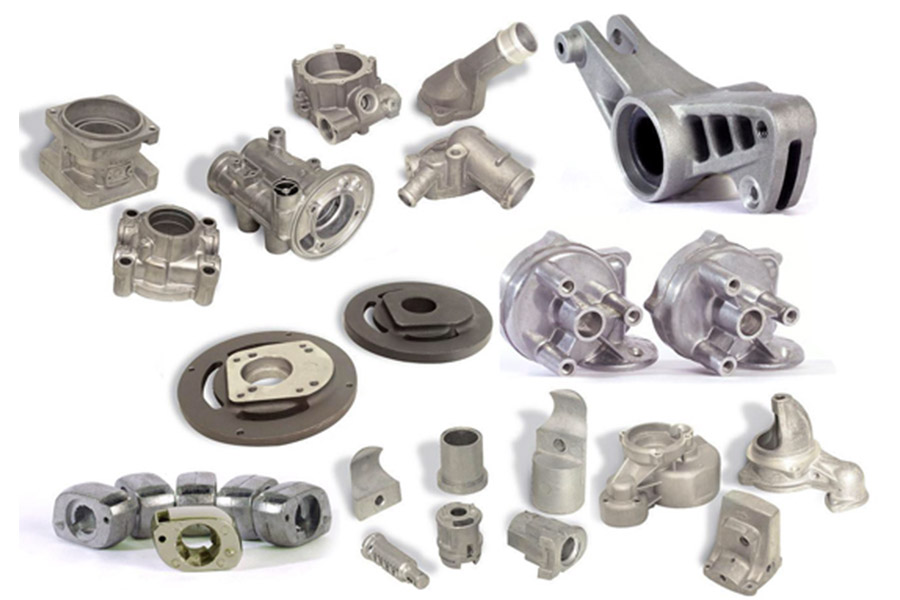
Sand casting is a versatile processthat can produce products of various sizes, shapes and complexity. Sand molds are affordable, extremely fire resistant, and can even be used for steel casting, which is why sand casting accounts for 60% of all metal castings. For cost-effective production of small batches, sand casting is considered the manufacturing method of choice. So what exactly is sand casting? In this article, theLS team will take you into the ocean of knowledge about sand castingand learn the definition, working principles, advantages, disadvantages and examples of sand casting.
What Is Sand Casting?
Sand casting is an extremely versatile process. It can be used for any metal alloy, whether ferrous or not. This process is used in large industrial units for mass production of automotive metal castings like engine blocks and cylinder heads.
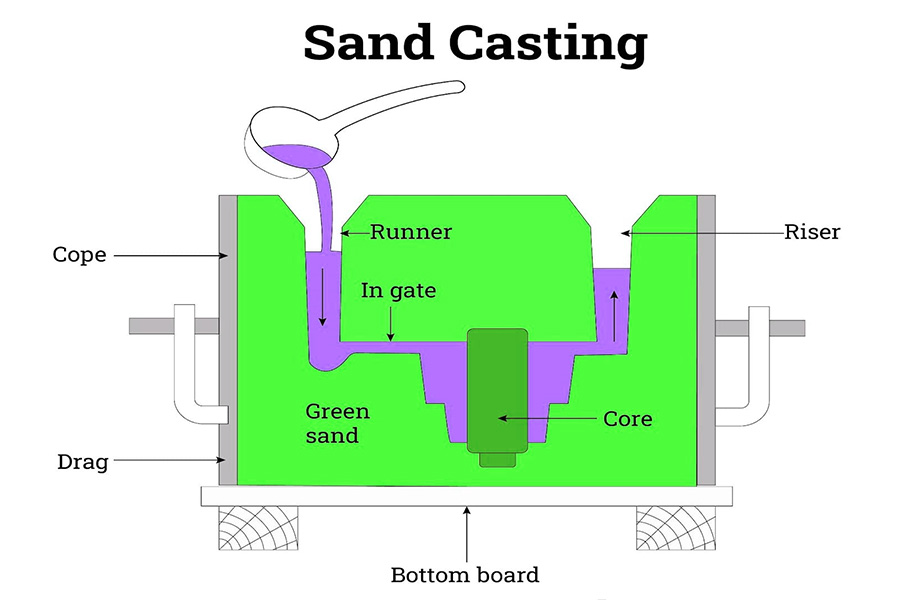
A mold made from silica-based material, such as naturally-bonded sand or synthetic sand, is used to create the mold’s smooth surface. The mold surface is divided into two parts: the upper half (cope) and lower half (drag). The pattern is filled with molten metal using a pouring pot and allowed to solidify. The final step is to trim off any excess metal for themetal casting.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sand casting?
