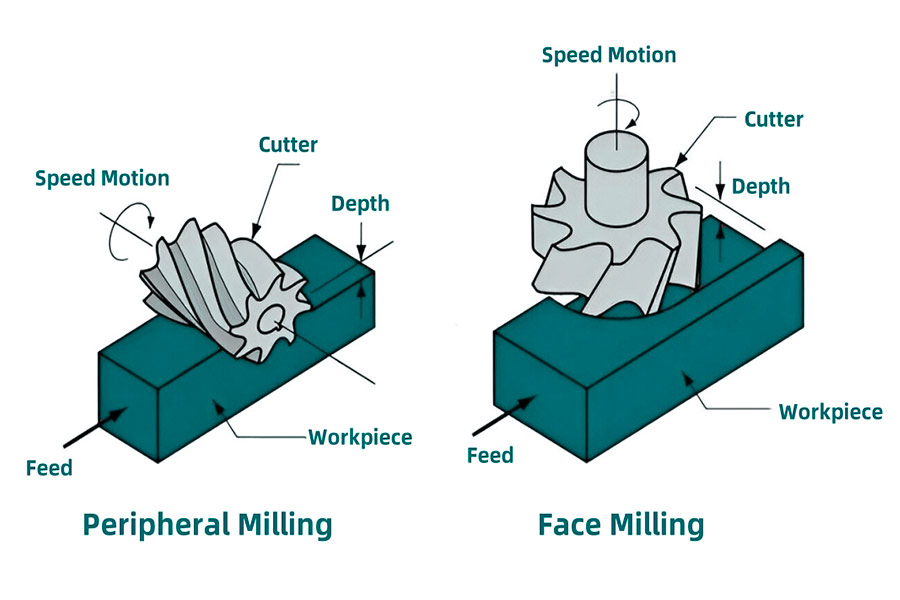
Milling is a key processing technology that can create a variety of shapes and is suitable for a variety of materials. Its operation method is to remove excess material from the part. In milling, the choice between face milling and peripheral milling has a great impact on process efficiency. If you choose the right one, you can achieve high precision throughout the entire processing process and control costs. Next, we will talk in detail about the differences between these two processing methods to help you choose the most suitable milling process according to your own processing needs.
What is face milling?
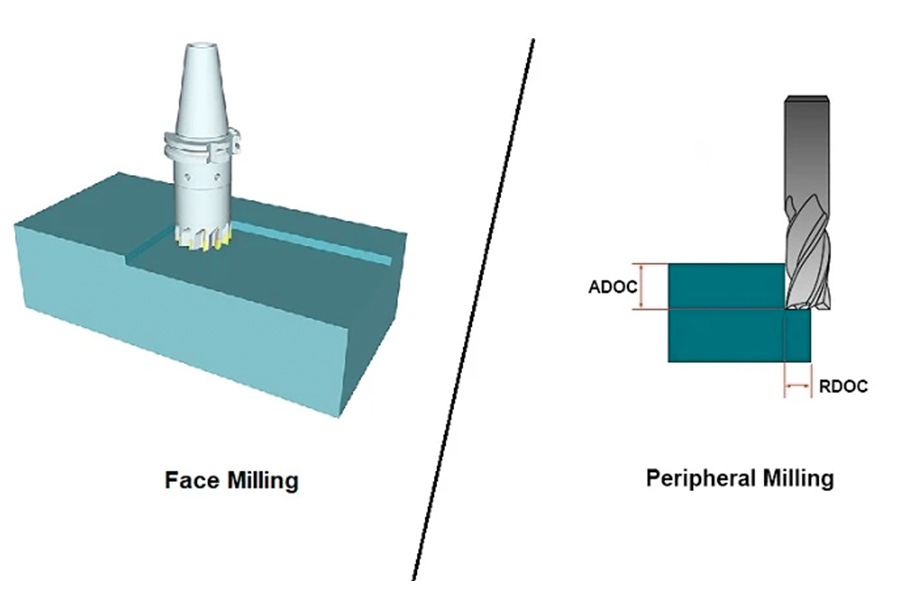
Face milling is a milling process that uses the cutting edge of the end face of the milling cutter to process the plane of the workpiece. In actual production, it is mainly used to process larger planes such as machine tool workbenches, flat plates, and bases. Face milling has an obvious feature that the cutting force is mostly transmitted along the axial direction. Whether it is efficient roughing or fine finishing, it can do it.
