When we walk through the world of various commodities, from electronic devices in our hands to sports shoes under our feet, from tableware in the kitchen to stationery in the office, it is not difficult to find that the outstanding performance of these products in design, function and aesthetics is often inseparable from the contribution of overmolding technology. Today, the Longsheng team will lead everyone to learn and explore what is overmolding?
What is overmolding?
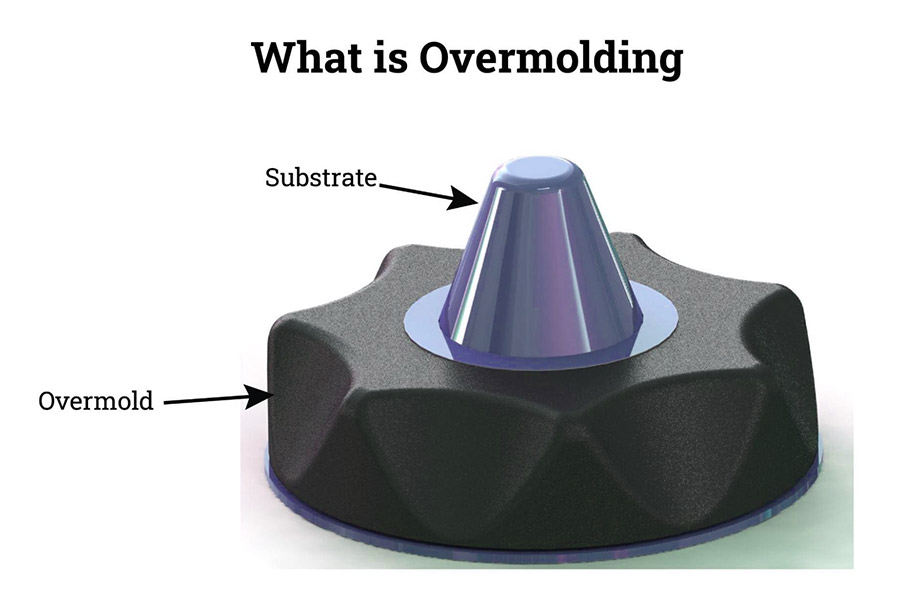
Overmolding is a production process that focuses on combining soft thermoplastic elastomers or similar materials with rigid plastic or other substrate materials through injection molding or wrapping to create a composite structure with specific functional properties and aesthetic appearance. This process is widely used to improve the feel, anti-slip effect, visual beauty of products, and enhance product durability and ergonomic design.
How does overmolding work?
The principle of the overmolding process is to inject molten TPE or other elastomeric materials onto a molded or unmolded rigid plastic substrate through a specific molding equipment. During the injection molding process, the TPE material will tightly wrap around the surface of the plastic substrate to form a strong bond. Because TPE materials have good flexibility and elasticity, they can significantly improve the comfort and durability of the product.
What are the advantages of overmolding?
Overmolding is a versatile process that has numerous advantage:
- Improve material flexibility:Overmolding technology gives designers the ability to combine the advantages of multiple materials to create complex components with diverse properties, thereby enhancing the visual level and tactile experience.
- No additional bonding required:The overmolding process allows different materials to be seamlessly combined in the mold, eliminating the use of glue or other permanent adhesives. This feature not only improves the overall robustness of the component, but also effectively reduces the cost of the assembly process.
- Integrated sealing solution:Overmolding also provides the option of molding soft seals directly as part of the part. For example, for electronic housings that need to meet specific IP ratings, the traditional approach is to reserve grooves on the parts and then install O-rings. With overmolding technology, the seal can be molded directly as a whole. This integrated design is not only more cost-effective, but also significantly improves the stability of the parts.
What are the disadvantages of overmolding?
Despite the many benefits of overmolding, a few disadvantages need to be considered before deciding to use this process.
- Multi-stage manufacturing process:The manufacturing of overmolded parts involves two steps, which results in longer production cycles and, therefore, higher costs than single-part molding. In addition, the process requires two molds or a complex two-shot mold, which further increases the initial investment cost. However, when faced with the alternative of subsequently assembling two independently molded parts, overmolding becomes a value-added solution.
- Bonding risk:When combining two different materials in an injection mold, there is a risk of material delamination. This delamination usually occurs when the temperature does not reach the optimal bonding range for the specific material combination. In some special cases, when heat is not enough to ensure a reliable bond between the materials, mechanical interlocking technology may be required to enhance the connection strength.

What are the applications of overmolding?
