En la fabricación moderna, La tecnología de corte láser se ha convertido en un proceso importante en el campo del procesamiento de metales debido a su alta precisión, alta eficiencia y capacidades de procesamiento flexible. Entre ellos, el corte con láser de fibra, como una de las tecnologías de corte láser de más rápido crecimiento en los últimos años, se usa ampliamente en fabricación de automóviles, equipos aeroespaciales, electrónicos y otras industrias con su excelente calidad de corte, bajo consumo de energía y bajo costo de mantenimiento.
Este artículo presentará el conceptos básicos, principios de trabajo, parámetros clave del proceso y diferentes tipos de láser de fibra cortando en detalle para ayudar a los lectores a comprender completamente las características centrales y las ventajas de aplicaciones de esta tecnología de procesamiento avanzado.
¿Qué es el corte láser de fibra?
El corte láser de fibra es una tecnología de procesamiento avanzada que utiliza haces de láser de fibra de alta potencia para cortar con precisión los materiales metálicos o no metálicos. El núcleo es generar un haz de láser de alta energía a través de un láser de fibra, que se enfoca e irradia en la superficie del material, lo que hace que el material se derrita, vaporice o ablata rápidamente, y al mismo tiempo, la escoria se desplome con la ayuda del gas auxiliar (como el oxígeno, el nitrógeno o el aire), logra de manera eficiente y de alta precisión.
El corte láser de fibra se usa ampliamente en la fabricación de automóviles , equipos aeroespaciales, electrónicos, procesamiento de metales y otras industrias debido a su alta eficiencia, alta precisión, bajo consumo de energía y bajo costo de mantenimiento.
¿Cómo funciona el corte con láser de fibra?
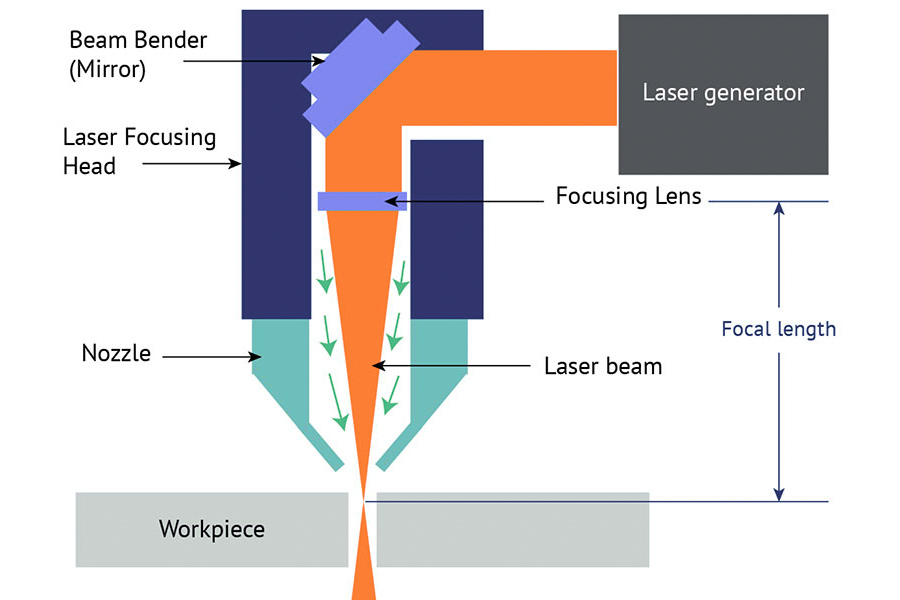
El flujo de proceso básico de corte láser de fibra es el siguiente:
- Generación del haz de láser: el láser de fibra genera láser a través de una fibra óptica dopada con elementos de tierras raras (como Ytterbium yb), y forma un haz de alta densidad de energía a través de un reflector y un espejo enfocador.
- enfoque de haz: el haz láser está enfocado por un lente o un espejo curvado para formar una spot muy pequeña ((1- densidad.
