Laser cuttingis an advanced processing technology widely used in the manufacturing fields of automobiles, home appliances, electronic products, etc. It achieves the purpose of cutting by irradiating the surface of the material with a high-power density laser beam, causing the material to melt, vaporize or burn rapidly. This article will introduce in detail theworking principle of laser cutting, its key components, its advantages in practical applications and future development trends.
What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a high-precision, non-contact material processing technologythat uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a "cutting tool" and accurately controls the movement path of the laser through a computer program, so that the laser beam is focused on the surface or inside of the material, generating high temperatures to quickly melt, vaporize, evaporate or reach the ignition point of the material, and at the same time, auxiliary gases (such as oxygen, nitrogen, argon, etc.) are used to blow away the melted or vaporized material, thereby achieving the purpose of cutting. This technology can process a variety of materials including metals (such as stainless steel, aluminum alloys, titanium alloys), non-metals (such as wood, plastics, glass, ceramics), etc., and has the advantages of fast speed, high precision, good edge quality, high degree of automation, and high material utilization.
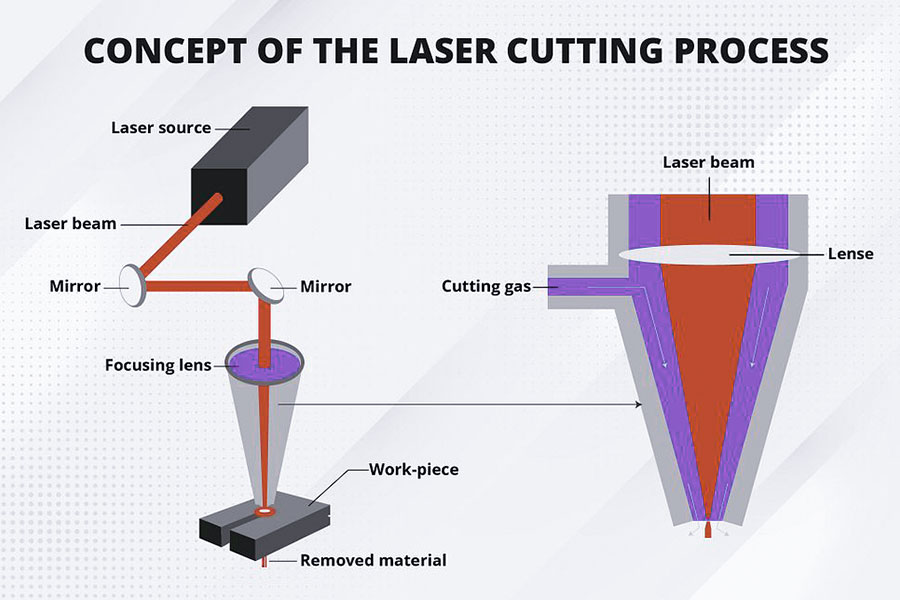
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
The basicprinciple of laser cuttingis to use a high-power density laser beam to irradiate the surface of the material, and through a series of physical phenomena, the material is quickly melted, vaporized or burned to form an incision. The generation of the laser beam needs to be realized by a laser, which mainly consists of three parts: a pump source, a gain medium and an optical resonant cavity. The pump source provides energy to the gain medium, which absorbs the energy and generates stimulated radiation. The optical resonant cavity amplifies and shapes the stimulated radiation, and finally forms a high-power density laser beam.
When the laser beam hits the surface of the material, a variety of physical phenomena occur, including reflection, absorption, scattering, and heat conduction. The energy density of the laser beam is high enough to quickly make the surface of the material reach the melting point or boiling point, thereby achieving cutting. This process can be subdivided into the following stages:
- Heat conduction:The laser beam hits the surface of the material, causing the surface temperature to rise rapidly, and the heat is transferred to the inside of the material through heat conduction, forming a heat-affected zone.
- Melting:When the surface temperature of the material reaches the melting point, the material begins to melt and forms a molten pool.
- Vaporization:When the surface temperature of the material continues to rise and reaches the boiling point, the material begins to vaporize and form steam.
- Combustion:For some flammable materials, such as wood, plastic, etc., the high temperature of the laser beam can cause a combustion reaction on the surface of the material, produce gas, and further accelerate the cutting process.
