In the rapidly developing fields of technology and innovative design, the importance of product design and development as a bridge connecting creativity and the market is self-evident. As an efficient and flexible product development strategy, "rapid prototyping" has gradually come into people's vision and has become a key force in promoting product innovation and market transformation. So, how exactly doesprototypingplay a role in product development? How does it help companies quickly respond to market demands and improve product competitiveness? In this article, we will delve into the definition, principles, technical methods and application value of rapid prototyping in product development, giving you a glimpse into the secrets behind this innovation strategy.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping, in short, refers to the use of advanced manufacturing technology or design software in the early stages of product development to produce a preliminary model or prototype of the product at a lower cost and in a shorter time. Theserapid prototypescan be functional, cosmetic,or even a combination of the two and are used for testing, validating design concepts, evaluating user experience, presenting to investors, or marketing.
The principle is to continuously revise and improve product design through the cycle of "build-test-learn-feedback". Compared with the traditional product development process, rapid prototyping focuses more on speed and flexibility, allowing designers and engineers to discover and solve problems early in product development and avoid costly and time-consuming modifications later.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
Rapid prototyping is an efficient product development method that allows teams to quickly create testable, verifiable prototypes in the early stages of product development. The following is therapid prototyping process:
Requirements analysis:Work closely with users or stakeholders to collect and clarify the basic needs and functional requirements of the product. Determine the goals and scope of prototype design by sorting out and analyzing requirements.
Preliminary design:Based on the results of demand analysis, conceptualize the product and form a preliminary design plan. Use hand-drawn sketches, design software and other tools to quickly draw preliminary design drawings of products.
Prototyping:Use prototyping tools or software, such as Axure RP, InVision, Marvel, etc., to quickly build digitalprototyping model. If a physicalrapid mockupis required, select appropriate materials and processes and produce it through 3D printing, CNC processing, hand-making, etc.
Testing and Validation:Invite target users or potential users to test the prototype and collect their feedback. Conduct functional testing, usability testing, performance testing, etc. on prototypes to ensure that the prototype meets design requirements and user needs.
Feedback and iteration:Make necessary modifications and optimizations to therapid prototype based on test results and user feedback. Repeat the process of testing and iteration until the prototype achieves satisfactory results.
Delivery and Evaluation:Deliver the final prototype to the project team, client, or stakeholders for evaluation and decision-making. Summarize and evaluate the entire prototype design process to provide reference for future product development.
What are the main methods of rapid prototyping?
1.SLA
SLA is an industrial 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, process that builds parts in a pool of UV-curable photopolymer resin using a computer controlled laser. The laser is used to trace out and cure a cross-section of the part design on the surface of the liquid resin. The solidified layer is then lowered just below the surface of the liquid resin and the process is repeated. Each newly cured layer adheres to the layer below it. This process continues until the part is completed.
| Pros | Cons |
| For concept models, cosmeticprototypes, and complex designs, SLA can produce parts with intricate geometries and excellent surface finishes as compared to other additive processes. Cost is competitive and the technology is available from several sources. | Prototyped parts may not be as strong as those made from engineering-grade resins, so the parts made using SLA have limited use for functional testing. Additionally, while parts undergo a UV-cycle to solidify the outer surface of the part, parts built in SLA should be used with minimal UV and humidity exposure so they don’t degrade. |
2.SLS
SLS is one of five additive processes available at Protolabs. During the SLS process, a computer-controlled CO2laser draws onto a hot bed of nylon-based powder from the bottom up, where it lightly sinters (fuses) the powder into a solid. After each layer, a roller lays a fresh layer of powder on top of the bed and the process repeats. SLS uses either rigid nylon or elastomeric TPU powders similar to actual engineering thermoplastics, so parts exhibit greater toughness and are accurate, but have rough surface and lack fine details. SLS offers a large build volume, can produce parts with highly complex geometries and create durable prototypes.
| Pros | Cons |
| SLS parts tend to be more accurate and durable than SLA parts. The process can make durable parts with complex geometries, and is suitable for some functional testing. | The parts have a grainy or sandy texture and the process has a limited resin choice. |
3.FDM
FDM uses an extrusion method that melts and re-solidifies thermoplastic resin (ABS, polycarbonate, or ABS/polycarbonate blend) in layers to form a finished prototype. Because it uses real thermoplastic resins, it is stronger than binder jetting and may be of limited use for functional testing.