- Calentamiento y fusión del material: El haz láser irradia la superficie del material, y la temperatura local aumenta rápidamente al punto de fusión o al punto de vaporización, y el material se derrite o se evapora.
- El gas auxiliar sopla escoria: gas auxiliar de alta presión (como nitrógeno, oxígeno o aire comprimido) quita el material fundido para garantizar un corte limpio.
- El sistema CNC controla la ruta de corte: El movimiento de la cabeza del láser está controlado con precisión por el sistema de control numérico de la computadora (CNC) para completar el corte de formas complejas de acuerdo con la ruta preestablecida.

¿Cuáles son los principales parámetros del corte láser de fibra?
el procesamiento "data-bm =" 555 "> procesamiento procesamiento "data-bm =" 555 "> Processing "/"/"/" y eficiencia de fiber láser Cutting es afectado por a número de clave parámetros , el siguiendo are el nore When usando fiber láser :
1.L aser m ode
t aquí a re t WAT m ain m odes o " span data> o f iber l aser
2.l aser p ower
Laser power is measured in w atts ( w ) a nd r epresents t he a verage e nergy de t he aser p ulse . T he h Ighere t he p ower, the more thick and hard m aterials c an b e c e c e c e c ut. c w l aser p ower i s s tabla, s uch as a 100W c w l aser w a continuous output of 100W; Pulsed lasers h ave extremadamente h iligh i nstantaneous span data-bm = "1817"> p eak p ower, w a 1 00w p ulsed aser p oking a t 1 t 1 0, 0 00w.
3.p ulse f requency
p ulse f requency r t o t él n o f l aser p p er s econd a " 873 "873" 873 "873" 873 "873" 873 "873" 873 "873" 873 "873". i s m facilated i h ertz ( h
4.b eam d iameter
The beam diameter r eflects t él t hickness o f t l aser b am , a nd t he s b eam d iameter c a Chieve n flecha i a nd h iligh- p c Utting, w hich i s uable f o p p arts p ROCASSing.
5.a TMOSHERIC PRESion
Air pressure is a n a uxiliary g s ystem p arameter t r elates t o t g as p reessure o f bajo r ate t b lows a way t m olten m aterial. a a ir p vuelve a reessure c b e d iScarged i t ime t o e c Utting q ualidad a 1071 "span data> 1071" nd data-bm "101" 101 "101" 1071 "101" 101 "101" 101 "101" 1071 ". e fificient.
6.c Utting s Peed
el c Utting s pIeed i measured in inches p er m inútil ( i pm) o r m illimeters data-bm = "1948"> p er m inute ( ( m/ m in) , t t hinner t he m a nd t he h el l aser p ower, t f aster t he c utting s data-bm="1141">peed, but t oo f AST w
7.t Hickness o f t f t m aterial
The thickness o f t él m a ffects t he c
8.c ondition o f t He l enos
t he s tate o t he f ocusing l o f t he c h ead a ffects
9.f ocus
t he f ocus i w aquí t he l e nergy i s c onCentrated, a nd el w orkpiebe data-bm = "2074"> n eeds t o b a ccuration p atado t o The a PPropriate f ocus p a ccording t o t o t thickness of the m aterial a nd t t c Utting d epth.
10.t ype o f m aterial
d UE t o t d ifference i n p "data-bm =" 1431 "1431" 431 ">" hysaly p rOperties, d ifferent m aterials have different l aser a bsorption a span class =" "data-bm =" 14448 "> nd onDuction c apabilidad, <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> <> data-bm = "2113"> s Uch a s d c Utting p arame de arame o m etal a nd n m etal m ateriales.
11.p Reasyeeat t he m aterial
f o m aterials
12.c Utting p hets
t he s traight c uttting 1546" Utting uttting uttting uttting " p ath i s s "1552" and fast; Complex paths, especially with sharp and angular patterns, reduce the cutting speed and require higher control accuracy of the laser cutting machine.
What are the types of fiber laser cutting?