Sand casting is a process that has both advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Costs of production are relatively low, particularly for low-volume production | Low accuracy compared to alternative methods |
| Fabrication of large components | This method is difficult to use for products that have predetermined weight and size specifications |
| Casting ferrous and non-ferrous alloys | This process produces products with a rough finish. |
| Recycling Ability | |
| Metals such as steel and titanium with high melting temperature |
How does sand casting work?
Sand casting follows the principle of gravity casting. Molten metal is poured into the mold, filling the cavity and forming the shape of the pattern. As the metal cools and solidifies, it forms the desired shape. The solidified casting is then removed from the mold and subjected to further finishing operations such as grinding and sandblasting.
During solidification, the metal shrinks, causing internal stresses and dimensional changes. To ensure the integrity of the casting, appropriate design factors must be considered, such as the use of risers or chillers.
How is sand casting done step by step?
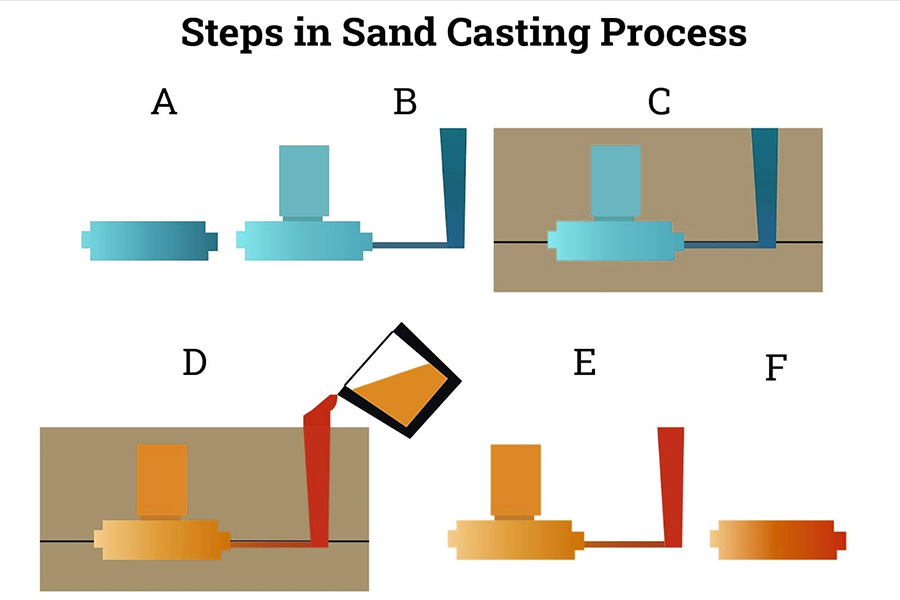
Thesand casting processis a complex and orderly process that involves multiple steps and links to ensure the quality and performance of the final casting. The following is the detailed process flow of sand casting:
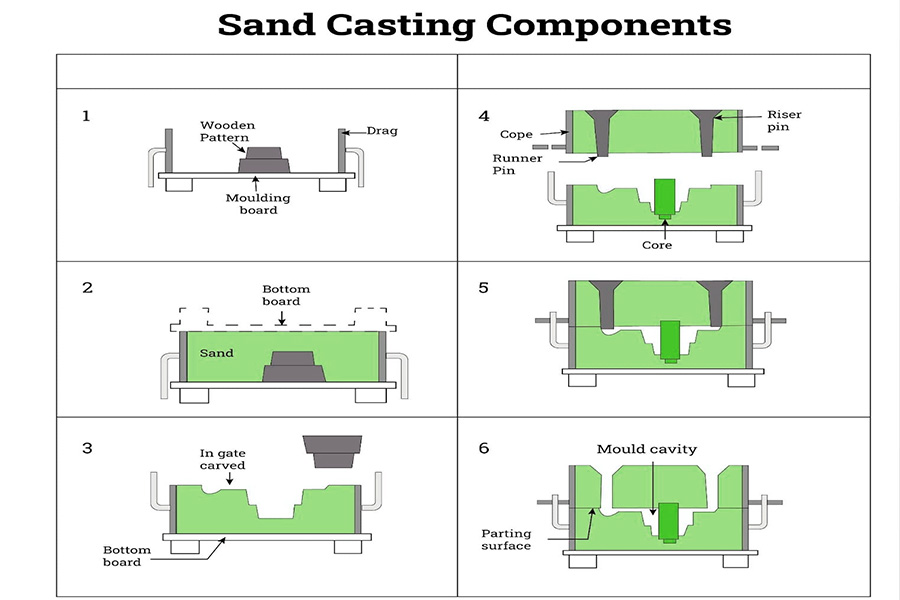
- Mold preparation:Make molds for modeling according tocasting drawings or design requirements. Molds can be wood, metal, or plastic, depending on the complexity of the casting and the production volume.
