3D printing technologyhas developed rapidly and is widely applied in manufacturing, healthcare, education, consumption and other fields.
PLA(polylactic acid) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are the most common thermoplastic materials. It has been dominating the printing materials materials market due to its low cost, convenient processing and wide applicability. Although they are basic materials, there are some differences in chemical properties, physical properties,processing technology, etc. This difference will be reflected in the selection of materials, according to the characteristics of different materials to match the processed products. The applicability ofPLA and ABS filamentwas determined according PLA their different chemical structures, physical properties and processing methods.
What is PLA?
polylactic acid is a thermoplastic polymer utilized in 3D printing and manufacturing.from renewable sources such as corn starch or sucrose through fermentation.PLA's molecular structure is flexible, impact resistance and temperature tolerance.For 3D printing, it issuitable for prototype creation, educational modelling, everyday items and food containers.Its recyclability and non-toxicity make it the preferred alternative to traditional petroplastics

What is ABS filament?
ABS filament is a thermoplastic polymer widely utilized in3D printing,injection molding, engineering and other fields. It exhibits exceptional ductility and thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity under complex stress conditions. In 3D printing, specific printing conditions are necessary for optimal ABS filament performance. Suitable for manufacturing auto parts that require strength and durability. The economic feasibility and practicability of ABS filament make it an ideal substitute for traditional petroplastics to meet various industrial needs.

What is the difference between PLA and ABS 3D printing?
Strength (mechanical properties)
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):Low Tensile strength (low (approximately 20-30 MPa), high brittleness, easy to impact fracture. Compressive strength moderate (around 50-60 MPa), but thin-walled structure is prone to deformation.
- ABS:High tensile strength (about 40-50 MPa), good toughness, can withstand large shocks and vibration. The compressive strength is significantly better than PLA (about 70-90 MPa) and suitable for load-bearing structures.
Quality of parts
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):The surface is smoother, featuring less prominent layering, and necessitates no intricate post-processing. Edges curl effortlessly, particularly during low-temperature printing, with hole edges susceptible to cracking.
- ABS:The surface is essentially smooth, but the the "step effect" tends to occur when the printing temperature is insufficient. The risk of cold shrinkage and deformation is high, so the bed needs to be preheated rigorously to 50-100 °C.
Stiffness
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):Moderate hardness, easy bending of thin walls (<1mm) requiring thicker walls or reinforced support.
- ABS:The hardness is higher, close to the equivalent thickness of PS and other engineering plastics. Ideal for fabricating rigid housing orsupport framessuch as drone mounts.
Chemical resistance
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):Mild acid/ alkali resistance, but sensitive to strong acids such as hydrochloric acid and oils, easy to degrade on long-term exposure. Intolerant to organic solvents such as acetone, easy to expand.
- ABS:Enhanced chemical resistance, especially to weak acids, bases, and oils. Acrylonitrile ingredients are chemically resistant to corrosion, while the styrene chain are vulnerable strong oxidant attack.
Durability
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):Low UV resistance, which can lead to yellowing and brittleness after prolonged use outdoors (UV stabilizer addition are required). Average humidity and heat resistance, easy to deform under high temperature andhumidity conditions.
- ABS:It is more UV-resistant than PLA, but it also ages after prolonged exposure to sunlight. Excellent moisture and heat resistance, ideal for temporary use in hot and humid conditions.
Heat resistance
- PLA (Polylactic Acid):The melting point is low (about 180-220 degrees Celsius) and the glass transition temperature is about 60 degrees Celsius, which softens easily when heated. Avoid exposure to high temperatures (e.g. oven,vehicle engine compartments).
- ABS:High melting point (about 230-260 °C), glass transition temperature of about 90 °C, short-term heat resistance. Suitable for medium-high temperature environment (such as household appliances accessories, pipeline connections, etc.).