| Pros | Cons |
| FDM parts are moderately priced relatively strong, and can be good for some functional testing. The process can make parts with complex geometries. | The parts have a poor surface finish, with a pronounced rippled effect. It is also a slower additive process than SLA or SLS and has limited suitability for functional testing. |
4.CNC machining
In machining, a solid block (or rod stock) of plastic or metal is clamped into a CNC mill or lathe respectively and cut into a finished part through a subtractive process. This method generally produces superior strength and surface finish to any additive manufacturing process. It also has the complete, homogenous properties of the plastic because it is made from solid blocks of extruded or compression molded thermoplastic resin, as opposed to most additive processes, which use plastic-like materials and are built in layers. The range of material choices allows parts to be made with the desired material properties, such as: tensile strength, impact resistance, heat deflection temperatures, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. Good tolerances yield parts suitable for fit and functional testing, jigs and fixtures, and functional components for end-use applications. A number of manufacturers, including Protolabs, use 3-axis milling and 5-axis indexed milling processes along with turning to manufacture parts in a range of engineering-grade plastics and metals.
| Pros | Cons |
| Machined parts have good surface finishes and are quite strong because they use engineering-grade thermoplastics and metals. Like 3D printing, custom prototypes can be delivered in as fast as one day at some suppliers. | There may be some geometry limitations associated with CNC machining, and it is sometimesmore expensive to do this in-house than 3D printing processes. Because the process is removing material instead of adding it, milling undercuts can sometimes be difficult. |
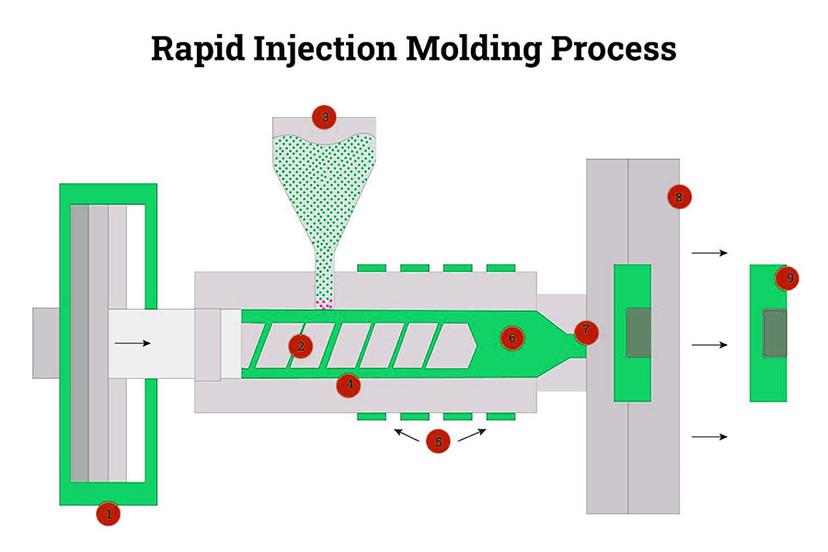
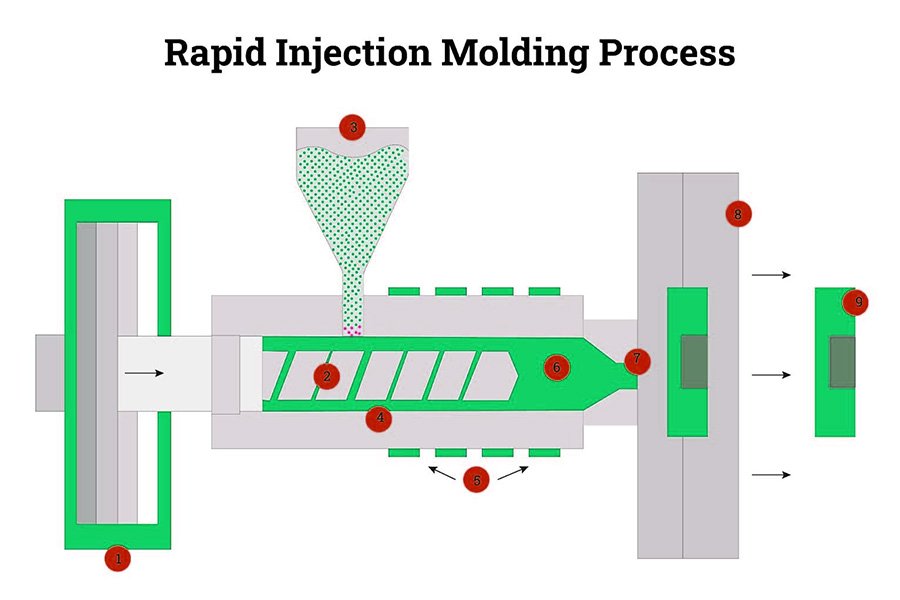
5.Injection Molding
Rapid injection molding works by injecting thermoplastic resins into a mold, just as in production injection molding. What makes the process “rapid” is the technology used to produce the mold, which is often made from aluminum instead of the traditional steel used in production molds. Molded parts are strong and have excellent finishes. It is also the industry standard production process for plastic parts, so there are inherent advantages to prototyping in the same process if the situation allows. Almost any engineering-grade plastic or liquid silicone rubber (LSR) can be used, so the designer is not constrained by the material limitations of the prototyping process.
