Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an advanced 3D printing processthat accurately sinters and fuses powder particles through the action of laser to build a three-dimensional structure. As an efficient, economical and high-precision additive manufacturing technology, SLS opens up more efficient manufacturing pathways for a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive manufacturing, healthcare, and consumer goods.
The key to SLS's ability to realize these applications lies in the materials used. Known for their exceptional versatility and strength, these3D printing materialsare capable of printing parts with complex structures, high durability, high precision and rich detail. These materials are used in a wide range of applications, from delicate jewelry to large industrial components, and are particularly good at producing prototypes, functional parts and personalized custom designs. This guide will provide an in-depth breakdown of the types of materials used in SLS to provide you with a comprehensive understanding.
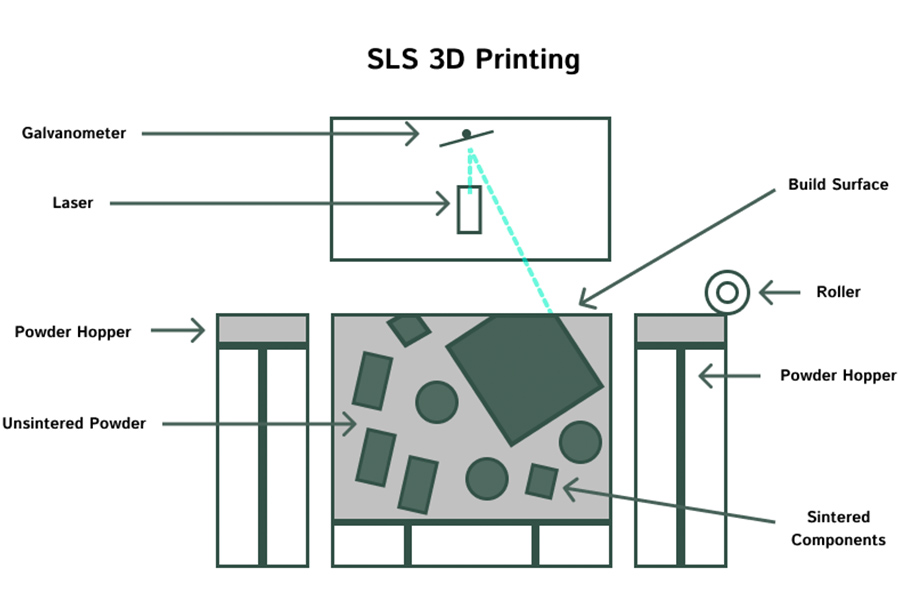
What Materials Are Used in Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
The most commonlyused materials for SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)mainly include nylon (PA12, PA11, PA6), polypropylene (PP), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) and PEEK (polyetheretherketone).
- Nylon 12 (PA12):This is ahigh-performance nylon materialwith excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance. It is often used to manufacture parts that need to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress. PA12 also has good chemical and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
- Nylon 11 (PA11):Similar to PA12, PA11 also has good mechanical properties and heat resistance. It is often used to manufacture parts that require high toughness and good flowability. PA11 also has excellent oil and chemical resistance,making it suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
- Nylon 6 (PA6):PA6 is a commonly used nylon material with high strength, abrasion resistance and chemical resistance. It is often used to manufacture parts that need to withstand higher loads.PA6 also has good processing properties and recyclability, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
- Polypropylene (PP): PP has high chemical resistance and is suitable for automotive and medical applications. In the SLS process, the sintering performance of PP powder is affected by a variety of process parameters, such as laser power, preheating temperature and energy density. By optimizing these parameters, PP parts with good molding accuracy, density and mechanical properties can be obtained.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane):TPU is a highly flexible and elastic material commonly used to manufacture partsthat require excellent wear resistance and rebound properties. TPU is particularly suitable for the production of seals, gaskets and protective cases for electronic equipment. In addition, it offers excellent resistance to oils, greases and various solvents, making it ideal for components exposed to harsh chemical environments.
