Metal welding is a key industrial manufacturing techniquethat uses heat and pressure to securely join two or more separate metal parts together. This process is not only suitable for the connection of various steel materials, but can also solve the connection problems of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper and special metal materials such as titanium and zirconium. Welding technology is widely used in many fields such as machinery manufacturing, shipbuilding, ocean development, automobile manufacturing, petrochemical industry, aerospace technology, atomic energy, electricity, electronic technology and construction. This article will take an in-depth look athow metal welding worksand its application in different welding methods.
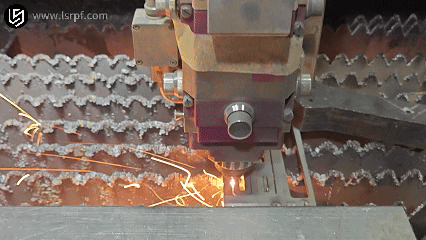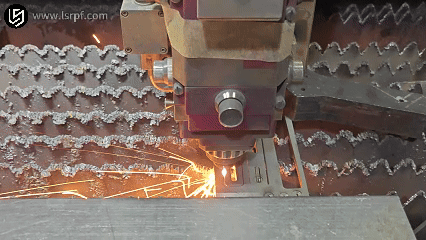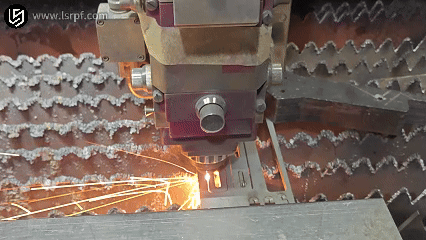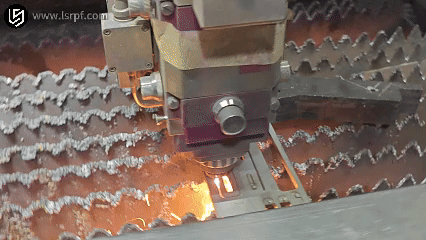
How Does metal welding work?
Theworking principle of metal weldingis mainly to combine two separated metal objects (same metal or dissimilar metal) at the atomic or molecular level through appropriate means, such as heating, pressure or a combination of the two, thereby connecting them into one body.
This process usually includes the following steps:
- Heating:Whenwelding begins, a heat source needs to be used to heat the metal at the weld. The heat source can be an arc, laser, resistor, electron beam or fuel combustion.
- Melting:Under the action of the heat source, the metal at the weld reaches the melting temperature and forms a molten pool. The metal atoms in the molten pool lose their binding force and can move freely.
- Cooling and Solidification:The molten pool gradually solidifies as it cools, forming a solid metal bond. During the solidification process, the metal atoms in the molten pool rearrange to form a crystal structure.
- Intermetallic bonding:Through the process of heating, melting and cooling, the metal atoms in the welding part diffuse and combine with each other to form a strong connection.
What Are the Key Steps in Metal Welding?
Thekey steps in metal weldinginclude preparing the metal surface, selecting theappropriate welding method, heating and melting the metal piece, and cooling and finishing the weld. Here is a detailed explanation of these steps:
1. Prepare the metal surface for welding:
This step is a critical preparation before welding and involves cleaning the metal surface to remove grease, dirt, oxides and other impurities to ensure that the weld area is clean and free of dirt. At the same time, the size and shape of the welded joints need to be checked and trimmed if necessary to ensure smooth welding.
2. Choose the appropriate welding method:
Choose the most suitable welding methodbased on factors such as the type, thickness, strength requirements of the metal to be welded, and the shape and location of the welded joint. Common welding methods include arc welding, resistance welding, laser welding, etc. Each method has its unique advantages and scope of application.
3. Heat and melt the metal piece:
Using a selected welding method, the weld area is heated to bring the metal to a molten state. During the heating process, welding parameters, such as welding current, voltage, welding speed, etc., need to be strictly controlled to ensure that the metal in the weld area can be melted evenly and form a good molten pool.