| Pros | Cons |
| Molded parts are made from an array of engineering-grade materials, have excellent surface finish, and are an excellent predictor of manufacturability during the production phase. | There is an initial tooling cost associated with rapid injection molding that does not occur with any of the additive processes or with CNC machining. So in most cases, it makes sense to do one or two rounds ofrapid prototypesto check fit and function before moving to injection molding. |
6. sheet metal fabrication
Rapid sheet metal manufacturing is an efficient and high-precision metal sheet processing technology. Through computer control, metal sheets are cut, bent, and welded according to design requirements to quickly produce the required parts. This technology combines advanced CNC equipment, laser cutting, stamping and other process methods to complete the production of sheet metal parts with complex shapes and high-precision requirements in a short time.
| Pros | Cons |
| Rapid sheet metal manufacturing technology has the characteristics of high efficiency, high precision, flexibility, low cost and environmental protection. | High equipment costs, high technical requirements, high scrap rates and high customization costs, etc. |
What are the applications of rapid prototyping in different fields?
Software Engineering
In the field of software engineering, rapid prototyping technology is mainly used in the initial stage of software development. Its purpose is to create software prototypes to imitate various functions and user interfaces of the system so that existing problems can be identified and solved earlier. With the rapid development of computer technology and software industry, rapid prototyping technology has been widely used in various fields and achieved good results. In the field of software engineering, the use of rapid prototyping technology can effectively shorten the development time cycle, reduce the total cost of development, and improve the overall quality of software. It allows developers to recognize the software as a complex and huge whole from a higher level and decompose it into a series of sub-modules with specific goals or task requirements. In addition, this also helps developers gain a deeper understanding of user needs, thereby reducing the difficulty of misunderstanding and communication.
UX design
In the UX (user experience) design process, rapid prototyping technology also plays an indispensable role. Rapid prototyping system is a method that uses computers to generate three-dimensional entities. It is based on virtual reality and can provide a virtual scene and control and modify it, thereby realizing the entire process from conceptual design to manufacturing finished products. UX designers imitate the product's various functions and user interface by creating a scaled-down version of the product - a prototype - so that users can test and verify it.Prototypescan be either simple paperprototyping modelsor fully functional digital prototypes that users can interact with. The application of this technology in UX design helps designers understand user needs more deeply and identify problems and deficiencies in product design, so that adjustments and optimizations can be made in a timely manner to improve the user experience of the product.
Design Thinking
Design thinking represents a human-centered, continuous innovation and iteration problem-solving strategy. As one of the most promising emerging technologies in the field of advanced manufacturing, rapid prototyping technology has the characteristics of low cost and high efficiency, and has gradually become an indispensable part of the product research and development process. Rapid prototyping technology has been widely used in many aspects of product design thinking, mainly used to quickly verify and optimize various design solutions. Based on this, this article proposes a design thinking method based on rapid prototyping, which combines rapid prototyping with design thinking to achieve the entire life cycle management of products from concept to physical object to delivery. Applying it to design thinking can help team members understand user needs more deeply, quickly verify the feasibility of design solutions, and continuously improve the quality of product design through continuous iterative optimization.

3D printing
3D printing technology is a keyrapid prototyping method that uses digital model files and uses layered printing technology to create three-dimensional objects. Due to its unique process characteristics, it has become one of the most advanced processing methods in the manufacturing field and has developed rapidly. In the field of 3D printing technology, rapid prototyping methods are commonly used in every step of product design and manufacturing. It can directly produce physical parts or product prototypes as needed, providing designers with more intuitive and effective data information. In the field of rapid prototyping technology, 3D printing has shown obvious advantages. For example, it can produce complex structures and geometric forms, thereby improving production accuracy and efficiency and reducing production costs. Therefore, it has become an emerging design method. At the same time, as3D printing technologycontinues to advance, its application areas are gradually expanding.
What are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
As an efficient product development method, rapid prototyping has many significant advantages. Here are theadvantages of rapid prototyping:
Shorten product development cycle
Rapid prototyping greatly shortens the product cycle from concept to market by quickly converting design concepts into touchable, testable physical models. In the traditional product development process, it often takes a long time from design to manufacturing prototypes to testing feedback. Rapid prototyping technology can complete this process within days to weeks, allowing developers to verify designs earlier, discover problems, and perform iterative optimization, thereby accelerating product launch.