According to the laser structure and application scenarios, fiber laser cutting is mainly divided into the following types:
(1) Continuous Fiber Laser Cutting (CW)
- The laser output is a continuous wave, which is suitable for high-precision, high-speed cutting, such as sheet metal fabrication.
- It is mainly used for fine cutting of stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum alloy and other materials.
(2) Pulsed Fiber Laser Cutting (QCW/Pulsed)
- The laser is output in the form of pulses and is suitable for highly reflective materials (e.g. copper, brass) or precision micromachining.
- It is often used for fine cutting and drilling in electronic components, precision instruments and other fields.
(3) Multi-mode fiber laser cutting
- It is suitable for medium and heavy plate cutting (usually < 30mm), with a wide beam pattern and uniform energy distribution.
- It is mainly used for industrial-grade sheet metal processing.
(4) Single-mode fiber laser cutting
- The beam quality is higher, the spot is smaller, and it is suitable for high-precision cutting of ultra-thin materials (<3mm).
- It is often used in the electronics industry, precision instrument manufacturing, etc.
What materials can be cut with fiber lasers?
With its high energy density, high beam quality and excellent focusing performance, fiber lasers can efficiently cut a variety of metallic and non-metallic materials, and are widely used in industrial manufacturing. The following are the main applicable material classifications and cutting characteristics:
1. Metallic materials (main application areas)
(1) Carbon steel (low carbon steel, medium carbon steel)
Applicability: ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ (Best Fit)
Cutting features:
- The fiber laser has a high absorption rate of carbon steel, a fast cutting speed, and a smooth incision.
- Oxygen (O₂) is often used as an assist gas to improve cutting efficiency by oxidation reaction.
- Cutting thickness: typically 0.5mm–30mm (ultra-high power fiber laser can cut thicker).
(2) Stainless steel (304, 316, etc.)
Applicability: ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
Cutting features:
- Nitrogen (N₂) is usually used when fiber laser cutting stainless steel to avoid oxidation and keep the cut silver and slag-free.
- Compared to CO₂ lasers, fiber lasers cut stainless steel faster and are especially suitable for thin sheets (<6 mm).
- Cutting thickness: usually 0.1mm–20mm.
(3) Aluminum and aluminum alloys
Applicability: ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ (highly reflective material, high power required)
Cutting features:
- Aluminum has a high reflectivity to laser and requires a high-power (≥1kW) fiber laser with nitrogen or compressed air for cutting.
- Slag is easy to occur during cutting, and parameters need to be optimized (e.g., increasing air pressure, adjusting focus).
- Cuttable thickness: usually 0.5mm–15mm.
(4) Copper and copper alloy (brass, copper)
Applicability: ⭐️⭐️⭐️ (high reflection, high thermal conductivity, difficult to cut)
Cutting features:
- Copper has an extremely high laser reflectivity (>90%) and requires either a pulsed fiber laser or a high-power CW laser (≥2kW).
- Nitrogen (N₂) or compressed air is usually used to assist in cutting to avoid oxidation.
- Cutting thickness: usually 0.1mm–5mm (thicker materials require special processing).
(5) Titanium alloy
Applicability: ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ (commonly used in aerospace and medical industries)
Cutting features:
- Inert gases (e.g. argon) need to be used to prevent oxidation at high temperatures.
- The incision quality is high and there are no heat-affected zone (HAZ) issues.
- Cuttable thickness: usually 0.5mm–12mm.
(6) Other metals (galvanized sheet, nickel alloy, etc.)
- Galvanized sheet: suitable for cutting, but the parameters need to be controlled to avoid volatilization of the zinc layer to contaminate the lens.
- Nickel alloys (e.g. Inconel): can be cut, but requires a high-power laser.
2. Non-metallic materials (partially applicable)
Fiber lasers are mainly optimized for metal cutting, but some non-metallic materials can also be cut, but the effect is not as good as CO2 lasers or UV lasers:
(1) Plastics (ABS, acrylic, etc.)
- Can be cut, but easy to melt, the edges may be carbonized, low power + high speed cutting is required.
- CO2 laser or UV laser processing is more recommended.