Main features of face milling
- Tool type: Face milling uses a face milling cutter (also called an end mill), and the blade is installed on the end face of the cutter disc.
- Cutting method: The main cutting is carried out by the end face cutting edge. This method is particularly suitable for the processing of large planes.
- Processing advantages: It removes materials quickly and can quickly process the surface of the workpiece very flat.
- Applicable materials: A variety of materials such as steel, cast iron, aluminum alloy, and composite materials can be processed.
How does face milling work?
The working principle of face milling is achieved by the rotation and feed motion of the milling cutter. When the milling cutter rotates, the end face cutting edge starts to cut the workpiece, removing the excess material little by little, thus forming a smooth surface.
Basic workflow of face milling
- Tool installation: Install the face milling cutter on the spindle of the milling machine or machining center, and make sure that the tool is installed firmly and does not shake when rotating.
- Workpiece fixation: Clamp the workpiece to be processed firmly on the workbench to ensure that the workpiece does not move during the processing, so as to ensure the processing accuracy.
- Cutting motion:①Spindle rotation (cutting motion): The milling cutter rotates at high speed, and the blade on the end face starts to cut the workpiece. ②Feed motion (X/Y/Z axis motion): The workpiece or tool moves along a pre-set path, slowly covering the entire surface to be processed.
- Chip formation: When the blade cuts the workpiece material, chips are generated, and these chips are discharged from the processing area.
- Surface forming: Through the processing of multiple tool paths, or another fine milling, a flat and smooth processing surface can be obtained in the end.

Cutting methods of face milling
| Method | Description | Applicable scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetrical face milling | The tool center is symmetrical to the workpiece, and the cutting force is balanced | Standard plane processing |
| Asymmetric face milling | The tool is biased to one side to reduce vibration | Processing workpieces with poor rigidity |
| Climb Milling | The cutting direction is the same as the feed direction, and the surface quality is better | Finishing |
| Conventional Milling | The cutting direction is opposite to the feed direction, and the tool wear is less | Rough processing or hard material processing |
What is Peripheral Milling?
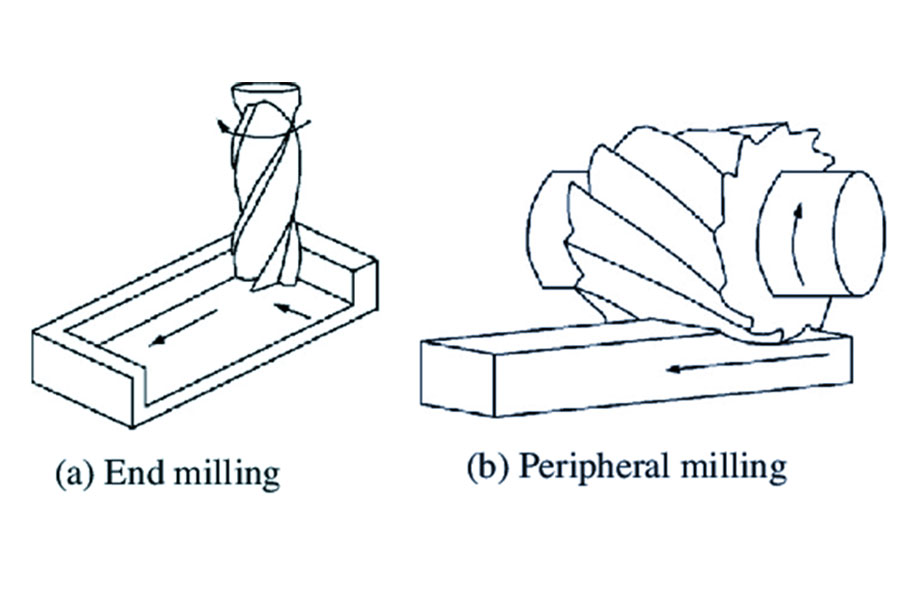
Peripheral milling is a milling process that uses the circumferential cutting edge of the milling cutter to perform contour or side processing on the workpiece. Unlike face milling, peripheral milling mainly relies on the cutting edge of the outer circumference of the tool to remove material, and is suitable for processing grooves, steps, complex contours and other features.