Overmolding technology has a wide range of applications, the following are some of the main application examples:
Aerospace field
Overmolding technology plays an important role in the aerospace sector. Because carbon fiber composites have excellent properties such as high strength and high modulus, and their strength is more than five times that of steel, they have been widely used in the aerospace field. By using overmolding technology, it is possible to precisely wrap a reinforcing material such as carbon fiber inside a matrix material such as resin to form a composite material with excellent mechanical properties. These composite materials are widely used in key parts of the aircraft, such as the main load-bearing components, wings, and fuselage, making the aircraft stronger and stronger, and improving the flight safety performance.
Medical industry
Overmolding is widely used in the medical industry. Different medical products, such as device housings and surgical equipment, are manufactured by overmolding to create ready-to-use finished parts. Some examples include syringes, patient monitors, needles, catheters, dilators, soft-touch buttons, and many more.
Everyday necessities
Overmolding technology is also widely used in the manufacture of everyday items such as toothbrushes, razors, power tools, cameras, and kitchen utensils. These products need to be pleasant to the touch and non-slip properties, and overmolding technology is able to meet these requirements and offer a wide range of color, texture, and haptic options.
Automotive industry
Overmolding technology is also widely used in automobile manufacturing. With the continuous development of the automotive industry, the requirements for automotive materials are also getting higher and higher. Overmolding technology plays an increasingly important role in automobile manufacturing due to its excellent properties such as light weight, high strength and impact resistance. For example, long-fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites prepared by overmolding technology can replace traditional short-fiber reinforced materials and are used to manufacture automotive bumpers, spare tires, dashboards and other components, which not only improves the performance of components, but also reduces manufacturing costs.
Electronics
In the field of electronics, overmolding technology can be used to prepare high-performance circuit boards, electronic packaging materials, etc., to improve the performance and reliability of electronic products. With the continuous miniaturization and integration of electronic products, the requirements for materials are also increasing. Overmolding technology is able to meet these requirements and provide high-performance packaging materials and circuit boards for electronic products.
What are the materials used in overmolding?
The choice of materials used in overmolding is very wide, depending on factors such as the performance, cost, processability and environmental requirements of the desired product. Here are some common materials used in overmolding:
- Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs):have excellent slip resistance and elastic touch, adjust hardness and physical properties. It is often used in handles, grips, electronics, etc., to enhance the tactile and grip of the product.
- Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU):divided into polyester type and polyether type, it has the characteristics of oil resistance, wear resistance, good mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and good resilience. At the same time, TPU is fashionable and environmentally friendly and can replace PVC. It is suitable for the wrapping of strips, threads and strips, such as pet belts, motor car handle straps, trailer straps, etc. It is also commonly used for the coating of luggage products and metal lines.
- Polyurethane (PU):It has excellent toughness, strong tear resistance, and super wear resistance. It is widely used in light industry, chemical industry, electronics, textile, medical, construction, automobile, national defense and other fields. In the paper industry, the new PU lagging roller can be used to replace rubber materials under high temperature and high line pressure conditions.
- Silicone:Silicone powder is classified by the amount of siloxane content, and the intermolecular force of siloxane is strong, and it is not easy to disperse uniformly by physical methods. Silicones are lubricating, wear-resistant, and can improve the compatibility of the interface between non-polar inorganic minerals and organic compounds. Silicone masterbatches can be used as flow promoters, anti-caking agents, synergistic flame retardants, lubricants, hydrophobic agents, release agents, etc. in plastic processing.
- Polyethylene (PE):good water and moisture resistance, good chemical stability, certain mechanical tensile and tear strength, good flexibility, good low temperature resistance, but poor high temperature resistance. It is often used in plastic bags and as a packaging material for composite bags. Films made of high-pressure low-density polyethylene (LDPE) can be used to package foods with low requirements, especially dry foods with moisture barrier requirements.
- Polypropylene (PP):high melting point, low price, small specific gravity, excellent mechanical properties, outstanding stress crack resistance and wear resistance, good chemical stability, easy molding processing. It is widely used in chemical, electrical, automobile, construction, packaging and other industries. Plastic films used in flexible packaging of goods, also used as a heat sealing layer for composite materials.
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS): is a thermoplastic with high strength, impact resistance, and heat resistance. It can be used for overmolding with specific requirements, such as parts that require high strength and heat resistance.
- Polycarbonate (PC):It has the characteristics of high transparency, high impact strength, and high thermal stability. In overmolding, PC can be used for parts that require high transparency and high impact strength.
- Nylon:Excellent abrasion resistance, impact resistance and self-lubrication. It is often used in the manufacture of components that need to withstand high loads and wear, such as gears, bearings, etc. In overmolding, nylon can be used for components that require wear resistance and self-lubrication.

What is the difference between insert molding and overmolding?