- PEEK (polyetheretherketone):PEEK is a high-performance polymer with excellent mechanical, thermal and chemical properties. PEEK has a high glass transition temperature and melting temperature, allowing it to withstand high temperatures and maintain its structural integrity in harsh environments. Suitable for industrial applications such as aerospace, medical and automotive, such as manufacturing gears, brackets and engine components.

What role does budget play in SLS material selection?
Here are some examples ofhow budget can influence SLS materialselection:
- The first consideration ismaterial cost. When choosing materials, cost is undoubtedly a key factor. For example, thermoplastics such as unfilled nylon are more affordable than metals or specialty polymers such as glass-filled nylon. If you're on a budget, you can choose a more cost-effective material while ensuring it still meets the technical specifications required for your application.
- Budget considerations can be very different betweenprototyping and production. During the testing phase, you may be tempted to choose less expensive materials for prototyping in order to reduce costs. However, at the production stage, it may make more sense to choose higher-cost, high-quality materials considering the performance and durability of the product.
- In addition, the different properties of materials are also important considerations when choosing. Your budget will determine whether you choose a material that performs well but is expensive, or opts for a more affordable option that offers modest performance.
- For special application needs, such as biocompatible or flame retardant materials, these special types of materials tend to be more expensive. Therefore, the size of your budget will directly affect your choice of these special materials.
- Finally, post-processing costs are also a factor that cannot be ignored. Some materials may require additional processing steps, such as surface treatment or heat treatment, which will increase the overall cost. Therefore, when working on a tight budget, you may be more inclined to choose materials that require minimalpost-processing.

What Are the Advantages of Nylon-Based SLS Materials?
Nylon-based SLS materials have many advantagesthat make them widely used in 3D printing and industrial manufacturing.
- Strong Mechanical Properties:Nylon-based SLS materials offer high strength, toughness and good wear resistance, making them ideal for making functional prototypes and end-use parts. These parts can withstand large mechanical stresses and maintain stable performance in a variety of application environments.
- Heat, Chemical, and Impact Resistant:Nylon-based SLS materials have good heat, chemical, and impact resistance, making them suitable for use in a variety of industrial applications. These properties allow nylon-basedSLS materialsto maintain their structural integrity and performance stability in high temperature, corrosive or impact environments.
- Smooth surface finish:Nylon-based SLS materials print parts with a smooth surface finish that requires little additional post-processing. Thisreduces manufacturing costs and timewhile improving the aesthetics and practicality of the part.
What Metal Powders Are Used in SLS Printing?
Themetal powders that can be used in SLS (selective laser sintering) printingtechnology mainly include the following:
1.Stainless steel:
- Advantages:High strength and corrosion resistance.
- Application:Widely used in aerospace, medical equipment, automobile manufacturing and other fields. For example, 316Lstainless steel powder has been widely used in SLS printingdue to its good comprehensive properties.
2.Aluminum:
- Advantages:Light weight, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Application:Mainly used in aerospace and automotive parts and other fields to reduce weight and improve energy efficiency.
3.Titanium:
- Advantages:high strength, low density and good biocompatibility.
- Applications:Suitable for medical implants and aerospace components. In the medical field, titanium alloys are widely used to make medical devices such as orthopedic implants due to their good biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
4.Cobalt Chromium Alloy:
- Advantages:wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and good biocompatibility.
- Application:Ideal for dental and medical applications.For example, cobalt-chromium alloys are widely used in the dental field to make dental crowns, bridges and other restorations.

How Do SLS Materials Compare to SLA and FDM?