Key features of peripheral milling
- Tool type: Use end mills, cylindrical milling cutters, etc., and the cutting edges are distributed on the circumference of the tool.
- Cutting method: The circumferential cutting edge performs the main cutting, which is suitable for contour and side wall processing.
- Processing advantages: High-precision contours and excellent surface quality (Ra 0.4~1.6μm) can be obtained.
- Applicable materials: steel, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, composite materials, etc.
How does peripheral milling work?
Peripheral milling uses the rotation and feed motion of the milling cutter's circumferential cutting edge to gradually remove the workpiece material to form the desired contour or groove.
Basic working process of peripheral milling
- Tool installation: The end mill is installed on the spindle of the milling machine or machining center to ensure that the radial runout of the tool is minimized.
- Workpiece fixation: The workpiece is firmly clamped on the workbench to prevent vibration or displacement during processing.
- Cutting motion:①Spindle rotation (cutting motion): The milling cutter rotates at high speed and the circumferential cutting edge cuts the workpiece.②Feed motion (X/Y/Z axis movement): The workpiece or tool moves along the set path to form a contour or groove.
- Chip formation: The circumferential edge continuously cuts the material and the chips are discharged along the spiral groove of the tool.
- Contour forming: The desired shape and size are finally obtained by precisely controlling the tool path.

Cutting methods of peripheral milling
| Method | Description | Applicable scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Climb Milling | The cutting direction is the same as the feed direction, and the surface quality is better. | Finishing, high-precision contours |
| Conventional Milling | The cutting direction is opposite to the feed direction, and the processing is more stable. | Rough processing, workpieces with insufficient rigidity |
| Full-circumference milling | The entire circumference of the tool is involved in cutting, and the efficiency is high. | Deep groove and cavity processing |
|
Partial circumference milling |
Only part of the circumferential edge is involved in cutting, and the cutting force is small | Thin-walled parts, precision contours |
Face Milling vs Peripheral Milling: What’s the Difference?
Below is a detailed comparison of face milling and perimeter milling in six key areas:
① Difference in tool direction
| Features | Face milling | Peripheral milling |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle direction | Tool axis perpendicular to the machining surface | Tool axis parallel to the machining surface |
| Cutting force direction | Main axial force (Z direction) | Main radial force (X/Y direction) |
| Typical clamping | Short overhang clamping (high stability) | Long overhang clamping (rigidity needs to be considered) |
Technical description:
The radial force of peripheral milling can easily cause tool deflection, and a reinforced tool holder (such as a hydraulic tool holder) is required; the axial force of face milling has a more uniform load on the machine tool guide rail.
② Material removal mechanism
| Features | Face milling | Peripheral milling |
|---|---|---|
| Removal method | Large area simultaneous cutting | Progressive cutting (thin cutting depth and multiple paths) |
| Chip shape | Short broken chips (easy to remove) | Long spiral chips (easy to entangle) |
| Efficiency comparison | Material removal rate can be as high as 300cm³/min | Low material removal per unit time |
Case data:
When processing 45# steel, the metal removal rate of φ50mm face milling cutter (8 blades) is 4-6 times that of φ20mm end milling cutter (4 blades).
③ Typical application scenarios
| Application type | Face milling | Peripheral milling |
|---|---|---|
| Main fields | Machine tool guide surface/engine cylinder block | Mold cavity/aviation structural parts |
| Feature processing | Large plane/end face/step surface | Deep groove/complex curved surface/thin-walled parts |
| Precision requirements | IT8-IT9 (high flatness) | IT7-IT8 (high contour accuracy) |
Industry distribution:
Face milling accounts for 60% in the automotive industry vs. 70% in the mold industry.
④ Surface treatment capability
| Parameters | Face milling | Peripheral milling |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | Ra 0.8-3.2μm | Ra 0.4-1.6μm (fine milling can reach 0.2μm) |
| Texture characteristics | Cross-net texture (overlapping tool marks) | Regular arc texture (determined by tool trajectory) |
| Subsequent treatment | Often need to be scraped | Can often be used directly |
Measured data:
When using a φ12mm ball-end milling cutter for finishing, peripheral milling can achieve a Ra 0.2μm mirror effect.