4. Cool and finish the weld:
Afterwelding is completed, allow the weld to cool naturally or take appropriate cooling measures to avoid cracks or deformation of the weld. After cooling, the weld is cleaned to remove welding slag and impurities. Grinding, polishing and other finishing treatments are performed on the welds as needed to improve the appearance quality and performance of the welds.
What Are the Different Types of Welding Processes?
Thewelding processis a technology that combines two or more pieces ofmetal materialsto achieve atomic bonding by heating, pressurizing, or both. Here are some of the main welding methods:
Arc welding:
- Principle:Uses an electric arc to melt and fuse metals. Arc is a strong and long-lasting gas discharge phenomenon. There is a certain voltage between the positive and negative electrodes, and the gas medium between the two electrodes should be in an ionized state. When a welding arc is ignited, two electrodes (one pole for the workpiece and the other pole for the filler wire or welding rod) are usually connected to the power supply, briefly contacted and then separated quickly. When the two poles contact each other, a short circuit occurs and an arc is formed.
- Features:Thearc welding equipmentis light and flexible in transportation, and can be used for welding operations anywhere where there is a power source. There are various arc welding methods, including manual arc welding, submerged arc welding, etc. Manual arc welding can perform multi-position welding such as flat welding, vertical welding, horizontal welding and overhead welding; submerged arc welding is mainly suitable for flat welding positions, and due to its large penetration depth, high productivity and high degree of mechanized operation, submerged arc welding can Therefore, it is suitable for welding long welds of medium and thick plate structures.
MIG welding (melted inert gas welding):
- Principle:Anarc welding methodthat uses a melting electrode and an external gas (such as argon or helium) as the arc medium to protect the metal droplets, welding pool and high-temperature metal in the welding zone.
- Features:MIG welding is a faster wire feeding process suitable for large projects. It can weld almost all metals, especially suitable for welding aluminum and aluminum alloys, copper and copper alloys, stainless steel and other materials. There is almost no oxidation and burning loss during the welding process, only a small amount of evaporation loss, and the metallurgical process is relatively simple. At the same time,MIG weldingdoes not use tungsten electrodes, and the cost is lower than TIG welding.
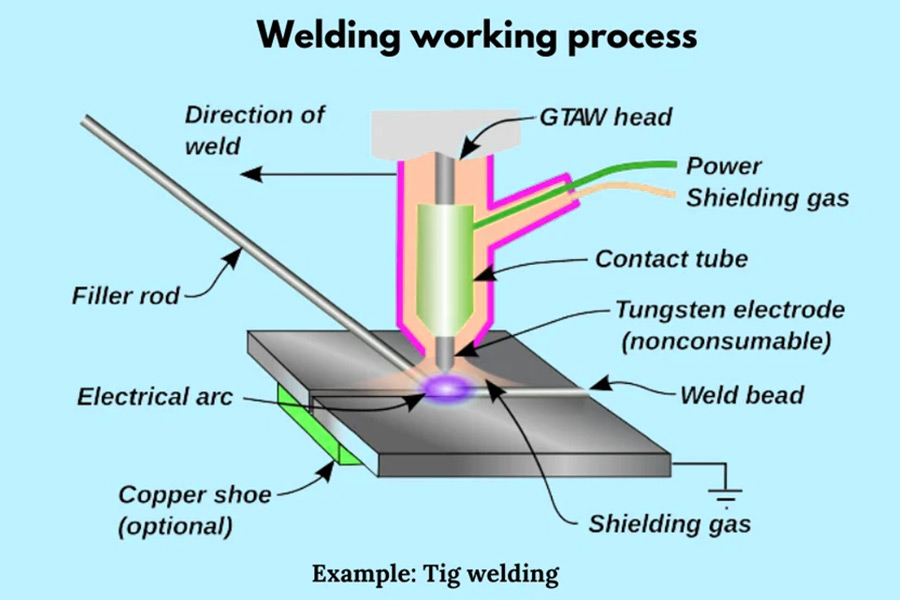
TIG welding (tungsten arc welding):
- Principle:The arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece is used to melt the metal to form a weld. The tungsten electrode does not melt during the welding process and only functions as an electrode. At the same time, argon or helium gas is fed into the nozzle of the welding torch for protection.
