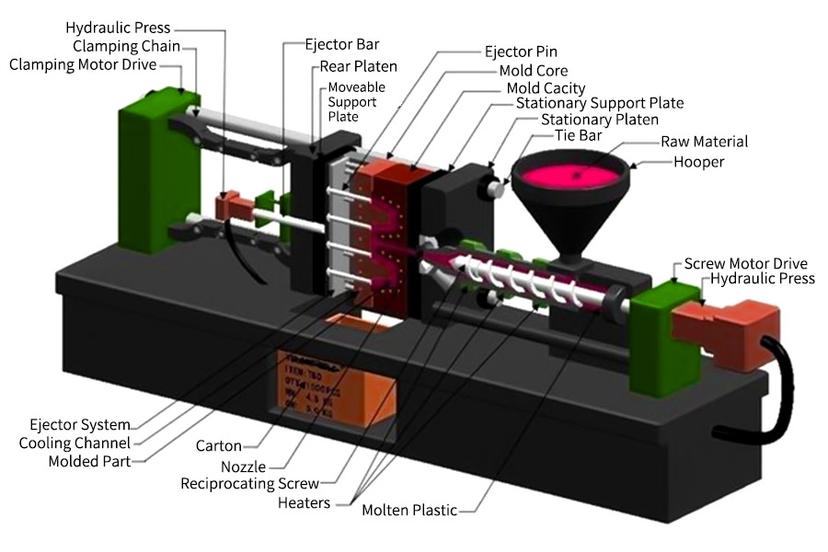
In the bright starry sky of modern manufacturing industry, injection molding technology has undoubtedly become a bright star. It brings light to all aspects of plastic product manufacturing with its efficient, flexible and precise technology. Injection molding, as an ancient yet young technology, has become one of the most widely used plastic processing methods in the world today with its many advantages that other manufacturing processes cannot match. So,how does injection molding work?In this article, we will introduce all aspects and key points of injection molding technology in a simple and easy-to-understand way, and help you fully understand the mystery and charm of this technology. Let us enter the world of injection molding and explore the infinite possibilities of plastic manufacturing!
What is Injection Molding?
In the vast field of manufacturing,moldingtechnologyoccupies a pivotal position.Molding meaning covers the entire process of transforming raw materials into products with specific shapes, structures and functions. Specific toinjection molding, it is an important method inplastic molding technology. It heats plastic particles to a molten state, injects them into the mold cavity under high pressure, and solidifies after cooling to produce various precision and complex plastic products.
In addition,silicone molding, as another special molding technology, focuses on the processing of silicone materials. Silica gel is widely used in medical, food, electronics and other fields because of its excellent high temperature resistance, aging resistance, environmental protection and non-toxic properties. The silicone molding process also requires precise control of temperature, pressure and other parameters to ensure the quality and performance of the final product. Whether it is injection molding, plastic molding or silicone molding, they are all important components of molding technology. Each plays an irreplaceable role in different fields and jointly promotes the progress and development of the manufacturing industry.


How does Injection Molding work?
The injection process is a complex and delicate manufacturing process, which mainly includes four key steps: clamping, injection, dwelling,cooling,mold opening,and ejection. The following is a detailed injection moulding process step by step introduction:
1.Clamping
Clamping, also called mold closing, is the first step and preparation stage of injection molding. At this stage, both sides of the mold are placed into the mold clamping unit, and the machine then pushes the two halves of the mold together to ensure that the mold is tightly closed and ready for the subsequent injection process. The tightness of the mold clamping will directly affect the melt flow and molding quality of the subsequentplastic injectionprocess. If the mold is not closed tightly, it will cause the plastic melt to leak, affecting the integrity and appearance of the product.
2.Injection
The injection stage is the most critical step in injection molding. The injection molding machine feeds the plastic raw materials into the injection molding cavity. The raw materials are heated and melted in the injection molding cavity, and then injected into the closed mold cavity at high pressure and high speed through the nozzle. During the injection process, the plastic melt needs to fill the mold cavity and cover all mold cavity surfaces to ensure that the product can be formed correctly.
