In the long history of human civilization, metal casting technology undoubtedly plays a pivotal role. From simple bronze vessels in ancient times to complex and sophisticated mechanical components in modern industry, metal casting, as an ancient and dynamic manufacturing process, has witnessed the glorious history of human technological progress. This technology not only profoundly affects our production methods, but also greatly enriches the material culture of human society. So,how does metal casting work?Today, theLongsheng Teamtakes everyone into the ocean of knowledge about metal casting to find out.
What is Metal Casting?
Metal casting is a manufacturing processthat involves pouring molten metal into molds to create 3D metal parts. The mold contains cavities of the desired geometry, and the molten metal cools to form the solidified part.
The word "cast" also refers to parts made through a casting process, which dates back 6,000 years. Historically, casting processes have been used to create complex and large parts that would be difficult or costly to create using other manufacturing processes.
Casting is the first choice for complex geometriesbecause it is more cost-effective and the process is simpler compared to, for example,CNC machining.But casting is also widely used for the simplest shapes because of its fast turnaround time and large production capabilities. Today, the use of cast products is so widespread that no matter what environment you are in, you cannot avoid using cast products. Some examples of cast metal products include engine blocks, fire hydrants, electric motors, tools, traffic lights, manholes, pipes, valves, and various fittings.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of metal casting?
As a metal forming process with a long history,metal casting plays a vital role in modern manufacturing. It is not only capable of producing metal parts with complex shapes and precise dimensions, but also has high material utilization and cost-effectiveness. However,metal casting also has some inherent challenges and limitations.
Advantages of metal casting
- Metal casting processes can manufacture workpieces with complex shapes especially complicated internal cavities, such as boxes, cylinder blocks, etc.;
- Wide range of adaptations;
- Themetal casting process can utilize low-cost ironand steel scrap, milling debris, etc., and casting equipment is relatively low.
- The size and weight are almost unrestricted with metal casting workpieces;
- The shape and size of the castings are very close to the workpiece. Therefore the metal casting process reduces the amount of further machining work and saves the metal materials.
Disadvantages of Metal Casting
- The relatively more involved production operations make casting processes more challenging to be fully controlled;
- The casting workpieces are more prone to take with casting defects;
- Relatively poor dimensional consistency and accuracy;
- Compared with forgings of the same size and shape, the intrinsic quality of castings is weaker, and the load-bearing capacity is less than that of forgings;
- Poor working environment with high temperature, dust, and high labor intensity.
How Does Metal Casting Work?
The metal casting process is a process in which metal is smelted into a liquid that meets certain requirements and poured into a mold. After cooling, solidification, and cleaning, a casting with a predetermined shape, size, and performance is obtained. The following is a detailed introduction to themetal casting process:
- Pattern Preparation:The initial steps in themetal casting process often involve the creation of a pattern, which is an exact replica of the final part used in subsequent mold making. Models are available in a variety of materials, including durable types such as wood and plastic, as well as single-use wax materials, depending on your casting needs.
- Core design:For parts that need to be cast with hollow structures, the design of the core is crucial. It is a solid piece of material placed within the mold cavity to define the internal geometry of the casting. For example, when casting tubular objects, a cylindrical core is placed inside a larger cylindrical mold to ensure that a corresponding hollow structure is formed inside the casting.
- Mold forming:The method of making the mold varies according to the casting process. Permanent metal molds are precision machined usingCNC machines, while sand molds are constructed by applying a sand mixture layer by layer to the surface of the model. Mold making is a professional skill that covers the entire process from design to molding.
- Mold filling:Metal is heated to a molten state and injected into the mold cavity by gravity or pressure. In gravity casting, the molten metal flows naturally into the mold; in high-pressure die casting, the metal is forced into the mold under high pressure, requiring high clamping force to ensure the integrity and safety of the mold.
- Part ejection:Once the casting has cooled and solidified, it can be removed from the mold. For sand casting, this usually means the destruction of the mold to release the casting; whereas for casting processes using permanent molds, the two halves of the mold can be separated to allow for reuse of the mold.
- Post-processing:Before the cast metal parts are put into use, they may need to be cleaned (such as removing mold residue) and other necessary post-processing steps to ensure the quality and performance of the parts.

What Types of Metal Casting Methods Exist?
