Metal casting is an important metal forming processthat heats solid metal to a liquid state and then pours it into a mold of a specific shape. After cooling and solidifying, a casting of the desired shape is obtained. This process is widely used in machinery manufacturing, aerospace, hydropower and many other fields. However, behind this complex and delicate process, a crucial question has always attracted the attention of engineers and materials scientists:What materials are used in metal casting, and how do these materials determine the performance and use of the castings?
This article aims to deeply explore the corematerials used in metal casting, from traditional cast steel and cast iron to modern widely used cast aluminum and cast copper, and even special alloys and composite materials. The selection and application of each material contains Profound scientific principles and engineering practical wisdom. We will analyze the composition, characteristics and behavior of these materials during the casting process, revealing how they affect the final performance of the casting, and how to achieve the best balance between casting performance and cost through material selection and optimization.
What is Metal Casting?
Metal casting is a manufacturing processthat involves pouring molten metal into molds to create3D metal parts. The mold contains cavities of the desired geometry, and the molten metal cools to form the solidified part.
The word “cast” also refers to parts made through a casting process, which dates back 6,000 years. Historically, casting processes have been used to create complex and large parts that would be difficult or costly to create using other manufacturing processes.
Casting is the first choice for complex geometriesbecause it is more cost-effective and the process is simpler compared to, for example, CNC machining. But casting is also widely used for the simplest shapes because of its fast turnaround time and large production capabilities. Today, the use of cast products is so widespread that no matter what environment you are in, you cannot avoid using cast products. Some examples of cast metal products include engine blocks, fire hydrants, electric motors, tools, traffic lights, manholes, pipes, valves, and various fittings.

What Materials Are Used in Metal Casting?
A wide variety ofmaterials are used in metal casting, each of which is widely used in different industrial fields due to its unique physical and chemical properties. Here are some of the major metal casting materials:
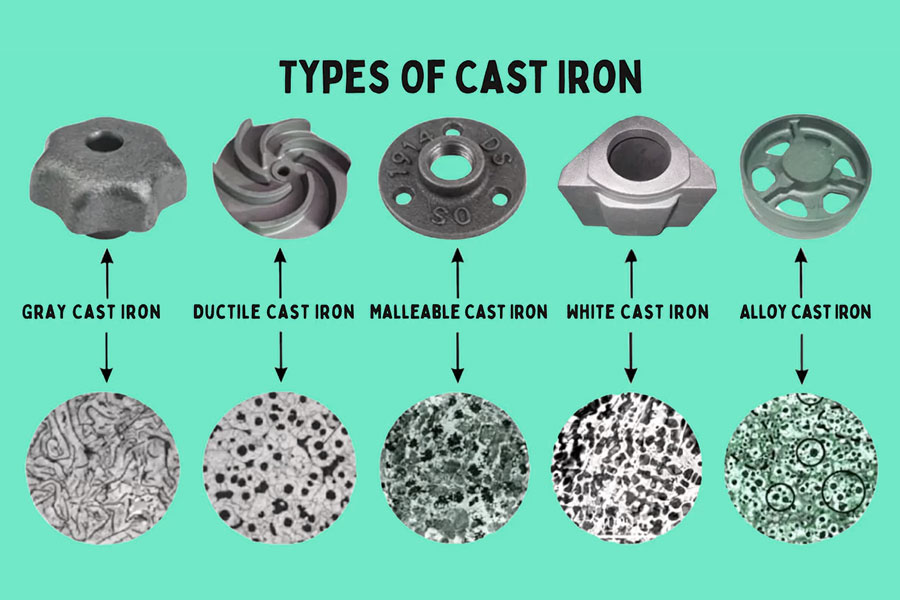
cast iron
Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy with a carbon content greater than 2.1%. It has excellent castability, wear resistance, shock absorption and other characteristics. There are many types of cast iron, generally divided into white cast iron, gray cast iron, malleable cast iron, ductile iron, etc. Gray cast iron has three structures: ferrite + graphite, ferrite + graphite + pearlite, and pearlite + graphite. It is suitable for manufacturing parts that bear static loads. Malleable cast iron is a high-strength cast iron obtained from white cast iron after long-term graphitization annealing. It is suitable for manufacturing parts that bear impact loads. Ductile iron is obtained by adding spheroidizing agents and inoculants to spheroidize graphite. Its strength, plasticity, and toughness are higher than other cast irons, and it is suitable for manufacturing complex parts that bear higher loads.
Aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloys are widely used due to their low density, high strength, good corrosion resistance and excellent casting properties.Aluminum alloy has good casting performance and high fluidity. It can die-cast precision parts with complex shapes and thin walls, and the surface of the castings is smooth. In addition, aluminum alloys can also undergo a variety of surface treatments, such as electroplating, spraying, etc. Common cast aluminum alloys include ZL101, ZL102, etc. They are suitable for casting parts with complex shapes and medium load, as well as parts requiring high air tightness, corrosion resistance and good welding performance.
zinc alloy
Zinc alloy is an alloy based on zinc with the addition of other elements. It has good casting properties and mechanical properties. Zinc alloy has a large specific gravity, low melting point, and is easy to die-cast. At the same time, zinc alloy castings have a smooth surface and can be processed in a variety of surfaces. However, zinc alloy has poor corrosion resistance. When the impurity elements in the alloy composition exceed the standard, it will cause the casting to age and deform. In addition, zinc alloy die castings are not suitable for use in high and low temperature (below 0°C) working environments. Common zinc alloys include Zamak3, Zamak5, etc., which are suitable for castings with low requirements for mechanical strength and castings with certain requirements for mechanical strength.
Magnesium alloy
Magnesium alloy has the characteristics of low density, good specific strength and stiffness, good vibration damping performance, and strong electromagnetic interference shielding ability. Magnesium alloy has relatively poor casting performance, low fluidity, and greater tendency to crack and shrink. However, magnesium alloys are widely used in automobiles, aerospace, electronics and other fields because it can significantly improve the fuel economy, reduce exhaust emissions and reduce weight of products. Common cast magnesium alloys include AZ91D, AM60B, etc., which are suitable for manufacturing automotive parts, aerospace parts, etc.
Copper alloy
Copper alloy has the characteristics of good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and low friction coefficient. Copper alloys have excellent casting properties and can be made into castings with complex shapes. Copper alloys are widely used in the electronics industry, machinery industry, aerospace industry, chemical industry and other fields. For example, in the electronics industry, copper alloys are often used to make electronic components; in the machinery industry, copper alloys are often used to make mechanical parts that require high wear resistance and corrosion resistance; in the aerospace industry, copper alloys are often used Used to make parts with high strength and toughness. Common cast copper alloys include brass, bronze, etc. The table below summarizes and compares theadvantages and disadvantages of common metal casting materials.
|
Cast material |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Aluminum Alloys |
Lightweight; high dimensional stability; easy to cast; good corrosion resistance; high thermal and electrical conductivity; retains strength at high temperature. |
Requires use of cold-chamber machines. |
|
Zinc Alloys |
Easiest to cast; high ductility; excellent surface smoothness; high impact strength; easily plated; economical for small parts; promotes long die life due to low melting point. |
Requires coating to resist corrosion; high density. |
|
Cast Iron |
Low price, good wear resistance, strong compression resistance |
Easy to produce pores, brittle high |
|
Magnesium Alloys |
Easiest to machine after casting; excellent strength-to-weight ratio; lightest; use both hot- and cold-chamber machines. |
Rapidly oxidized. |
|
Copper Alloys |
High hardness; high mechanical properties; high corrosion and wear resistance; high dimensional stability. |
High cost; low die life; requires use of cold-chamber machines. |
What Are the Components and Additives in Metal Casting?
Ingredients and additives in metal casting vary depending on the specific metal type and casting needs. Here is an overview of some commonmetal casting ingredients and additives:
1.Main components of metal casting
- Metal elements:The materials to be cast are mostly metals that are originally solid but are heated to a liquid state, such as copper, iron, aluminum, tin, lead, etc. These metallic elements are the main components of casting alloys.