(2) Composite materials (carbon fiber, glass fiber)
- Can be cut, but the resin matrix may burn, and gas protection needs to be optimized.
- Professional composite material cutting usually uses water jet or ultrafast laser (picosecond/femtosecond).
(3) Wood, leather, cloth
- Theoretically, it can be cut, but the heat effect is large and the edges are easy to burn. CO2 laser is more suitable.
3. Materials not suitable for fiber laser cutting
- Highly reflective materials (such as gold and silver): The reflectivity is too high and the laser head is easily damaged.
- Ceramics and glass: They are easy to crack and are more suitable for ultrafast laser (picosecond/femtosecond) or water jet cutting.
- PVC and other chlorine-containing plastics: Toxic gases will be generated during cutting, so laser cutting is prohibited.
Fiber laser cutting is most suitable for metal materials, especially carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum, but its cutting ability for highly reflective materials (such as copper) and non-metallic materials (such as plastics) is relatively limited. It is necessary to select the appropriate laser type according to specific needs.

What are the advantages of fiber laser cutting?
Fiber laser cutting has many advantages over other industrial cutting technologies. These include:
- High energy efficiency: Photoelectric conversion efficiency reaches 30%-50%, which is much higher than CO2 laser (10%-15%), and energy consumption is lower.
- High precision: Good beam quality (M² close to 1), small spot diameter (0.1-0.3mm), suitable for fine cutting.
- Fast speed: Cutting thin plates is 2-3 times faster than CO2 laser (such as 1mm stainless steel can reach 30m/min).
- Simple maintenance: No need for reflector calibration, maintenance-free optical fiber transmission, and service life of more than 100,000 hours.
- Low cost: Low power consumption, no need to regularly replace gas laser tubes, and the comprehensive use cost is more than 30% lower.
- Material adaptability: Especially suitable for cutting highly reflective metals (aluminum, copper) and thin medium plates.
What are the disadvantages of fiber laser cutting?
Fiber laser cutting is a widely adopted technology with a wide range of uses. Even so, fiber laser cutting machines still have some limitations for some users. These limitations include:
- Material limitations: Certain materials, such as plastics that release toxic gases, cannot be cut with fiber laser cutting machines. These materials include PVC, ABS, polycarbonate, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Maintenance and care: Fiber laser cutting machines require proper care and regular maintenance. Neglecting maintenance can cause damage to internal parts such as the focusing lens, which can significantly reduce cutting performance.
- Initial cost: While fiber laser cutting machines have low operating costs, they still require a certain initial investment to purchase the equipment. The only consumable for this type of laser is electricity.
- Material thickness: Fiber lasers can only cut materials up to a few centimeters thick. This may not be sufficient for some applications.
What are the differences between fiber laser and CO₂ laser?
The difference between fiber lasers and CO2 lasers lies in the type of laser system. Fiber lasers use a rare earth material doped fiber laser cavity to produce an amplified beam. On the other hand, CO2 lasers use a gas discharge tube to produce the laser light.
| Comparison item | Fiber laser | CO₂ laser |
|---|---|---|
| Working principle | Fiber doped with rare earth elements emits light | Gas discharge excites CO₂ molecules to emit light |
| Wavelength | 1.06μm (high metal absorption rate) | 10.6μm (good non-metal absorption) |
| Cutting speed | Thin plate 2-3 times faster | Thick plate (>15mm) slightly better |
| Energy consumption | 30%-50% conversion efficiency | 10%-15% conversion efficiency |
| Maintenance | Basically maintenance-free | Need to clean the lens and replace the gas regularly |
| Applicable materials | Metal (especially highly reflective materials) | Metal/non-metal (such as acrylic, wood) |
| Equipment cost | Medium and high power models are more expensive | Low power models are less expensive |
What are the applications of fiber laser cutting machines?
Fiber laser cutting machines are widely used in various industries, including:
- Automobile manufacturing: cutting of precision parts such as body sheet metal, exhaust pipes, gears, etc.
- Aerospace: processing of high-temperature resistant materials such as titanium alloy casings and aluminum alloy skins.