3. Dwelling
In the dwelling phase, the melted plastic fills the entirety of the mold. Pressure is applied directly to the mold to ensure the liquid fills every cavity and the product comes out identical to the mold.
4.Cooling
After injection is completed, the mold needs to be left alone to cool. During this stage, the plastic melt inside the mold gradually cools and solidifies into a solid form. The length of cooling time depends on the type and thickness of the plastic material and the cooling efficiency of theplastic moldings.
5.Mold Opening
Once the part has cooled down, the clamping motor slowly opens both parts of the mold for safe and simple removal of the final product.
6.Ejection
With the mold open, an ejector bar will slowly push the solidified product out of the open mold cavity. The fabricator should then use cutters to eliminate any waste material and perfect the final product for customer use. Waste material can often be recycled and reinjected for the next part, decreasing your material costs.


What Materials are Used in Injection Molding?
1.Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Propylene butadiene (ABS) is a very common injection material that offers strength and impact resistance and is available in various grades in the thermoplastic market.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Strong mechanical properties | Low heat resistance |
| Excellent machinability/customization | Not suitable for food contact |
| Budget-friendly | Not UV stable |
Uses
- Hard hats
- Helmets
- Vacuum Cleaners
- Printers
- Musical Instruments
- Kitchen Utensils
2.Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon or polyamide (PA) is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer with excellent thermal and mechanical properties.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Good chemical resistance | Prone to absorb moisture |
| Excellent wear resistance | Poor dimensional stability |
| Great shock absorption | Limited heat resistance |
| Lightweight polymer | Sensitive to UV radiation |
Uses
- Clothes
- Fishing lines
- Fishnets
- Conveyors
- Seatbelts
- Parachutes
- Camping gear
3.Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is another easy-to-machine thermoplastic polymer suitable formolding injection. It is lightweight, and machined parts can withstand harsh environmental factors like sunlight.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Flame and chemical resistance | Produces harmful chlorine gas during recycling |
| Very durable | Limited heat resistance |
| Budget-friendly | |
| Electrical insulator |
Uses
- Building materials
- industrial products
- daily necessities
- pipeline
- wire and cable
- packaging film
4.Acetal Or Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Acetals are sometimes referred to as Delrin plastics or polyoxymethylene (POM). You can use them forplasticinjection moldingapplicationsthat require fine machinability properties and low surface friction.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Can withstand harsh environmental conditions | Low compatibility with adhesives |
| Impact resistance | Flammable |
| Good aesthetics | Poor acid resistance |
Uses
- Seat belt parts
- Electronic Cigarettes
- Insulin pens
- Water meter
- Guitar picks
5.Polycarbonate (PC)
Customers interested in themolding design of custom machined parts that are clear and durable should consider polycarbonate (PC) plastic parts for their next injection molding project.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy-to-machine plastics | Highly susceptible to scratches |
| Great for transparent applications like windows | Low chemical resistance |
| Excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
Uses
- Safety glass
- Bulletproof glass
- Room divider
- Electronics
- Construction
6.Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is also known by its common name Polypropene. It belongs to the thermoplastic polymer category. Its properties are a slight improvement to polythene.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It is not expensive | Low heat resistance |
| Excellent moisture resistance | Not UV stable |
| Durable and lightweight |
Uses
- Machine parts
- Flexible packaging
- Rigid packaging
- Tote bags
- Bottle caps
- Medical equipment
7.Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a commoninjection molding materialknown for its versatility. PE can be found in the form of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Safe for industrial food packaging | Not UV stable |
| Easily available and affordable | Difficult to bond |
| High flexibility |
Uses
- Food packaging
- Bottles
- Pipes
- Trays
- Grocery bags
- Trash bags
- Insulations
- Toys
8.Polystyrene (PS)
PS is a lightweight and economical option often used to manufacture single-use products such as cutlery and containers. It can be crystal clear, making it ideal for food packaging and laboratory equipment. However, its brittleness and weak resistance to UV radiation and harsh weather conditions limit its use in outdoor applications.
