Blanking, as a vital process in metal processing, is widely used in various industrial fields.Whether it is automobile manufacturing, aerospace, electronic equipment and various metal products in daily life, blanking plays an indispensable role. However, the success of the blanking process not only depends on the advancement of mold design and equipment, but also on the precise selection of materials. This article will delve into the materials used in blanking and analyze the characteristics of different materials and their impact on theblanking process.
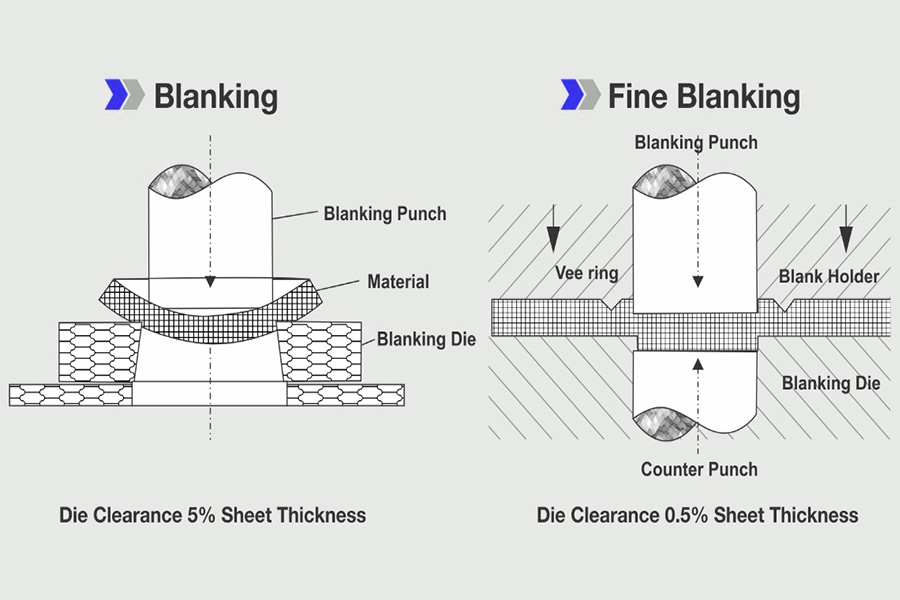
What Is Blanking in Metal Fabrication?
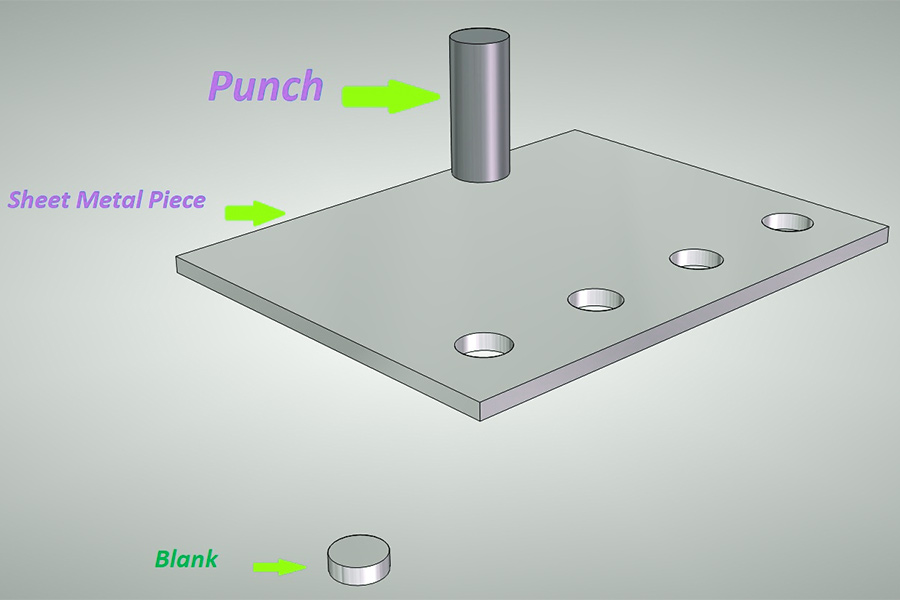
Blanking in metal manufacturing is a stamping process, specifically the process of using a die to separate part of the material or process piece from another part of the material, workpiece or scrap. It is a general term for the separation processes of shearing, blanking, punching, punching, grooving, sectioning, chiseling, trimming, tongue cutting, cutting, and trimming. During the punching process, the cutting edge of the die will cause the sheet to shear and deform along a certain contour line and eventually separate, thereby obtaining parts or blanks of the required shape and size. This process is widely used in many fields such as automobile manufacturing and electronics industry, and is an indispensable and important part of metal processing.