Insert molding and overmolding are both effective ways to produce multi-material products without adhesives, streamlining the production process, reducing secondary assembly steps, and improving the quality of the final product. However, there are significant differences between the two molding technologies, which are manifested in the following aspects:
1.Process
The overmolding process involves two separate injection steps, first forming the substrate and then overmolding on it.
Insert molding is a one-time injection molding process that involves pre-placing metal inserts in the mold, which are separately sourced or manufactured.
2.Productivity
Since insert molding only requires a single molding, the production cycle is theoretically shorter than that of overmolding.
However, if the manufacturer is unable to find a prefabricated metal insert that meets the requirements, custom production is required, which may extend the overall production time. As a result, insert molding is not always the fastest production option.
3.Cost Considerations
Both insert molding and overmolding can help reduce assembly costs and increase productivity, resulting in cost savings and increased profits when producing large quantities.
However, overmolding is comparatively more expensive because it involves two steps, especially when prototyping or low-volume production. In addition, overmolding requires the manufacture of two tools, one for substrate and one for overmolding, which also increases the cost.
4.Applications:
Overmolding is widely used in toothbrushes, medical devices, disposable shavers, mobile phone cases, and the packaging of electronic circuit boards (such as USB flash drives).
| Feature | Insert Molding | Overmolding |
| Primary Purpose | Integrate inserts into plastic parts | Add layers/features to existing parts |
| Process Steps | Insert placed in mold, then plastic injected | Initial part molded, then overmolded with additional material |
| Materials Used | Combination of metal and plastic | Typically plastic over plastic, or plastic over metal |
| Typical Applications | Automotive components, electronic housings | Grips for tools, soft-touch handles, seals |
| Benefits | Enhanced strength, durability, and conductivity | Improved ergonomics, added insulation, enhanced appearance |
| Complexity | High, due to precise insert placement | High, due to multi-stage molding |
Scenarios where overmolding technology is considered include:
- When the surface of your part needs to exhibit specific differences in electrical or thermal properties.
- If you want to improve the shock absorption or cushioning performance of your part.
- When you need a colorful plastic part to meet your design needs.
- If your component requires a handle that is both comfortable and non-sticky.
- When you need to incorporate a soft seal into a part structure.
On the other hand, insert molding technology is popular in several fields, especially for the following scenarios:
- When you have metal elements in your part.
- If your substrate integrates complex components such as wires, electronic components, or circuit boards.
- When you want to avoid the high cost of two-color mold development.
- Insert molding is ideal for your part design that requires the integration of threaded inserts, which are widely used in connectors, instrument
- panels, electrical socket and wire assemblies, dials, remote control housings, handles including scissor handles and surgical instrument handles.

FAQs
1.What is an example of overmolding?
Overmolding is an injection molding process in which one material (usually thermoplastic elastomer TPE, thermoplastic polyurethane TPU, polyurethane PU, etc.) is molded onto a second material (usually a rigid plastic such as ABS, PC, PE, PP, etc.). This process allows product teams to mold ergonomic devices, power tool handles, rubber gaskets, etc. directly onto pre-existing parts without adding additional manual labor. For example, when manufacturing a mobile phone case, the overmolding process can be used to mold a soft TPE material onto a hard plastic substrate to enhance the feel and anti-slip properties.
2.What is the difference between insert molding and overmolding?
There are significant differences between insert molding and overmolding in terms of process, production efficiency, cost considerations and application areas. When choosing between them, manufacturers need to make comprehensive considerations based on specific needs, production scale and cost budget.
3.How is overmolding done?
The principle of the overmolding process is to inject molten TPE or other elastomeric materials onto a molded or unmolded rigid plastic substrate through a specific molding equipment. During the injection molding process, the TPE material will tightly wrap around the surface of the plastic substrate to form a strong bond. Because TPE materials have good flexibility and elasticity, they can significantly improve the comfort and durability of the product.
4.What materials are commonly used for overmolding?
Materials commonly used for overmolding include plastic materials such as thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU), polyurethanes (PU), silicones, polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), and metal materials or other special materials that may be used in some special cases. The choice of these materials depends on the specific application scenario, the required physical and chemical properties, and cost factors.
Summary
As an advanced injection molding process, overmolding achieves comprehensive improvement in product function, aesthetics and environmental protection by combining the characteristics of different materials. From insert molding to multiple injection molding, from improving safety to optimizing ergonomic design, overmolding plays an increasingly important role in modern manufacturing. With the continuous advancement of material science and injection molding technology, overmolding will continue to provide strong support for product innovation and quality improvement.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
This article was written by multiple LS contributors. LS is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.