- Electronics and electrical appliances: cutting of microstructures such as mobile phone middle frames, PCB templates, and heat sinks.
- Metal processing: stainless steel kitchenware, metal artworks, building steel structures, etc.
- New energy: cutting of lithium battery pole pieces and solar brackets.
How to choose a fiber laser cutting machine?
The choice of fiber laser cutting machine directly affects processing efficiency, cost and product quality. The following are the key factors to consider when purchasing to help you choose the most suitable equipment:
Power Options:
- 500W-1kW: suitable for 0.5-5mm thin plates (e.g. electronic components).
- 2kW-6kW: mainstream industrial grade, can cut 3-20mm carbon steel/stainless steel.
- 8kW-20kW: Thick plate cutting (>20mm) or high-speed production needs.
Processing Format:
- Small machine (1.5m×3m): Precision parts.
- Standard machine (2m×4m): General purpose sheet processing.
- Customized oversized countertops: shipbuilding, construction machinery industry.
Core Configuration:
- Laser brands: IPG, Ruike, Chuangxin, etc.
- CNC system: Baichu, PA, Siemens.
- Guide rails/gears: high-precision linear guides/helical gear transmissions.
Accessibility:
- Autofocus: Adapt to different thickness materials.
- Changing workbenches: Increase continuous production efficiency.
- Dust removal system: Handling of cutting fumes (optional).
Budget & After-sales:
- Domestic equipment (100-3 million yuan): cost-effective, fast after-sales response.
- Imported equipment (300-8 million yuan): ultra-high precision, suitable for high-end manufacturing.

Summary
Fiber laser cutting is an advanced processing technology based on high-brightness fiber lasers, which generates high-energy laser beams through fiber media doped with rare earth elements, and cooperates with precisely controlled parameters such as power, speed, focus and auxiliary gas to achieve efficient precision cutting of metals and other materials. Its core advantages lie in excellent beam quality, high energy conversion efficiency and flexible processing adaptability, the main types include continuous, pulsed and ultrafast fiber laser systems, which are widely used in sheet metal fabrication in industrial manufacturing, auto parts production and other fields, and have become an indispensable key process for modern precision manufacturing.
📞 Teléfono: +86 185 6675 9667
📧 Correo electrónico: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐 Sitio web: https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.LS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy,completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the Longsheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers, we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast,efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization,we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseLS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
Preguntas frecuentes
1.What are the parameters of the laser cutting process?
The main parameters of the laser cutting process include laser power, cutting speed, focus position, type and pressure of the assist gas, pulse frequency (for pulsed lasers), nozzle diameter and nozzle height, etc. These parameters need to be adjusted and optimized according to the type of material being cut, the thickness and the desired cut quality in order to achieve the best cutting results.
2.What is Fiber Laser Cutting?
Fiber laser cutting is an advanced processing technology that uses a high-energy-density laser beam generated by a fiber laser to cut materials. It focuses the laser energy on the surface of the material, so that the local area is rapidly melted or vaporized, and at the same time, the molten substance is blown away with the help of high-pressure auxiliary gas, so as to achieve a high-precision, high-efficiency cutting process, especially suitable for precision cutting of metal materials.
3.What are the 4 important parameters of the laser cutting setup?
The four most critical parameters in laser cutting are: laser power (which determines cutting capacity), cutting speed (which affects productivity), focus position (which controls the energy density distribution), and assist gas pressure (which affects slag removal). The proper matching of these parameters directly affects the cutting quality, speed and cross-sectional finish, and needs to be finely tuned according to the specific material and thickness.
4.What is the process of a fiber laser?
The core process of fiber lasers is to produce high-brightness lasers under the excitation of a pump source through fibers doped with rare earth elements such as ytterbium as a gain medium. Process features include an all-fiber construction to ensure beam quality, multimode pumping for high power output, a flexible fiber transmission system for energy delivery, and an intelligent control system for precise parameter adjustment to meet a variety of industrial processing needs.