What Types of Materials Are Commonly Used in Blanking?
A wide variety ofmaterials are commonly used for blanking. The following is a detailed introduction to these commonly used materials:
1.Aluminum
- Features:Aluminum is a lightweight metal with good plasticity and toughness, and is easy to process and shape. At the same time,aluminum has good corrosion resistanceand is suitable for a variety of environments.
- Application:In the blanking process, aluminum is often used to manufacture lightweight parts and structural parts, such as components in the aerospace field, automobile body panels, and casings of electronic products, etc.
2.Stainless steel
- Features:Stainless steel has high hardness. When punching, the die punch needs to have high hardness and wear resistance, such as ASP-23, ASP60 and other powder high-speed steel punches. At the same time, stainless steel has poor plasticity and is prone to cracks and deformation during blanking. Reasonable design of the mold structure and blanking process is required.
- Application:Stainless steel is widely used in blankingdue to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, especially where high corrosion resistance and high strength are required.
3.Copper
- Features:Copper is relatively soft, and the mold wear is small during punching, but care needs to be taken to avoid burrs and deformation.
- Application:Copper and its alloys are also commonly used materials in blanking and are widely used in electrical, electronic and decoration fields due to their good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Type:Commonly used copper alloys include brass(copper-zinc alloy) and bronze (copper-tin alloy or copper-aluminum-silicon alloy, etc.). The drawing performance of brass is better than that of some pure copper materials.
4.Carbon steel
- Features:The blanking performance of carbon steel is greatly affected by the carbon content and heat treatment state. Low carbon steel is easy to punch and is not prone to cracks; high carbon steel requires appropriate heat treatment before punching to improve its plasticity and reduce hardness.
- Application:Carbon steel is one of the most commonly used materials in blankingand is widely used in the manufacture of various structural parts and components due to its high strength and low price.
- Types:Depending on the carbon content, carbon steel can be divided into low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel. Low carbon steel has good plasticity and punching properties and is suitable for punching parts with complex shapes; high carbon steel has higher hardness and is suitable for occasions that require higher strength and hardness.
5.Galvanized steel
- Features:The punching performance of plated steel is affected by the base material andgalvanized layer. The strength and plasticity of the base material determine the shape and dimensional accuracy of the blanking parts; the galvanized layer needs to remain intact during the blanking process to avoid corrosion. At the same time, galvanized steel blanking dies need to have high hardness and wear resistance to cope with the wear of the galvanized layer.
- Application:Galvanized steel is a material that is coated with a layer of zinc on the surface of the steel plate to improve its corrosion resistance. In blanking, galvanized steel is widely used where high corrosion resistance is required.
- Type:According to different galvanizing methods, galvanized steel can be divided into electro-galvanized steel sheets (such as SECC) and hot-dip galvanized steel sheets (such as SGCC). Electro-galvanized steel sheets have better formability and paintability; hot-dip galvanized steel sheets have higher corrosion resistance.
Which products are manufactured using stamping?
Blanking is an important manufacturing process that is widely used in the production of various products. The following is a specific analysis of products manufactured using blanking:
| Industry | Example |
| Auto parts | such as body panels, bumpers, seat brackets, etc. |
| Electronic equipment | such as mobile phone casings, computer motherboard brackets, electronic components, etc. |
| Household appliances | such as refrigerator door panels, washing machine barrels, air conditioner casings, etc. |
| Hardware tools | such as screwdrivers, wrenches, pliers, etc. |
| Building hardware | such as door and window frames, door locks, guardrails, etc. |
What Challenges Do Materials Present in Blanking?
During the blanking process,materials will face a variety of challenges, which not only affect the blanking efficiency, but are also directly related to the quality and cost of the blanked parts. The following is a detailed analysis of these challenges:
- Deformation and cracks:The material may deform or crack due to large shear force and tensile stress during the blanking process.