- Alloying elements:In order to improve and enhance certain properties of metals or obtain certain special properties, alloying elements are added during the smelting process. Commonly used alloying elements include chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, titanium, silicon, manganese, etc. These elements can enhance the hardenability, heat strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. of metals.
2.Additives for metal casting
- Carburizing agent:used to increase the carbon content in metal and improve the hardness and wear resistance of metal. Common carburizing agents include calcined coal carburizing agents, graphite carburizing agents, etc.
- Deoxidizer and desulfurizer:used to remove harmful elements such as oxygen and sulfur from metals to improve the purity and quality of metals. For example, calcium wire, calcium cored wire, etc. can be used as deoxidizer and desulfurizer.
- Alloy additives:used to adjust the chemical composition of metals to obtain the required alloy properties and structure. These additives can be compounds or mixtures of metallic elements (such as ferrochrome, ferronickel, ferromolybdenum, etc.) or non-metallic elements (such as silicon, manganese, etc.).
- Casting additives:such as bentonite, etc., can be used as a binder for casting sand to improve the strength and stability of the casting mold. In addition, there are some special casting aids, such as fluxes, opacifiers, etc., used to improve the metal smelting and casting process.
How to choose materials based on metal casting process?
Selecting materials based on metal casting processes is a complex processthat requires consideration of multiple factors, including the structure of the casting, performance requirements, production batch size, cost budget, and characteristics of the casting process. The following are some basic principles and suggestions for selecting materials according to different casting processes:
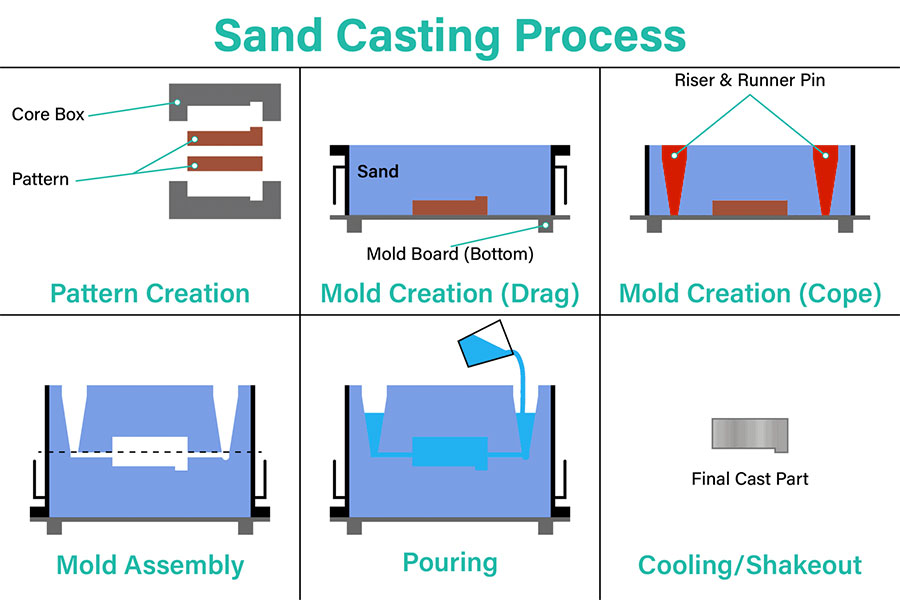
Sand Casting
Sand casting is a universal casting process that can be used to cast any metal alloy, whether ferrous or non-ferrous. It is widely used in mass production in industrial units such as automotive metal casting parts such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, etc.
The process uses molds made of silicon-based materials, such as naturally bonded sand or synthetic sand, to create a smooth mold surface. The mold surface has two parts, the upper mold (upper part) and the lower mold (lower part). A pouring cup is used to pour molten metal into the mold, where it solidifies to form the final shape. Finally, excess metal is trimmed off to complete the final metal cast product.