Improve design accuracy
Rapid prototyping technology usually combines advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software andCNC processing equipment to achieve high-precision and high-complexity product prototypes. These technologies can ensure a high degree of consistency between prototypes and design drawings, reducing errors caused by manual production or traditional processing methods. High-precision prototypes help to more accurately evaluate the function and performance of the product, providing a reliable basis for subsequent production and manufacturing.
Reduce costs
Althoughrapid prototyping technologymay require a higher investment in initial equipment, it actually helps reduce costs when viewed throughout the product development cycle. First, through rapid prototyping, developers can detect problems in the design early and avoid large-scale modifications in the later production stage, thereby reducing unnecessary waste and costs. Secondly, rapid prototyping supports small-batch, multi-variety production models, which helps companies flexibly respond to market changes and reduce inventory backlogs and capital occupation. In addition, with the popularization and cost reduction of rapid prototyping technologies such as 3D printing, its production costs are also gradually declining.
Enhance user experience and feedback
Rapid prototyping allows users or customers to have early access to physical products and provide feedback through first-hand experience. This kind of intuitive and instant feedback helps developers more accurately grasp user needs and market trends, so as to make targeted improvements and optimizations. At the same time, rapid prototyping also provides investors and partners with an intuitive display method, helping to enhance their confidence and recognition of the product.

What are Some Examples of Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping technology has a wide range of applications in practical applications,rapid prototyping examples are as follows:
auto industry
In the automobile research and development stage, 3D printing technology is widely used to produce automobile prototypes. These prototypes can be used for design verification, assembly verification and functional verification, helping automakers identify and resolve issues early in product development. For example, Ford used 3D printing technology to produce a large number ofprototypesof auto parts during the research and development stage to improve research and development efficiency.
electronic products
In the design and development process of smartphones, rapid prototyping technology is used to prototype mobile phone casings, internal structures and other components. By making mobile phone prototypes, designers can visually verify the feasibility and aesthetics of the design plan, and promptly discover and modify problems in the design. Users can actually operate and experience the mobile phone prototype and provide valuable feedback to help developers improve the user experience of the product. Rapid prototyping shortens the product development cycle, allowing smartphones to be brought to market faster to meet consumer needs.
Medical equipment
In medical device development, rapid prototyping technology is used to createprototypesof medical devices for clinical testing and verification. Prosthetics and rehabilitation equipment customized for patients often require rapid prototyping technology to produce personalized prototypes to ensure the comfort and functionality of the equipment.
Education and Research
In the field of education, rapid prototyping technology is used to produce teaching tools, such as physical models, demonstration devices, etc. In the field of scientific research, researchers use rapid prototyping technology to build experimental devices or system prototypes to conduct scientific experiments and verify hypotheses.

FAQs
1.What is meant by rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a product development method that emphasizes accelerating the product development process by quickly building and testing product prototypes. This approach allows designers, engineers, and developers to obtain performance models early in product development for functional verification, design evaluation, and user testing.
2.Is rapid prototyping the same as 3D printing?
Rapid prototyping is similar to 3D printing in some ways, but not exactly the same. Rapid prototyping is a broader concept that encompasses a variety of technologies and methods, including 3D printing. 3D printing is a technology commonly used in rapid prototyping, which converts digital models into physical models by stacking materials layer by layer. However, rapid prototyping also includes other technologies such as laser cutting, CNC machining and injection molding.
3.What is prototyping in 3D printing?
Prototyping in 3D printing refers to the process of using 3D printing technology to directly transform digital models into physical prototypes. This technology allows designers and engineers to obtain physical models early in product development for functional verification, design evaluation, and user testing. 3D printing prototyping has the advantages of being fast, flexible and economical, which can significantly shorten the product development cycle and reduce development costs. In the 3D printing process, materials are piled up layer by layer to build a three-dimensional solid, which makes it possible to create complex shapes and structures.
4.What is an example ofrapid prototyping?
Ford used 3D printing technology to produce a large number of prototypes of auto parts during the research and development phase; in the design and development process of smartphones, rapid prototyping technology was used toprototypemobile phone casings, internal structures and other components; in the development of medical equipment , Rapid prototyping technology is used to make prototypes of medical devices for clinical testing and verification; in the field of education, rapid prototyping technology is used to make teaching tools, such as physical models, demonstration devices, etc.
Summary
Rapid prototyping is an efficient, flexible, and low-cost product development method.prototyping meaning is that it uses advanced manufacturing technology to quickly transform design ideas into touchable and testable physical prototypes, which greatly accelerates product development. process and reduce development costs and risks. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous expansion of application fields, rapid prototyping technology will play a more important role in the future, providing strong support for product innovation and industrial upgrading.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
This article was written by multiple LS contributors. LS is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.