⑤ Tool wear and setting
| Project | Face milling | Peripheral milling |
|---|---|---|
| Wear parts | Wear of the crescent of the tool tip | Boundary wear of the flank of the circumferential blade |
| Tool change standard | Processing area per blade 2-5m² | Processing length up to 300-500m |
| Tool setting requirements | Only axial tool setting is required | Precise radial compensation setting is required |
Maintenance tips:
It is recommended to check the radial runout of peripheral milling tools every 50 processing hours (should be <0.01mm).
⑥ Tool design differences
| Design elements | Face milling tool | Peripheral milling tool |
|---|---|---|
| Blade structure | Straight blade/wiper blade | Helical blade (30°-45° helix angle) |
| Material selection | Coated cemented carbide (high temperature resistant) | Ultrafine grain cemented carbide (anti-chipping) |
| Innovative design | Damping vibration reduction structure/modular cutter head | Variable helix angle/unequal tooth pitch |
Frontier technology:
The latest peripheral milling cutter adopts 5-axis grinding and forming technology to achieve a cutting edge profile accuracy of ±2μm; the face milling cutter has developed a ceramic blade with internal cooling oil holes.
When to Choose Face Milling?
The following points help us understand when to choose face milling. Next, we will discuss these aspects in detail.
1. The preferred solution for plane machining
When it comes to creating high-precision planes, face milling offers irreplaceable technological advantages. The perpendicular nature of the tool axis to the machined surface makes it particularly suitable for handling large sheet metal and block workpieces. Through the collaborative cutting of multi-edge tools, the unevenness of the surface of the workpiece can be effectively eliminated, and the typical machining accuracy can reach a flatness of 0.02mm/m. This processing method is particularly prominent in the plane machining of key components such as machine tool guide rail surfaces and hydraulic valve blocks.
2. Efficient material removal capability
Face milling offers significant advantages in terms of material removal rate (MRR) due to its unique cutting geometry:
- The contact area can be 3-5 times larger than that of peripheral milling
- Typical roughing parameters: axial depth of cut 3-5mm, radial depth of cut 50-80% of tool diameter
- The metal removal rate in cast iron processing can reach 800 cm³/min
This high efficiency makes it ideal for casting blank cleaning, weldment alignment and roughing operations, laying the foundation for subsequent finishing.
3. Simple process implementation
The simplicity of the face milling process is reflected in:
- Clamping positioning only requires that the tool is perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece
- No complex angle adjustment is required
- Typical makeready time is 40% shorter than perimeter milling
This feature is particularly suitable for mass production scenarios, such as the flat machining of automobile engine blocks, which can significantly improve the cycle time efficiency of the production line.
4. Excellent surface consistency
Surface Quality Control Benefits of Face Milling:
- Multi-edge synergy ensures uniformity across the entire machined surface
- The optional wiper insert design achieves a Ra0.8μm finish
- Cross-cut textures improve surface load-bearing performance
This characteristic is particularly valuable in the machining of workpieces that require uniform surface characteristics, such as precision flat plates and optical tables.
Extended application of technology
- Modern face milling technology has developed a variety of advanced applications:
- High Feed Milling (HFR): Feed rates up to 3000mm/min
- Variable depth of cut milling: Automatically adjusts the depth of cut to compensate for workpiece deformation
- Intelligent face milling: Integrated vibration monitoring optimizes parameters in real time
Suggestions for selection:
Face milling should be prioritized when your machining needs meet all three of the following characteristics:
(1) The main processing feature is a flat surface
(2) Material removal> 5cm³/cm²
(3) The surface roughness is required to be Ra1.6 or above
Note: For ultra-precision machining (Ra<0.4μm), it is recommended to use the composite process scheme of face milling roughing and perimeter milling finishing.
When Choosing Peripheral Milling?
In the field of mechanical processing, it is extremely important to know when to use the peripheral milling process. The following will explore the relevant influencing factors in depth.
1.Significant advantages in complex contour processing
Peripheral milling is particularly suitable for complex contour processing tasks, and can produce high-precision processing results and fine edges. Its tool uses a circular cutting method, usually at an angle of 180 degrees to the surface of the metal part. This unique cutting angle brings higher precision and accuracy to the processing of complex parts, and plays an important role in many application scenarios such as gear cutting and thread milling.