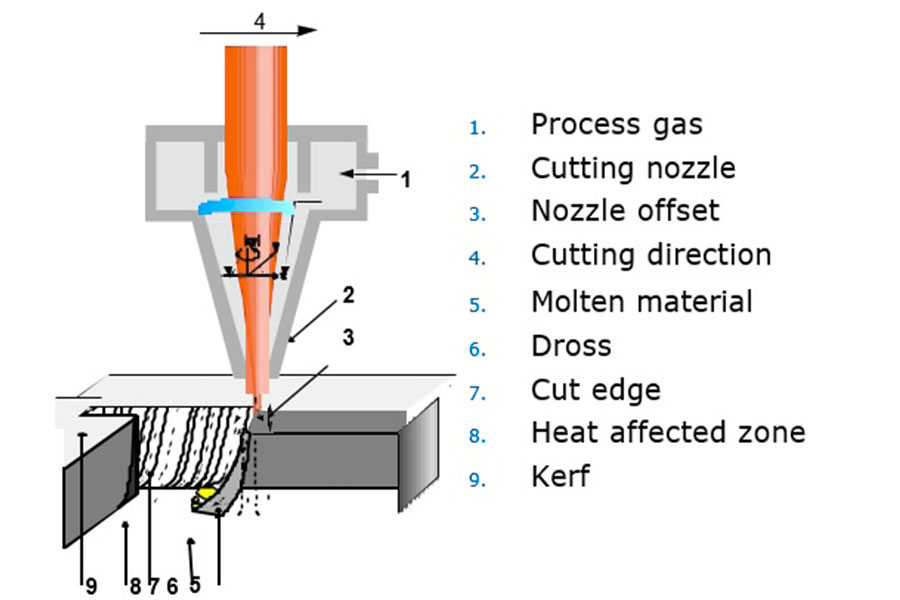
What Are the Steps in the Laser Cutting Process?
Theprocess of a laser cutting machineusually includes a series of orderly and detailed steps. The following is its process:
- Start-up preparation:First, turn on the power supply, check and ensure that all parts of the equipment are normal, including the cooling system, gas system, etc.
- Material preparation and parameter setting:Place the material to be cut on the cutting table, enter the corresponding cutting parameters such as laser power, speed, etc. on the operation interface according to the material type and cutting requirements, and import the cutting graphics.
- Focus and positioning:Adjust the focal position of the laser beam to ensure that the laser can accurately focus on the material and determine the starting point of cutting.
- Start cutting:Start the laser and machine tool, and cut according to the preset graphics and parameters.
- Monitoring and adjustment:During the cutting process, the operator needs to pay close attention to the cutting situation and adjust the cutting parameters according to the actual situation if necessary.
- Cutting completion and shutdown:After the cutting is completed, check the product quality and then shut down the equipment in the correct order.
- Maintenance and care:Clean, inspect and maintain the equipment regularly to ensure that the equipment is in good condition. Maintenance results after points redemption speech surprise tuna join hot pot but join the guild good condition Ruyi check post need him scold too much to replace as soon as possible.

What are the advantages of laser cutting?
Theadvantages of laser cutting technologyare mainly reflected in the following aspects:
| Advantages | Description |
| Accuracy | The accuracy of the laser cutting machine is the highest among all cutting methods. High accuracy comes from the fact that the light is reduced to a very fine diameter. The accuracy of laser cutting is even higher than that of processes such as waterjet cutting. |
| Speed | The speed at which laser cuts thin materials is extremely fast, and the speed can easily exceed 3 meters per minute, so laser cutting machines are common in mass production lines. |
| Versatility | Laser cutting is suitable for many different applications and uses. This makes it a very versatile method of cutting. |
| Customization | Personalized and customized shapes can be created simply by changing the CNC program. |
| Automation | Modern CNC laser cutting adopts a numerical control system. The CNC system can automatically control the movement of the cutting head. |
| Dust-free cutting | The use of a laser does not generate any material dust in the workpiece. For example, sawdust is not produced when cutting wood with a fiber laser. |
| Less waste | The laser cutter is very precise and removes very little material from the workpiece. This results in minimal material waste. When cutting precious metals, the metal can be processed by simply putting it in a laser cutting machine. |
What are the Applications of Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting has a wide range of applications, covering a variety of industrial production and manufacturing industries. Here are some of the main application areas:
1.Car
Laser cutting machines are commonly used in the automotive sector to cut sheet metal. It manufactures components such as exhaust systems, frames, suspensions, and other body parts.