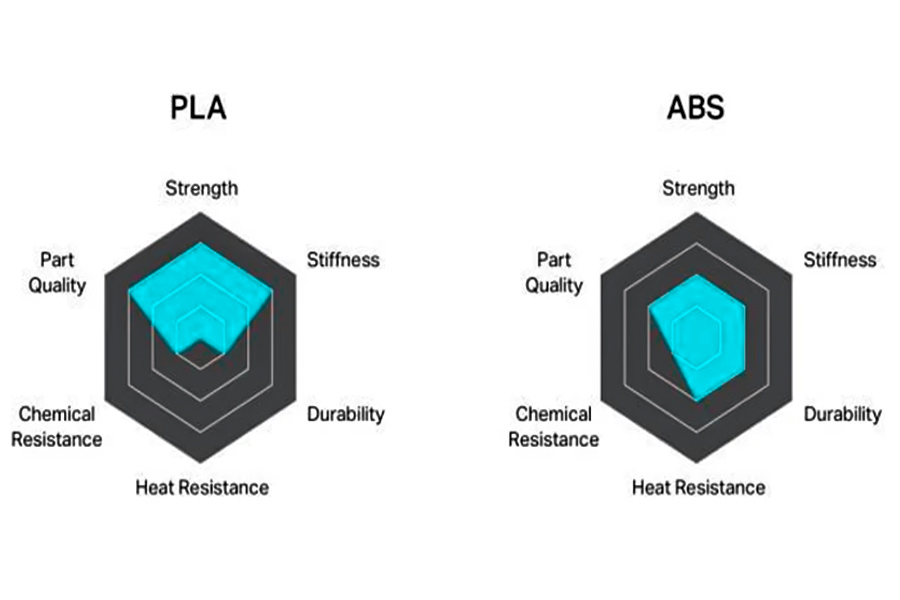
What are the differences in processing technology between PLA and ABS?
Printing Specifications:
- PLA recommends a temperature range of 190-220 degrees (layers 0.1-0.3mm high), with no need for preheating or low temperatures.Maintain medium tohigh speed printing to minimize interlayer adhesion, followed by general ventilation.
- ABS can be chemically corroded and electroplated and needs to be annealed at 60-80 °C for 2 hours to relieve internal pressure.
Post-processing Technique:
-
PLA supports sandpaper polishing, painting and plating, and UV stabilizers are necessary to prevent aging.
-
ABS can undergo chemical etching and electroplating processes, necessitating annealing at 60-80 °C for 2 hours to relieve internal stress.
How environmentally friendly are ABS and PLA?
Source of raw materials:
- PLA is arenewable resourcederived mainly from plant starch, including corn and sugarcane.Fermentation produces lactic acid monomers that reduce dependence on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions.
- ABS is an oil-derived material made from acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene monomers.It relies entirely on non-renewable resources and emits far more carbon than PLA.
Waste Disposal management:
- In industrial composting environments (high temperature, humidity, microbial activity), PLA can be broken down into carbon dioxide and water within 6-12 months.
- ABS can linger in the natural environment for a long time, potentially contaminating soil and oceans.In addition, incineration contributes to the emission of toxic gases, including hydrogen cyanide and styrene oxide, which contribute to air pollution, while landfills consume land resources.
Recycling techniques:
- PLA recovery is not very difficult and must therefore be strictly separated from plastics such as PET, resulting in a significant decrease in performance after recovery (about 30% loss of strength).
- ABSrecycling technologymatured and achieved melt regeneration (granulation) with a recovery rate of 70-90%.
Which has a longer usage time, PLA or ABS filament?
The usage duration of PLA and ABS depends on specific application scenarios and environmental conditions:
Characteristics usage duration PLA:
- Short-term and mild conditions:PLA can maintain stability for years in normal and dry conditions,such as food packaging and upholstery.
-
Ageing:Prolonged exposure to sunlight or UV rays can quickly cause skin to turn yellow and brittle (outdoor application can shorten to a few months). When the temperature is below 0 degrees Celsius, toughness decreases significantly and fracture is more likely to occur.
-
Biodegradability:Soil takes 1-5 years to degrade naturally (more rapidly under industrial composting conditions) and is therefore not suitable for long-term outdoor use.
Characteristics of ABS filament usage duration:
- Medium to long term or industrial environment:High temperature resistant (-20 ° C -80 ° C), good chemical corrosion resistance, can be used indoors or in mild industrial environments for more than 5 years. Adding UV absorbers can slow yellowing, but prolonged exposure to the outdoors can still lead to aging.
-
Impact resistance:Flexibility and abrasion resistance are superior to PLA and are suitable for high frequency use or dynamic load scenarios (e.g.car parts, tool handles).
ABS is often more durable in traditional industrial and domestic settings because it is more temperature resistance and impact resistance.PLA meets the demands of greener, purer indoor environments and cooler temperatures.Both require long-term exposure to stabilizers, but ABS is still better than PLA.
