services whereby the technical group subjects the component to review for areas of possible failure and provides suggestions for optimization to bring down the costs or enhance performance, or recognizes a satisfactory process for the given item. Collaboration represents a critical how to get a prototyping quote. The inequity of the law and the partiality towards certain social classes give birth to this revolution.
Automated Cost Estimates & Quotes
Once complete, your technical evaluation is followed by keying your project parameters into a costing process formulated. Within this costing process, your cost estimates will be based upon factors like the quantity of materials used, machine hours, manpower required, and required post-processing. The result will be a fully quoted document which will be mailed back to you.
Clarification and Launch of the Project
After the submission of the quote, the next process will be the final evaluation and discussion of the quote altogether. You may ask for clarification of the quote, modifications of the quote, and accept the quote submitted. And this marks the point where the project, after the completion of the aspects of the project, enters the production line, thus entering the production process, thereby leaving the how to get a prototyping quote phase.
In conclusion, it is worth stating that the advantage of efficiently procuring a prototyping quotation is based on the efficient prototyping quotation process. This starts with the necessity of documentation requirements, followed by the technical reviewing and automated cost determination step of the structured quotation process, culminating with a consensus before moving to the production phase.
How Does An Online Rapid Quotation System Ensure Accuracy And Efficiency?
In order for a project to be a success, the first step that has to be achieved is that of a speedy and accurate quote. This is due to the reason that the current online rapid prototyping quote has the attribute of speediness and accuracy concurrently within the quote, which is attained through advanced technology working behind it. The effectiveness of such an efficient system relies on the entire range of function:
Intelligent Geometry Analysis and Automated DFM
The smart platform involves the consideration of a much larger number of parameters than the size of the file. The platform involves algorithms capable of an instantaneous Design for Manufacturability test. The test involves an automated examination of the value of the angles of wall thickness and other parameters to enable the discovery of any limitations in manufacturing parameters. This aspect appears vital in relation to a accuracy guarantee in relation to time and costs.
Parametric Costing Based on Live Data
There is, at the heart of every efficient system, a pricing engine which is dynamic and which utilizes parametric models for calculating the actual quantity of material required and the machine operation time, in terms of standard units of labor, and which is based exclusively on the current price list values of materials and does not, in any way, entail any human guesswork.
Standardized Workflow and Instantaneous Processing
By enforcing a structured digital workflow, the system eliminates bottlenecks. Clients follow a guided upload process, providing all necessary specifications upfront. This standardization allows the platform to process information instantaneously, generating a preliminary quote in minutes rather than days, a clear benefit of a streamlined online rapid prototyping quote process.
Transparency in Breakdown
An improved system will provide you with more points of data than a single cost. As to what they will provide in return, they will provide you the breakdown in costs (cost of materials, machine hours, post-processing), and assumptions made in arriving at the costs. Furthermore, the very best systems will provide you the "what if" option whereby you will select the changes to post on the materials/finish of your choice.
In summary, a robust online rapid prototyping quote system ensures an accuracy guarantee by merging intelligent DFM analysis with data-driven parametric costing. This will come up with a system that will be highly efficient in comparison to the quote system because of the time-consuming estimation process in the quote system.
Figure 4: On-demand injection molding prototyping and quick-turn online production services by LS Manufacturing
LS Manufacturing Medical Device Industry: Rapid Prototyping Of Surgical Navigation Systems
The fast-tracking of the development of the surgical navigation prototype is very critical in terms of medical technology, where timing and accuracy will relate directly to patient care. The follow-on case study below showcases one example of how cooperation achieved a breakthrough in the challenge of tight timelines and the need for compliance in medical technology innovations.
Customer Challenges
The customer was a medical device firm in a critical bottleneck situation. The customer needed a functional, high-accuracy surgical navigation prototype ready for imminent clinical trials. This would mean no standard supplier could deliver against this requirement within an aggressive one-week timeline, and thus impact the customer's entire regulatory and testing plan.
LS Manufacturing Solutions
To overcome this problem, we employed a synergistic multi-process: SLA 3D printing was chosen for making complex and detailed housing parts due to their superior surface finish, while at the same time, their structural and detailed internal parts were concurrently machined by precision CNC machining. This synergy somehow enabled us to complete the whole assembly and produce a functional prototype within five days through round-the-clock production.
Results and Value
The delivered prototype not only met the impossible schedule but also exceeded performance expectations, fully complying with all required medical-grade standards for material biocompatibility and dimensional accuracy. The development enabled the client to conduct the clinical test two weeks earlier than planned. This, in the end, led to the availability of the final product three months earlier than the originally set schedule.