2.Aerospace
Precision is a primary consideration in aerospace applications. The laser cutter proved to be the perfect solution for the job. Lasers in aerospace are used to make aircraft frame components, turbine blades, and other smaller components.
3.Manufacturing
Fiber lasers are common on assembly lines in manufacturing plants. These include metalworking shops, textile mills, plastic components, and more.
4.Electronics
Laser cutters can conveniently manufacture consistent parts for electronic devices such as TVs, smartphones, laptops, tablets, and more.
5.Advertisement
Advertising materials, such as decoupage, signage, and brand logos, can be achieved with a laser cutter for smooth edges and aesthetics.
6.Architecture
Lasers can be used to manufacture decorative products for the construction industry. Common examples are cladding and art installations.
7.Medical
Laser power is used in the healthcare industry to manufacture medical devices. In addition, surgical equipment also uses a laser system.
What Materials Can Be Processed With Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting technologyis widely used in industrial production for processing a variety of materials due to its high precision, high speed and strong flexibility. The following are some common laser cutting materials:
1.Metal
(1)Aluminium
- Characteristics:light weight, corrosion resistance, easy processing and molding, and has good electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Application:Widely used in construction, transportation, packaging, electronics and other fields, aluminum cladding materials are often used to make doors and windows, furniture, decorative materials, etc.
(2)Steel
- Characteristics:high strength, good toughness, wear resistance, and good weldability and processability.
- Application:Widely used in automobiles, construction, machinery and other fields, steel cladding materials are often used to make structural parts, connectors, etc.
(3)Stainless steel
- Characteristics:Excellent corrosion and high temperature resistance, and easy to clean and maintain.
- Application:Widely used in medical, food, chemical and other fields, stainless steel cladding materials are often used to make medical equipment, tableware, containers, etc.
(4)Copper
- Characteristics:It has good electrical and thermal conductivity, and has certain antibacterial properties.
- Application:Widely used in electrical, construction, plumbing and other fields, copper cladding materials are often used to make wires and cables, pipes, etc.
(5)Titanium alloy
- Characteristics:high strength, low density, good corrosion resistance, and good biocompatibility.
- Application:Widely used in aerospace, medical and other fields, titanium alloy coating materials are often used in the production of aircraft engine parts, medical equipment, etc.
2. Non-metallic materials
- Plastics:Laser cutting can cut various types of plastics, such as polyester, polypropylene, polyethylene, polyurethane, polystyrene, etc. However, it is important to note that some plastics, such as polyvinyl chloride PVC, may emit toxic fumes during the cutting process, which can be harmful to the operator and the laser cutter itself, so laser cutting of such materials should be avoided.
- Wood:Laser cutting can cut various types of hardwoods and softwoods, such as oak, elm, maple, pine, etc. However, due to the flammability of wood and the average laser cutting effect, the use of laser cutting wood is relatively rare in practical applications.
- Rubber and leather:These materials absorb laser light and can be processed by laser cutting.
- Paper and cardboard:Laser cutting usually leaves no marks on these materials, so they are often used to make labels, packaging, and more.
- Ceramic:For some types of man-made or decorative ceramics, laser cutting is also feasible.

What Are the Different Types of Laser Cutting Techniques?
Thetypes of laser cuttingare mainly classified according to the material removal method and characteristics during thecutting process. The following are the main types:
CO2 laser cutting
In CO2 laser cutting, laser amplification occurs via CO2 gas discharge. CO2 lasers are one of the earliest and most popular types of lasers. The gas discharge is not exclusively CO2. It contains CO2, nitrogen, hydrogen, xenon, and helium.
There are two options for C02 laser cutting: using oxygen or nitrogen. Oxygen is preferred when laser cutting thicker materials. Nitrogen is preferred when laser cutting thin sheets. C02 laser cutting with oxygen forms an oxide layer on the cut surface. To avoid this, pre-treatment processes such as sandblasting are required on the workpiece.
Fiber laser cutting
Fiber laser cutting uses optical fibers for light amplification, rather than traditional gas discharges. Light from a laser diode travels through the fiber. The resulting beam is strong enough to melt stainless steel up to 1 cm thick.
The beam is usually accompanied by a powerful gas flow system. The gas flow pushes the molten material away, allowing for a clean cut. The fibers of these lasers utilize a variety of elements such as ytterbium, neodymium, erbium, and dysprosium.