- Features:TIG weldingcan provide high precision for thin or complex metals. It is an excellent method for joining thin sheet metal and underlay welding due to the good control over heat input. This method can be used to join almost all metals, and is especially suitable for welding aluminum, magnesium, metals that can form refractory oxides, and active metals like titanium and zirconium. The weld quality is high, but the welding speed is relatively slow.
Spot welding:
- Principle:Spot welding is a type of resistance welding. The electrode applies pressure to the workpiece and energizes it, causing the metal at the contact point to melt to form a solder joint.
- Features:Spot welding is mainly used for stamped and rolled thin plate components that can be overlapped, the joints are not required to be airtight, and the thickness is less than 3mm. It is widely used insheet metal fabrication, automobile manufacturing and other fields.

What Happens When Metal Is Welded?
Whenmetal is welded, a series of complex processes occur, including both physical and chemical changes. The following are the main phenomena and changes that occur during metal welding:
Physical Changes
- Metal melting: Under the action of the welding heat source, the metal in the weld area is heated above the melting point, resulting in melting. The molten metal forms a molten pool, which lays the foundation for subsequent cooling and solidification and the formation of welds.
- Metal evaporation and splashing: At high temperatures, some metals will evaporate to form metal vapor. In some welding methods, such as gas shielded welding, metal may spatter due to the action of the arc.
- Thermal expansion and contraction of metal: During thewelding process, the metal expands when heated and shrinks when cooled. This thermal expansion and contraction may cause deformation and residual stress in the weld area.
- Weld cooling and solidification: After the heat source leaves, the molten pool begins to cool and gradually solidifies. During solidification, metal atoms rearrange to form a new crystal structure.
Chemical Changes
- Metal oxidation:At high temperatures, metals react with oxygen in the air to form metal oxides. These oxides may affect the quality and performance of the weld.
- Metal nitriding:If nitrogen is present in the welding environment, the metal may also react with the nitrogen to form metal nitrides.
- Weld alloying:The alloying elements in the added filler material or base metal may be redistributed or undergo chemical reactions during the welding process, thus affecting the alloy composition and properties of the weld.
- Gas absorption and precipitation in the weld:During the welding process, the weld may absorb some gases (such as hydrogen, nitrogen, etc.). These gases may precipitate during thecooling processof the weld, forming defects such as pores.
What Equipment Is Used in Metal Welding?
Theequipment required for metal weldingmainly include welding machines, electrodes, welding clamps, filling materials, etc.
1. Welding machine
Thewelding machineis the core equipment for metal welding and is used to convert electrical energy into the heat energy required for welding. Common welder types include:
- Welding machine: A welding power source used to convert alternating current into low voltage and high current. It is an essential equipment in welding operations.
- Laser welding machine: Using laser beam as a heat source for welding, it has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and small heat affected zone.
- Ultrasonic welding machine: The energy generated by ultrasonic vibrations melts and joins metals together,suitable for welding some specific materials.
2. Electrode
Electrodes play the role of transmitting current, melting metal and forming welds during the welding process. Depending on the welding method, the form of the electrode is also different:
- Welding rod:In electric welding, the welding rod acts as an electrode and consists of a metal core and a coating. When the welding rod comes into contact with the weldment and is energized, the welding rod melts and forms a weld with the weldment.
- Welding gun electrodes:In gas welding or some special welding methods, the welding gun may contain electrodes for generating and maintaining an arc or flame.
- Resistance welding electrode:In resistance welding, the electrode is used to clamp the weldment and pass electric current, so that the weldment melts and joins together under the action of resistance heat. These electrodes are usually made of materials such as copper, chromium, zirconium and copper that are resistant to high temperatures and have good electrical conductivity.