- Sand preparation and sand mixing:Select appropriate sand (such as quartz sand, silica sand, etc.) and binder (such as clay, resin, etc.) and mix them evenly in a certain proportion to form molding sand with a certain strength and fluidity.
- Shaping:Fill the mixed molding sand into the mold, and form the required sand mold through compaction, vibration, etc. Thesand moldis divided into upper mold and lower mold, which form a complete casting cavity after combination.
- Core making:For castings that require internal cavities, make corresponding sand cores. The core making process is similar to molding, but usually requires the use of a special core box and core sand.
- Combining:Combining the upper sand mold and lower sand mold (and sand core) together to form a complete casting cavity. During the box closing process, it is necessary to ensure that the sand mold and sand core are positioned accurately and that appropriate fasteners are used to secure them together.
- Melting metal:According to thematerial requirements of the casting, select appropriate smelting equipment and methods to melt the metal raw materials into liquid state. The composition and temperature of the molten metal need to be controlled during the smelting process.
- Pouring:Pour molten metal into the mold cavity quickly and evenly. During the pouring process, the pouring speed and the flow rate of molten metal need to be controlled to avoid defects such as pores and inclusions.
- Cooling:The molten metal cools and solidifies into a solid state in the mold. The cooling rate and temperature gradient need to be controlled during the cooling process to reduce stress and deformation inside the casting.
- Sand falling out and cleaning:After the casting is completely cooled, destroy the sand mold and take out the casting. Then sand, oxide scale and other impurities on the surface of the casting are removed, usually using sandblasting, grinding and other methods.
- Inspection and repair:Quality inspection of castings, including dimensional inspection, appearance inspection, non-destructive testing (such as X-ray testing, ultrasonic testing, etc.) and mechanical property testing. Unqualified castings need to be repaired or reworked.
What Are the Types of Sand Casting?
Sand casting can be divided into various typesbased on the preparation method and material properties of the sand mold. Here are some of the main types of sand casting:
1.Wet sand
Green sand casting is a casting method that uses molding sand and core sand as modeling materials to make a mold, and liquid metal fills the mold under gravity to produce castings. It mainly uses clay and an appropriate amount of water as the main binder of the molding sand. After the sand mold is made, it is directly molded and poured in a wet state.Wet casting has a long history and is widely used. Steel, iron and most non-ferrous alloy castings can be obtained by this method. Its main advantages include abundant clay resources, low price, short mold manufacturing cycle and high work efficiency. Most of the used clay green sand can be recycled and reused after appropriate sand treatment. However, there are also some shortcomings, such as low rigidity of the casting mold, poor dimensional accuracy of the castings, and castings are prone to defects such as sand washout, sand inclusions, and pores.
2.Dry sand
Compared with green sand casting,dry sand mold casting has a lower moisture content in the sand mold. When making dry sand molds, the wet moisture content of the molding sand is slightly higher than that of the molding sand used for wet molds. However, after the sand mold is made, the surface of the mold cavity must be coated with refractory paint and then placed in an oven to dry. After cooling, the mold can be closed. and pouring. This method is generally used to manufacture steel castings and larger iron castings. However, since drying clay sand molds takes a long time and consumes a lot of fuel, and the sand molds are prone to deformation during the drying process, which affects the accuracy of castings, dry sand molds have tended to be eliminated since the widespread adoption of chemically hardened sand. However, in modern sand casting, dry sand is still used as core material, especially for cores with complex shapes, thinner cross-sections, high dry strength and good collapse properties.
3.Core sand
Core sand is the material used to make the core of a sand mold. According to the different binders used, core sand can be divided into many types, such as clay core sand, water glass core sand, oil core sand, grease core sand, resin core sand, etc. The main function of the core sand is to support the cavity in the casting mold and prevent molten metal from flowing into the outside of the mold cavity during the pouring process. Different types of core sand have different characteristics and application ranges, and can be selected according to the specific requirements of the casting.