Nd:YAG laser cutting
Nd:YAG (neodymium: yttrium aluminum garnet) laser is a solid-state laser whose active material is yttrium aluminum garnet crystal (YAG crystal) doped with a small amount of neodymium (Nd). This laser can produce pulsed or continuous lasers, emitting infrared light of a specific wavelength, usually 1064nm.
The laser source is focused by a lens in the cutting head to a spot size of a few tenths of a millimeter and melts the material, usually metal. A coaxial gas flow "blows" the melt downward, forming a cut in the process.
Excimer laser cutting
Use excimer laser to precisely cut materials. The laser beam is controlled by a computer, and the energy of laser photons is used to open the chemical bonds of tissue molecules, gasifying the tissue to achieve cutting effect.
Direct diode laser cutting
Based on the stimulated radiation effect of semiconductor materials. In semiconductor materials, when electrons jump from high energy levels to low energy levels, energy is released, which is emitted in the form of photons.
Laser diodes use specific structural design and doping processes to repeatedly amplify and enhance these photons inside the semiconductor, ultimately forming a beam of high-brightness, high-coherence laser.
What are the alternatives to laser cutting technology?
Here are a few alternative cutting technologies used in the industry and how they compare to laser cutters:
1.Waterjet technology
Compared to laser cutting, waterjet technology stands out with its unique cold cutting method. The technology does not require the melting of the material, which is a significant advantage. However, laser cutting performs better in terms of edge definition and precision. In addition, the fact that laser cutting does not require the use of water is another advantage.
2.Plasma cutting technology
Plasma cutting is achieved by melting the material in the cut area, but its application is limited and is only suitable for conductive materials such as metals and alloys, which is a major limitation. In contrast, laser cutters have a wider range of material applicability, including non-metals and metals, and also have engraving capabilities.
3.Wire EDM technology
Wire EDM removes material by means of electrical discharge, which is also limited to the application of conductive metals. Compared with laser cutting, wire EDM is slightly inferior in terms of material applicability and effect. Laser cutting is not only suitable for all materials, but also provides better cutting results and engraving capabilities, which is not the case with wire EDM.
4.CNC milling and turning
Machining methods such asCNC milling and turningrely on physical cutting tools that wear out quickly as they rub against the material. Laser cutting, on the other hand, does not require physical tools and is more accurate thanCNC machines.
5.Stamping
Stamping is a low-cost metalworking process that creates a cut through the physical force of the die, but it has significant shortcomings in terms of quality and accuracy. In contrast, laser cutters are able to provide superior results.
6.3D printing technology
3D printing technologyis mainly used for additive manufacturing of plastic materials, and the results are significantly different compared to laser cutting machines. 3D printed products may have obvious defects, and the printed results are nowhere near as good as those of laser cutters. In addition, 3D printers have a relatively limited range of material options.
FAQs
1.How does laser cutting work step by step?
Laser cutting uses a laser to generate a high-energy laser beam. After being focused, the beam is irradiated onto the surface of the material, causing the material to heat up locally and quickly to a melting, vaporizing or ignition point. At the same time, the molten material is blown away with the help of a high-speed airflow, thereby achieving material cutting step by step.
2.How does laser cutting metal work?
When laser cutting metal, a high-energy laser beam is focused and irradiated onto the metal surface. After the metal absorbs the laser energy, it quickly heats up to a molten or vaporized state. At the same time, auxiliary gases (such as oxygen, nitrogen, etc.) blow away the molten metal to form a cutting path and complete the metal cutting.
3.How does the laser process work?
Laser technology uses a high-energy laser beam generated by a laser to focus, transmit and irradiate the surface of the material. The high energy density of the laser interacts with the material, such as melting, vaporization, ablation, etc., thereby realizing material processing, cutting, welding and other process.
4.How does the laser cutter cut material?
The laser cutting machine generates a high-energy laser beam through a laser. After focusing, the beam irradiates the surface of the material. At the same time, a high-speed airflow device is activated to blow away the melted or vaporized material to form a cutting path, thereby achieving cutting of the material. The laser cutting machine has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and high flexibility, and is widely used in the processing of various materials.
Summary
As an advanced manufacturing technology, laser cutting has played an increasingly important role in modern industry. By gaining a deeper understanding of its principles, process types, and application areas, we can better grasp its development trends and give full play to its advantages in industrial production. With the continuous advancement and innovation of technology,laser cutting technologywill surely show a broader application prospect in the future.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
This article was written by multiple LS contributors. LS is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.