3. Welding clamp
Thewelding clampis a tool used to hold the welding rod and transmit the welding current during welding operations. It not only ensures that the welder can control the electrode stably during the welding process, but also protects the welder's hands from high temperature and arc light to a certain extent. Therefore, a welding clamp can also be considered a type of safety gear.
4. Filling materials
In some welding methods, in order to increase the strength and sealing of the weld, filler materials need to be used:
- Welding wire:In welding methods such as gas shielded welding and gas tungsten arc welding, the welding wire is fed into the weld as a filler material and forms a weld together with the molten base metal.
- Solder:In low-temperature welding methods such as soldering, solder is used to fill the weld and join the metal parts. Solder is usually made of metal alloys with low melting points, such as tin-lead alloys.

What Are the Common Materials Used in Metal Welding?
There are manymaterials commonly used in metal welding. The following are some common metal materials and their applications in welding:
1 Steel:
- Mild steel:has good weldability and is often used to manufacture various structural parts and components.
Medium carbon steel: such as 45 steel, which has good comprehensive mechanical properties and is often used to manufacture high-strength moving parts, such as turbine impellers, compressor pistons, etc. - Alloy steel:such as 40Cr, which has good comprehensive mechanical properties after quenching and tempering. It is often used to manufacture medium-speed and medium-load parts, such as machine tool gears, shafts, etc. Mold steel is also atype of alloy steeland is often used to manufacture various molds.
2. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys:
Aluminum alloys are lightweightand corrosion-resistant and are widely used in aerospace, automotive, electronic equipment, and home appliances industries. Laser welding of aluminum alloys can produce welded structures with extremely high strength and no risk of pores or cracking.
Stainless steelincludes austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel and martensitic stainless steel. Austenitic stainless steel has good welding performance, ferritic stainless steel has strong toughness, and martensitic stainless steel has unsatisfactory welding effect but low cost. Stainless steel is commonly used in the food and medical industries due to its hygienic properties.
4. Copper and Copper Alloys:
Copper and its alloys have high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and strength. Laser welding can weld copper materials quickly and efficiently and can be used to manufacture complex structural parts and electronic components.Copper and copper alloysare also commonly used in electrical and decorative applications.
5. Cast iron:
Althoughcast ironhas poor weldability, it can still be used to repair some important cast iron parts after proper welding repair processes, such as preheating and selecting appropriate welding rods.
6. Other non-ferrous metals:
Such as titanium, nickel, tin, chromium, niobium, gold, silver and other metals and their alloys. These metals show different welding characteristics in laser welding or other welding methods, and can be selected according to specific needs.
7.Special alloy:
Such as nickel-based alloys, cobalt-based alloys, etc. These alloys have special physical and chemical properties and are often used for welding in harsh environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of metal welding?
As an important joining technology, metal welding has a series of advantages and disadvantages. The following table is a detailed overview of theadvantages and disadvantages of metal welding:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High strength connection | Easy to deform |
| Good sealing | Reduced performance of the heat-affected zone |
| Adaptable | High skill requirements for operators |
| Cost-effective | Large equipment investment |
| Permanent connection | High energy consumption |
| Design flexibility | Welding smoke and pollution |
| Automation and mechanization | Prone to cracks |
| Lightweight | Porosity and inclusions |
What Are the Applications of Metal Welding?
Metal welding has a wide range of applicationsin many fields. Here are some of the main application areas:
1. Aerospace field:
Metal welding is vital in the aerospace industryand is used to manufacture and repair various metal parts such as aircraft fuselages, wings, engines, fuel tanks, etc. These parts require high strength, high corrosion resistance, high durability and high temperature resistance, and metal welding technology can meet these requirements.