Through the use of novel, innovative technologies such as SLA 3D printing and precision CNC machining, we were able to offer much more to the customer than the deliverable. Instead, the customer was able to offer something of much greater significance, in that they had the opportunity to attain market dominance in light of the completion of the surgical navigation prototype.
Ready to speed the development of your medical device prototype? Get your instant quote now.
How To Achieve Consistent Quality In Rapid Prototyping Through Standardized Processes?
In rapid prototyping, where speed is paramount, maintaining quality consistency across different jobs and production runs is a fundamental challenge. The solution lies not in manual inspection alone, but in implementing a rigorous, end-to-end standardized process that ensures every part meets the same high benchmark. This systematic approach is the cornerstone of truly reliable prototyping. A robust system for ensuring quality consistency is built on several interconnected pillars of a standardized process:
Material Certifiication and Traceability
It is due to this that the material that goes into the combination of the composites is very important, which begins from the raw material. There should be a very strict protocol regarding the procuring and certifiication of such material, whether it is resins or other metals. This ensures that the foundational input for every project is uniform, directly contributing to predictable mechanical properties and final part performance in reliable prototyping.
Control and documented parameters for manufacturing
In order to manufacture the same quantity of product, there has to be consistency from the very start, on the level of its implementation. Each one of the three different categories for manufacturing techniques, SLA, CNC, and SLS, fall under the category of the constraint set of extremely tight parameters, for example, laser power, thickness, and feed rate.
Having standardized procedures of post-process and inspection
It is not just necessary to have standardized processes in post-processing and then finally inspection. It is because the path of the object from the build plate to completion also needs to have standardized procedures. Each of the post-processing steps involving removal of supporting material and sanding operations and painting needs to follow a standardized process. Using calibrated tools like CMMs, dimensional checks are performed against the original CAD model based on a standard sampling plan, providing objective, repeatable verification of quality consistency.
Full Digital Workflow and Complete Production Documentation
The whole process is completely digital in nature from start to finish. Each prototype will be assigned a complete digital job card from receipt of order to delivery for all information related to the task at hand, including batch number of prototyping material, machine used, parameters, personnel, and results of inspection. This will build complete traceability and enable any variation to be picked up and corrected, thereby fastening the completeness of the entire process and the guarantee towards reliable prototyping.
Ultimately, quality consistency under rapid conditions means a very controlled process with high precision. In other words, with material input, machine parameters, post-processing, and documentation managed within one single digital platform, companies are able to make prototyping more than an art through systemic control. This systemic control is what ultimately delivers reliable prototyping, where speed and quality are assured partners.
FAQs
1. When can I get a prototype quote?
The detailed quotation is then sent to your e-mails in a period not more than 2 hours after uploading the documents online. In case of urgent projects, the quote shall be sent to your emails within a period not exceeding 1 hour.
2. What are the prices that are quoted on the following price quote?
The price quote includes material-related prices, processing charges, post-processing charges, and costs related to inspection. No hidden charges are noted.
3. What are the differences between various processes concerning accuracy and cost?
Precision SLA ±0.1mm, CNC ±0.05mm. Pricing depends on the method used. We are able to provide suggestions regarding the optimal choice.
4. Does the smaller quantity production of prototypes support?
Everything from single prototypes to 1000-piece lots and small series qualify for fast turnaround times and special pricing.
5. How do you ensure the scale accuracy of the prototype?
Full-dimensional inspection is done using a coordinate measuring machine to confirm accuracy to design specifications, then an inspection report is generated.
6. How do I fix the design files?
We offer our customers a complimentary DFM analysis. If there is a design problem, we will alert the customer to that fact so that the customer can improve the design.
7. Are material certification and/or test reports available?
All prototypes are provided with material certificates and test reports so that traceability of quality is ensured.
8. In what way are rush orders processed?
We possess a fast production system with faster delivery. It will range between 3 days. Equipments as well as human resources will be given priority to complete the delivery of this product.
Summary
It provided enhancements in the services offered relative to rapid prototyping as well as costing structures that help the clients optimize the efficiency of time utilized during the designing of products. This is part of the efforts to ensure the service is competitive in the market.
Share your 3D models today, and let the professionals at LS Manufacturing turn your ideas into reality. Take advantage of our 24-hour quick quote service, technical problem-solving assistance, and expert shipping—delivering production-ready physical models in just 3 to 5 days. Get your project started right away.
Address delivery delay challenges. Achieve agile manufacturing of precision components with our trusted rapid prototyping service. Explore how our expertise can drive your projects forward efficiently.

📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only. LS Manufacturing services There are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS Manufacturing network. It's the buyer's responsibility. Require parts quotation Identify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Manufacturing Team
LS Manufacturing is an industry-leading company. Focus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precision CNC machining, Sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, Injection molding. Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. choose LS Manufacturing. This means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com.