1.Material selection principles:
- Casting material:various metal alloys, such as cast iron, cast steel, non-ferrous metal alloys, etc.
- Mold materials:high-temperature materials such as quartz sand and clay, which are required to have good high-temperature resistance, air permeability and plasticity.
2.Applicable scenarios:
- Suitable for castings with complex shapes and large sizes, especially thick-walled parts.
- Suitable for single pieces, small batches or large castings that are difficult to use other casting methods.
Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, uses a disposable wax pattern coated with ceramic material that solidifies into the shape of the casting. The first step in this casting process is to create a wax pattern, usually made of wax or plastic. Because the process requires precise measurements, multiple trials and errors make investment casting an expensive manufacturing process. The wax is poured into the mold, carefully removed, and then coated with adhesive or refractory material to form a thick shell. Additionally, multiple models are assembled onto the main gate. Once the shell has hardened, the model is turned over and heated in the oven to remove the wax. The molten metal is poured into the remaining shell and solidifies into the shape of the wax mold. Additionally, the refractory shell is broken off to reveal the finished casting. This casting process is commonly used to make power generation, automotive and aerospace components.
1.Material selection principles:
- Casting material:cast steel and high melting point alloys, such as stainless steel, high temperature alloys, etc.
- Mold materials:Wax pattern (for making prototypes), ceramic shell (for forming castings).
2.Applicable scenarios:
- It is suitable for small and complex precision castings of various batches of cast steel and high melting point alloys.
- Especially suitable for casting artworks, precision mechanical parts, etc.
The Casting
While sand casting can melt alloys with higher melting points, you can use die casting to shape metals with lower melting points. After changing the material from a solid to a hot molten liquid, you can inject it into a long-life die-cast mold made of hardened steel. These tools consist of a cavity, a core, and sometimes an insert. Unlike plastic injection molding, machining side features after casting is sometimes more feasible than using side actions. Die casting dates back to the 19th century.
Since its emergence in the manufacturing world, two types of programs have been developed for your use. The first is a hot chamber, which features a built-in furnace within the machine to melt the material. If you use the cold chamber process, the second procedure, you melt the material in a separate furnace and then move the molten material into the injection chamber. You can implement die casting for high-volume production of aerospace and automotive parts, as well as toys, furniture, and electronics. Die casting is provided through Longsheng’s core services, and quotes can be created through the instant quote engine.
1.Material selection principles:
- Casting materials:aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, zinc alloy, etc., which require good fluidity and processability.
- Mold material:high-strength alloy steel, carbide or ceramic materials, requiring high hardness, high wear resistance and high thermal stability.
2.Applicable scenarios:
- Suitable for mass production of various small and medium-sized non-ferrous alloy castings, thin-walled castings, and pressure-resistant castings.
- Die castings have high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface, dense structure, high production efficiency and low cost.
What Equipment is Required for Metal Casting?
Metal casting is a complex and delicate process that requires a variety of equipment to work together to ensure the quality and efficiency of the casting.
Melting Furnace
The smelting furnace is a key equipment in the metal casting process. It is responsible for heating the metal raw materials to a molten state for subsequent pouring and shaping. The performance of the melting furnace directly affects the melting efficiency of the metal, the uniformity of the composition and the quality of the casting. Common smelting equipment include:
- Dome:Used for melting metals, especially cast iron etc.
- Electric arc furnace:uses the high temperature of the arc to melt metal.
- Induction furnace:heats and melts metal through the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- Resistance Furnace:Uses the heat generated by the passage of electric current through a resistor to melt metal.
- Reverberatory Furnace:Heats and melts metal by reflecting heat.
Pouring and Cooling Equipment
The pouring equipment is responsible for pouring the molten metal into the mold, while the cooling equipment is responsible for accelerating the cooling and solidification process of the casting.
Pouring equipment:including pouring bags, pouring pipes, etc. The pouring bag is used to contain the molten metal and control the pouring speed and flow rate; the pouring pipe is responsible for introducing the molten metal from the pouring bag into the mold.