2.Efficient processing of deep grooves and complex contours
Why choose LS Precision Manufacturing for face and peripheral milling?
In our factory, all kinds of advanced technologies and equipment are available. Whether it is small-batch customized production or large-scale batch production, we can calmly deal with it and complete the processing tasks accurately and efficiently. Throughout the production process, we always adhere to the bottom line of quality and never sacrifice quality. At the same time, we also tailor economical and efficient solutions according to the specific needs of each project to help customers reasonably control costs while ensuring product quality.
Summary
In the field of mechanical processing, the precise selection of technology is directly related to product quality and production efficiency. When faced with the need to focus on smooth or flat surfaces, face milling is undoubtedly the best choice; if the project involves deep cutting, grooving and other tasks, peripheral milling is indispensable. In the decision-making process, many factors such as material type, desired surface quality, tool availability, production scale, processing speed and cost need to be fully considered.
With the continuous innovation of the mechanical processing industry, timely grasping of cutting-edge information and applying practical skills are of great significance to improving production efficiency.Taking face milling technology as an example, a deep understanding of its principles and applications can bring significant benefits to enterprises. For those companies that want to delve deeply into these processes and seek reliable equipment, LS Precision Manufacturing is an ideal partner.
With its deep accumulation in the field of face milling and peripheral milling, LS can not only provide high-quality products that meet the industry's top standards, but also provide companies with valuable resources to help them move forward steadily in the machining track and achieve the dual goals of efficient production and excellent quality.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.LS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy,completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the Longsheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers, we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast,efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization,we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseLS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1. Can face milling and peripheral milling be performed at the same time?
Yes, modern composite milling cutters (such as shoulder milling cutters or modular milling cutters) can achieve face milling and peripheral milling at the same time through special design. Such cutters usually arrange finishing inserts on the end face for plane milling, and roughing inserts on the circumference for contour processing. For example, Sandvik Coromant's Coromill 390 series can complete 90° shoulder face and side wall processing in one clamping, which can shorten the processing time by more than 30% compared with traditional processes. It is particularly suitable for efficient processing of batch parts, but it should be noted that the cutting parameters need to be compromised and optimized according to the mechanical properties of the two processing modes.
2. Which milling method is more suitable for thin-walled parts?
Peripheral milling, especially down-milling, is more suitable for thin-walled parts processing because its radial cutting force can be controlled at a lower level (usually 40-60% lower than face milling), and the small cutting depth (ae<0.5mm) and high speed strategy can effectively suppress vibration. For example, when processing thin-walled cabins of aviation aluminum alloys, peripheral milling with a φ10mm thin-necked end mill can control the wall thickness error within ±0.05mm, while the axial force of face milling can easily lead to elastic deformation of more than 0.1mm. For thin-walled titanium alloy parts with poor rigidity, axial layered peripheral milling (Zig-Zag path) is even required to further reduce the cutting force.
3. How high a surface finish can be achieved by face milling?
Under ideal conditions, the surface finish of face milling can reach up to Ra 0.4μm, which requires meeting three key conditions: using a fine milling insert with a wiper edge (such as Iscar's F3S series), using a high-rigidity machine tool (spindle radial runout <0.005mm), and cooperating with micron-level feed (feed per tooth 0.03-0.05mm). For example, when machining cast iron machine tool guides, a combination of PVD-coated inserts, 0.2mm wiper edge overlap, and 800m/min cutting speed can achieve a mirror effect of Ra 0.5μm, but it should be noted that this high-finish processing will sacrifice about 25% of tool life.
4. Is the tool life of peripheral milling usually longer than that of face milling?
Tool life comparison cannot be simply concluded. For example, when machining hardened steel (HRC55), the small cutting width (ae=0.1D) strategy of peripheral milling can make the tool life reach 120 minutes, far exceeding the 40 minutes of face milling cutter; but in high-speed machining of aluminum alloy, the life of face milling cutter is 2-3 times higher than that of peripheral milling cutter because of the multi-edge sharing of cutting load. Key influencing factors include: cutting heat distribution (higher tool tip temperature in peripheral milling), difficulty in chip removal (closed chip in face milling is prone to secondary cutting), and modern coating technology (AlCrN coating of face milling insert has better heat resistance). In actual production, dynamic optimization is required through cutting force monitoring and tool wear analysis.