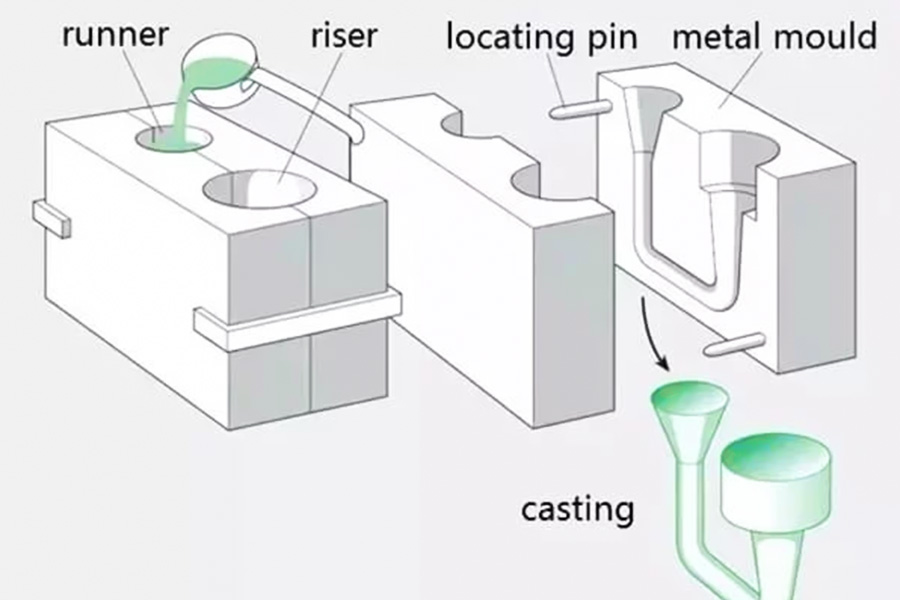
1.Sand Casting
Sand casting is a universal casting process that can be used to cast any metal alloy, whether ferrous or non-ferrous. It is widely used in mass production in industrial units such as automotive metal casting parts such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, etc.
The process uses molds made of silicon-based materials, such as naturally bonded sand or synthetic sand, to create a smooth mold surface. The mold surface has two parts, the upper mold (upper part) and the lower mold (lower part). A pouring cup is used to pour molten metal into the mold, where it solidifies to form the final shape. Finally, excess metal is trimmed off to complete the final metal cast product.
2.The Casting
While sand casting can melt alloys with higher melting points, you can use die casting to shape metals with lower melting points. After changing the material from a solid to a hot molten liquid, you can inject it into a long-life die-cast mold made of hardened steel. These tools consist of a cavity, a core, and sometimes an insert. Unlike plastic injection molding, machining side features after casting is sometimes more feasible than using side actions. Die casting dates back to the 19th century.
Since its emergence in the manufacturing world, two types of programs have been developed for your use. The first is a hot chamber, which features a built-in furnace within the machine to melt the material. If you use the cold chamber process, the second procedure, you melt the material in a separate furnace and then move the molten material into the injection chamber. You can implement die casting for high-volume production of aerospace and automotive parts, as well as toys, furniture, and electronics. Die casting is provided through Longsheng's core services, and quotes can be created through the instant quote engine.
3.Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, uses a disposable wax pattern coated with ceramic material that solidifies into the shape of the casting. The first step in this casting process is to create a wax pattern, usually made of wax or plastic. Because the process requires precise measurements, multiple trials and errors make investment casting an expensive manufacturing process. The wax is poured into the mold, carefully removed, and then coated with adhesive or refractory material to form a thick shell. Additionally, multiple models are assembled onto the main gate. Once the shell has hardened, the model is turned over and heated in the oven to remove the wax. The molten metal is poured into the remaining shell and solidifies into the shape of the wax mold. Additionally, the refractory shell is broken off to reveal the finished casting. This casting process is commonly used to make power generation, automotive and aerospace components.
4.Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting, also known as spin casting, is a process that uses centrifugal force to manufacture cylindrical parts industrially. This type of metal casting uses a preheated rotating mold into which molten metal is poured. Centrifugal force helps disperse the molten metal within the mold at high pressure.
There are three types of centrifugal casting: true centrifugal casting process, semi-centrifugal casting process and vertical centrifugal casting process. Semi-centrifugal casting differs from true centrifugal casting in that it uses a gate to completely fill the mold. However, in true centrifugal casting, the molten metal sticks to the sides due to the continuous rotation. In contrast, vertical centrifugal casting, as the name suggests, uses directional molding, following the same process as true centrifugal casting.
Typically, centrifugal casting produces a rotating shape that resembles a cylinder. Especially parts such as bearings, clutch plates, piston rings and cylinder liners. Additionally, pouring metal in the center of the mold helps reduce defects such as porosity, shrinkage, and air pockets. However, it does not work with all types of metal alloys.
5.Continuous Casting
Continuous casting is an advanced casting method. Its principle is to continuously pour molten metal into a special metal mold called a crystallizer. The solidified (crusted) castings are continuously poured from the other end of the crystallizer. out, and then pull it out from one end to obtain a casting of any length or a specific length.
6.Lost Foam Casting
Lost foam casting is similar to investment casting, except that it uses foam instead of wax as the model. Once the model is formed, it is coated with refractory ceramic by dipping, coating, spraying or brushing. The molten metal is then poured into molds to form the desired product.