SLS (selective laser sintering), SLA (stereolithography) and FDM (fused deposition modeling) are the three main methods in 3D printing technology,and they each use different materials and processes to create three-dimensional objects. The table below compares SLS to SLA, FDM, and SLM (Selective Laser Melting):
| SLS material | SLA material | FDM material | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material morphology | Powder form | liquid | filiform |
| Type of material | Plastics, metals, ceramics and other powder materials | Liquid photosensitive resin | Thermoplastics (e.g. PLA, ABS, etc.) |
| Material Properties | The powder materials are diverse and can be adapted to different needs, such as strength, heat resistance, etc | The liquid resin has a smooth surface and high precision after curing | Thermoplastic materials are susceptible to melt and deposit, but have relatively weak strength and heat resistance |
| Print accuracy | Moderate, the layer thickness is generally between 0.1mm and 0.2mm | Height, layer thickness can be as small as 0.025mm | Relatively low, the layer thickness is usually between 0.1mm and 0.4mm |
| Surface | Depending on the powder size and sintering process, post-treatment may be required | Smooth and delicate, with excellent details | There are distinct streaks and a staircase effect |
| Support structure requirements | Usually there is no need for a support structure, and the powder is naturally supported | Support structures need to be designed and fabricated | Complex shapes may require support structures |
| Print speed | Relatively slow, each layer requires laser sintering and cooling | Fast, especially for high-precision, small-size models | Medium, suitable for small to medium-scale production |
| Equipment costs | Medium to high | Higher | Lower |
| Material costs | Depends on the type of powder chosen | Relatively high | Relatively low |
| Fields of application | Automotive, aerospace, medical implants and other high-strength, complex structural parts | High-precision models for jewelry, medical, dental, aerospace, etc | Education, rapid prototyping, manufacturing, and more |
Summary
Selective laser sintering (SLS) technology exhibits broad material compatibilityand can use a variety of powder materials to create physical objects. Each of these powder materials has unique properties that are sufficient to meet the diverse needs of different industries and application scenarios. Looking to the future, as SLS technology continues to progress and mature, we have reason to believe that more innovative materials will be developed to further broaden the application scope of SLS technology.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1.What types of materials do SLS technology mainly use?
SLS technology mainly uses powdered materials, which can be roughly divided into several categories such as metal-based synthetic materials, ceramic-based synthetic materials, foundry sand and polymer powders. Metal-based composite materials: composed of metal powder and binders, have high hardness and working temperature, and are suitable for manufacturing parts that need to withstand high temperatures and high pressures. Ceramic-based synthetic material: It is composed of ceramic powder and binder. It has higher hardness than metal-based materials and a higher working temperature. It is also suitable for the manufacture of high-temperature molds. Foundry sand: Mainly used for the production of low-precision prototypes. The main component is coated sand, with polymer bonding components attached to the surface, such as low molecular weight phenolic resin. Polymer powder: including nylon (PA) powder, polycarbonate (PC) powder, polystyrene (PS) powder, ABS powder, casting wax powder, etc.
2.Can SLS technology use biodegradable materials?
Yes, with the improvement of environmental awareness, more and more biodegradable materials have been developed and used in SLS technology. These materials can be decomposed by microorganisms in the natural environment after printing, thereby reducing the impact on the environment. Common biodegradable materials include polylactic acid (PLA), etc.
3.Can all materials used in SLS technology be recycled and reused?
Most of the materials used in SLS technology, especially polymer powder materials, have high recyclability. Through specialized recycling and processing technology, these powders can be reused for printing, reducing material waste and costs. However, some special materials such as metal-based and ceramic-based composite materials may face greater challenges during the recycling process.
4.What new materials may be used in SLS technology in the future?
With the continuous development of science and technology, SLS technology may use more new materials in the future. These materials may have higher strength, better heat resistance, better biocompatibility or more environmentally friendly properties. For example, some research teams are developing composite materials based on nanotechnology in order to improve the mechanical properties and wear resistance of printed parts. In addition, with the rise of bio-3D printing technology, SLS technology may also use more bio-ink materials to create bioactive tissues and organs in the future.
Resource
2.Study on high temperature sintering processes of selective laser sintered Al2O3/ZrO2/TiC ceramics