Which material is the optimal solution to choose?
Next, I'm going to combine the two from different levels of requirements:
| Demand Priority | Recommended materials | Reasons |
| Processing costs |
PLA(Polylactic Acid) |
Low raw material prices and low energy consumption for production. |
| Impact resistance and durability | ABS | It has high toughness and mechanical strength. |
| Environmental compliance | PLA(Polylactic Acid) | biodegradable and meet green sustainable development requirements. |
| Heat resistance | ABS | Good temperature resistance (>100 ° C). |
PLA is inexpensive (about $20 to $30 perkilogram), low processing temperature, FDA food exposure standards, no pungent odors and is suitable for manufacturing disposable tableware, medical catheters and more.
ABS filament possessesexcellent shock and wear resistance.Because of its chemical composition, it shows a high degree of toughness, minimizing the possibility of cracking.Suitable for precision and intricate workpiece, but also make durable,cost-effectivecomponents.
There is no absolute best material, only solutions that tailor the needs.It is recommended that a decision be taken in accordance with the following procedure:
- Specifies the object (force, temperature, environment) of the component.
- Assess expenses and operational requirements
- Small batch sample test (tensile and temperature resistance test).
- Achieving a balance between environmentally friendly and sustainable development.
What is the scope of adaptation for PLA and ABS filament?
Application of the People's PLA
1.Food containers and packaging:
Due to theirbiodegradability and non-toxicity, they can be made into a variety of food containers such as meal boxes, cups, trays, etc. These containers not only effectively protect food, but also degrade naturally after treatment, reducing environmental pollution.
2.Environmentally friendly tableware and disposable products:
knives, forks, spoons, chopsticks, bowls, dishes, etc. These products degrade quickly after use and do not cause long-term environmental pollution.
3.Medical Absorbable implants:
PLA is used in a variety of medical implants due to its good biocompatibility and degradability. These implants can gradually degrade and be absorbed into the body, eliminating the need for secondary surgery and greatly reducing patient pain.
Application of ABS filament
1.Mechanical components and tools in industrial manufacture:
ABS is characterized by high strength, impact resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, etc., and can be used in gear, bearings, handles, etc. These components and tools can withstand heavy loads and wear and tear to ensure proper operation of equipment.
2.Auto parts:
ABS can be used to make key components such ascar dashboards and bumpers. These components are not only beautiful in appearance, but also have good impact resistance and heat resistance and stable performance in all kinds of harsh environments.
3.Consumer electronics shell:
ABS is also widely used inconsumer electronics. Can be made into a variety of electronic products, not only durable, but also has a good touch and visual effects, to meet consumer requirements for the appearance and performance of electronic products.
Summary
In 3D printing, PLA and ABS are two key thermoplastic filament materials with differences in material properties, sustainability and physical properties. PLA specialises in rapid prototyping, low-cost modelling and single-use items such as food containers, especially in small-scale manufacturing to provide economic benefits. On the contrary, ABS continues to play a vital role in industry due to its superior mechanical properties and mature recycling processes.
The final choice should depend on specific requirements: PLA stands out if it aims for quick iteration, eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness; ABS is better for complex structures, temperature resistance or industrial-grade reliability.

Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1.Which filament is best for 3D printing?
Ordinary models and economical materials should be selected by PLA, while ABS, with its high strength and complex structure, is better suited.In short, there is no single best option; performance, cost and eco-friendliness must be reconciled with practical applications.
2.What are the common applications for PLA and ABS?
PLA is an ideal choice for prototypes, models, and decorative parts.Because of its environmental protection characteristics, it also produces food packaging bags, cling film, tableware and other daily necessities.Common items in the medical profession include disposable surgical instruments and sutures.ABS is used for mechanical components, functional prototypes, and high temperature and wear resistant automotive components required for high strength.
3.How does warping affect the two materials during printing?
PLA has low shrinkage and melting temperature, little change in volume and slight warping tendency when cooling.ABS, on the other hand, has a higher shrinkage and melting temperature, and will undergo significant shrinkage variations during cooling, making it prone to warping or deformation.
4.How do PLA and ABS compare in terms of surface finish?
PLA materials exhibit low mobility, secure interlayer bonding, and a smooth post-printing surface, ideal for high smoothness models.ABS materials have high mobility but are prone to thermal stress, causing bubbles, streaks or slight step effects.
Resource