2. Construction field:
In the field of construction,metal welding is widely used in the manufactureof structural frames of large buildings, bridges, tunnels, subway stations and other structures. Metal welding provides high strength, precision and durability while reducing production costs and increasing productivity.
3. Automobile manufacturing field:
Automotive manufacturingis another major application area for metal welding. Components such as automobile chassis, body, exhaust pipe, fuel system and engine all require welding technology to be manufactured and repaired. Metal welding enhances the durability of automotive components and improves vehicle performance and safety.
4. Electronic field:
In the electronics field,metal welding is used in the production and repair of various electronic devices, such as printed circuit boards, packaged devices, thermal devices, etc. Metal welding enables high precision, reliability and durability, improving the performance and life of electronic devices.
5. Energy industry:
In the energy industry,metal welding is used to weld oil and gas pipelines, power plant equipment, nuclear power plant components and other key facilities to ensure the normal operation and safety of energy facilities.
6. Manufacturing:
In the wider manufacturing industry, metal welding is used to produce a variety of metal products, such as machinery and equipment, ships, etc. It works by joining metal parts together to form a finished product with the required strength and functionality.

FAQs
1.How is metal welded together?
Metal welding is done by heating the metal to a molten state (or in some welding methods, such as pressure welding, the metal is not completely melted but plastically deformed), and then cooled and solidified to create a bonding force between metal atoms, thereby joining two or more pieces together. The process of joining pieces of metal together.
2.How exactly does welding work?
The basic principle of welding is to use a heat source to heat the metal to be welded to an appropriate temperature, causing the metal to melt (or undergo plastic deformation during pressure welding), and then solidify through cooling. The metal atoms are rearranged and tightly combined to form a weld. The heat source can be an arc, flame, laser, electron beam, etc., depending on the welding method.
3.What happens when metal is welded?
During the metal welding process, the main phenomena that will occur are: the metal is heated to a molten state, forming a molten pool. The metal in the molten pool reacts with oxygen, nitrogen, etc. in the air to generate impurities such as oxides and nitrides. At the same time, the metal in the molten pool may undergo metallurgical reactions with the alloying elements in the welding materials, changing the chemical composition and properties of the metal. During the welding process, it is usually necessary to provide inert gas or active gas protection to prevent oxygen, nitrogen and other impurities in the air from entering the molten pool and affecting the quality of the weld. As the heat source is removed, the molten pool begins to cool and gradually solidify. During the cooling process, bonding forces are generated between metal atoms to form a weld.
4.How do you weld metal step by step?
The step-by-step process of welding metal usually includes: ① Preparation work: select appropriate welding methods and equipment, prepare the metal to be welded and welding materials (such as electrodes, wires, flux, etc.), and perform surface treatment on the metal to be welded to remove oil stains and rust and other impurities. ②Preheating: Depending on the type of metal and welding method, it may be necessary to preheat the metal to be welded to reduce welding stress and cracks. ③ Positioning and clamping: Accurately position and clamp the metal to be welded to ensure that the metal does not move or deform during the welding process. ④Welding operation: ignite the heat source, adjust the welding parameters (such as current, voltage, welding speed, etc.), melt the welding material and form a molten pool with the metal to be welded. Control the size, shape and temperature of the molten pool to ensure the quality of the weld.⑤Weld cooling and inspection: After welding is completed, let the weld cool to room temperature naturally. Conduct visual inspection and necessary non-destructive testing (such as X-ray testing, ultrasonic testing, etc.) on the welds to ensure that the quality of the welds meets the requirements. ⑥Follow-up processing: As needed, the welds are ground and polished to improve their appearance quality and corrosion resistance.
Summary
Metal welding is an ancient and sophisticated process that plays a vital role in modern industry. It uses heat and pressure to firmly connect disparate metal parts together, giving countless structures and equipment their durability. By in-depth understanding of the basicprinciples of weldingand the working principles of different welding methods, we can better master this technology and continuously optimize and improve welding quality in practical applications.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
This article was written by multiple LS contributors. LS is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.