- Mold wear:During the blanking process, the friction between the mold and the material will cause mold wear, affecting the mold life and blanking quality.
- Thermal impact:The heat generated during the blanking process may cause the material to soften or harden, affecting the blanking effect.
Material springback: After blanking, the material may rebound due to elastic recovery, affecting the accuracy and shape of the part.
What are some ways to overcome these challenges?
Regarding the challenges faced by materials during the blanking process, here are some specific ways to overcome these challenges:
1. Methods to overcome material deformation and distortion
Design a reasonable mold gap to avoid material deformation caused by too large or too small a gap. Use a pressing device or add a strong pressing function to prevent the material from turning and twisting during the punching process. The cutting edge of the mold should be sloped or arc-shaped to reduce the cutting force and thereby reduce material deformation. Use appropriate stamping speed and pressure to avoid material deformation caused by too fast or too slow stamping speed. For stamping parts with complex shapes, step-by-step stamping or multi-stationstamping processesshould be used to reduce the amount of deformation in a single stamping. Choosematerials suitable for blanking, such as materials with moderate toughness and uniform hardness. Pre-treatment of the material, such as annealing, tempering, etc., to improve its blanking performance.
2. Methods to overcome mold wear and damage
Choose mold materials with high hardness, high wear resistance and high impact resistance, such as carbide, high-speed steel, etc. Optimize mold geometry and dimensions to reduce stress concentrations and wear. It adopts a replaceable mold cutting edge design to facilitate replacement and repair after wear. Clean, lubricate and inspect molds regularly to detect and deal with wear and damage in a timely manner. Replace or repair severely worn mold parts to extend the service life of the mold.
3. Methods to overcome thermal effects and material rebound
A cooling device is used to cool the blankingarea to prevent performance degradation caused by overheating of the material. Reasonably arrange the punching sequence to avoid excessive thermal stress on the material during the punching process. Use a springback compensation device or adjust the mold gap to reduce material springback. Choose a material that is suitable for blanking and has less springback. Parts with severe springback are subjected to subsequent shaping processing to ensure dimensional accuracy and shape requirements.

FAQs
1.What metal materials are commonly used in blanking?
Commonly used metal materials for blankinginclude carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, non-ferrous metals (such as copper, aluminum and their alloys), etc. The choice of these materials depends on the specific application scenario and requirements. For example, carbon steel is widely used because of its good strength and workability; stainless steel is suitable for parts that need to be exposed to harsh environments for a long time because of its corrosion resistance; alloy steel is used for parts that require higher strength and wear resistance. sexual occasions.
2. How to choose a blanking tool according to the thickness of the material?
The thickness of the material is one of the key factors affecting the selection ofblanking tools. Thinner materials can use thinner punches and smaller die gaps to reduce friction and heat generation during the blanking process. As the thickness of the material increases, it is necessary to choose a thicker punch and a larger die gap to ensure the smooth progress of the blanking process and the quality of the parts.
3. Why are carbide commonly used in blanking dies?
Carbide is commonly used in blanking dies due to its high hardness, high wear resistance and high thermal fatigue resistance. It can withstand the high stress and high temperature generated during the blanking process and maintain the shape and dimensional stability of the mold, thereby extending the service life of the mold and improving the quality of the blanked parts.
4. How to avoid material deformation and cracks during blanking?
In order to avoid material deformation and cracks during the blanking process, it is necessary to select appropriate materials, reasonable mold design and blanking process parameters. For example, for materials with higher toughness, a larger die gap and a lower punching speed can be used to reduce the plastic deformation of the material; for brittle materials, a smaller die gap and a higher punching speed need to be selected to reduce plastic deformation. Make sure that material breakage occurs within the mold gap.
Summary
What materials to use when blanking is a complex and critical issue. When selecting blanking materials, we should comprehensively consider multiple factors such as the material's mechanical properties, processability, cost-effectiveness, and application prospects of new materials to ensure the smooth progress of the blanking process and the high-quality output of the final product. At the same time, we should continue to pay attention to the development trends of new materials and technologies, and actively innovate and explore to adapt to changing market demands and industry development.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com