Cooling equipment:including cooling fans, cooling water systems, etc. They accelerate the cooling process of castings by reducing the temperature around the casting mold, thereby improving the production efficiency and quality of castings.
Finishing and Cleaning Tools
Finishing and cleaning tools are indispensable post-processing equipment in the metal casting process. They are used to improve thesurface quality and dimensional accuracy of castings.
- Deburring tools:such as burr grinder, magnetic polisher, etc. These devices remove burrs and impurities from the surface of castings through physical or chemical methods to improve the surface finish of castings.
- Polishing equipment:such as abrasive belt polishing machine, surface polishing machine, etc. They polish the surface of the casting by rotation or friction to achieve the required surface quality and gloss.
- Other cleaning tools:such as cleaning agents, sandblasting machines, etc. These tools are used to remove oil, oxides and other impurities on the surface of castings to ensure the cleanliness and quality of castings.
FAQs
1.What tools are needed for metal casting?
A variety of tools are required in the metal casting process, and each of these tools performs different functions to ensure the smooth progress of the casting process and the quality of the castings. Common metal casting tools mainly include sand foundry: used to turn the sand mold over so that the casting can be processed throughout the casting process. Mold Tongs: Used to hold molds or castings for machining and movement throughout the casting process. Gate scraper: used to clean the gate and ensure that molten metal is poured into the mold smoothly. Hardness tester: used to test the hardness of castings to determine whether their quality meets standards. Grinding machine: used to modify the surface of castings and cut castings to remove bad surfaces and cuts andimprove the surface quality of castings. In addition, there are air angle grinders, scrapers, electric drills, grinders, electric hammers, etc.
2.What are the most common materials used in metal casting?
The most commonly used materials in metal casting include iron, aluminum, copper, zinc and other metals and their alloys. Each of these materials has its own unique characteristics and applicable scenarios. For example, iron: has good castability and mechanical properties and is widely used in various fields. Aluminum: has a low melting point and good corrosion resistance, suitable for manufacturing lightweight and high-strength castings. Copper: has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity and is often used in the manufacture of electrical appliances and thermal components. Zinc: has a low melting point and good fluidity, suitable for manufacturing castings with complex shapes.
3.How do I choose the right material for my casting project?
Choosing the right material for a casting project is a complex processthat requires consideration of multiple factors to ensure the material selected will meet the needs of the project. First of all, it is necessary to clarify the specific use, working environment, stress conditions, etc. of the casting to determine the required performance requirements. According to the needs of the project, select materials with corresponding physical properties (such as density, thermal conductivity, linear expansion coefficient, etc.), chemical properties (such as corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, etc.) and mechanical properties (such as strength, hardness, toughness, etc.) Material. Consider the casting fluidity, shrinkage, segregation tendency and other process properties of the material to ensure the smooth progress of the casting process and the quality of the castings. Including material price, processing cost, service life, etc., to ensure that the selected material not only meets the performance requirements, but also has good economics.
4.What are the advantages of using alloys in casting?
The use of alloys in casting has many advantages over single metals, and these advantages make alloys widely used in the casting field. The main advantage is that the alloy can improve its physical, chemical and mechanical properties by adjusting its composition, such as improving strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. Alloys usually have better fluidity, which is beneficial to reducing casting defects and improving the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of castings. Through alloying, alloy materials with specific properties can be developed to meet the needs of different fields and specific uses. In some cases, using alloys can reduce overall costs by reducing processing costs, improving material utilization, or extending service life.
Summary
Common casting materials mainly include aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, cast iron, copper alloy, magnesium alloy, etc.Each material has its own unique characteristics and scope of application. When selecting casting materials, you need to comprehensively consider the shape, size, and performance requirements of the casting. and production costs and other factors to ensure that the quality and performance ofcastings meet design requirements.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.Longshengdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
Longsheng Team
This article was written by multiple Longsheng contributors. Longsheng is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.