9.Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
PET is a versatile plastic with excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties. It is widely used in soft drink bottles, food packaging and synthetic fibers. However, it is important to note that PET absorbs moisture from the environment, which may affect the molding process.


Which Plastic Material Is Right for Your Injection Molding Project?
For plastic injection molding projects, the correctselection of suitable plastic materialsis crucial. Different projects have different requirements and characteristics, so all factors need to be considered. Here are some specific examples:
Medical device parts
For medical device parts, hygiene and safety are the primary considerations. The material should have excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance to ensure that the product does not have adverse effects on the human body. Commonly used material choices include polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC), which have excellent medical grade performance.
Electronic product shell
The electronic product shell needs to have good electrical insulation performance and weather resistance. Material selection should consider characteristics such as anti-static, flame retardant, and high-temperature resistance. Common choices include polyimide (PI) and Polyphenylene sulfide (PPE), which can meet the special requirements of electronic product housings.
Household appliance parts
For household appliance parts, important considerations include heat resistance, wear resistance, and chemical resistance. The material should have good mechanical strength and stability to meet the requirements of daily use. Commonly used choices include nylon (PA) and polyamide (POM), which have a wide range of applications in the field of household appliances.
What Machines are Used in Injection Molding?
In theplastics moldingprocess, the main machine used is aninjection molding machine(also called an injection machine).The working principle of theinjection molding machineis similar to that of a syringe for injection. It uses the thrust of the screw to inject the shaped plastic into the closed mold cavity, and then obtains the product after solidification and shaping. The injection molding machine mainly includes the following parts:
1.injection unit
Hopper: This place is used to fill the various raw materials into the mechanical equipment. The hopper is responsible for transporting various materials into the bucket.
Cartridge: The screw is installed inside the drum and heated through a series of electric heaters. When the screw rotates, it drives the material forward and melts the material in the process.
Screw: When the screw rotates, it pushes the material forward and puts some pressure on it to inject the melted material into the mold. The tool enables a mixture of the polymer and other components to form a continuous flow channel at its extrusion end to obtain the product of the desired shape. Moreover, it also helps to ensure the uniformity of the mixed material.
Nozzle: It is the tip that connects the injection device to the mold. It ensures that the melted material effectively enters the inside of the mold.
2.mold clamping unit
Template: This template consists of dynamic template and fixed template, which together form the fixed space of the mold. The dimensional accuracy and surface quality of injection molded products are significantly affected by the accuracy and stiffness of the template.
Mold: The mold is the corecomponent ofinjection-molding,which determines the shape and size of the product. During the injection molding process, molten plastic is injected into the cavity of the mold and cools to form the desired product.
Mold clamping mechanism: The mold locking mechanism is a key part of the mold clamping unit. It is responsible for tightly locking the upper mold and the lower mold together to ensure that the mold will not be separated due to the high pressure of the plastic during the injection molding process, thus ensuring the quality and stability of the product.
3.Hydraulic system
Oil pump: The oil pump is the power source of the hydraulic system. Its function is to convert the mechanical energy of the prime mover (such as an electric motor, internal combustion engine, etc.) into the pressure energy of the liquid to provide power for the entire hydraulic system.
Oil tank: The oil tank is a container used to store hydraulic oil in the hydraulic system. It not only plays the role of storing and supplying hydraulic oil, but also has certain functions such as heat dissipation, precipitation of impurities, and gas separation.
Hydraulic Valve: A hydraulic valve is a device whose main function is to control the flow direction and pressure exerted by hydraulic oil, thereby enabling the injection molding machine to perform various operations. The accuracy and stability of the hydraulic valve directly determines the stability of the injection molding process and the quality of the final product.

4.Electrical control system
PLC:PLC: As the key control module of theinjection molding machine, PLC is mainly responsible for receiving input signals and controlling output devices to realize automatic control of the injection molding machine. PLC programming technology and functional configuration play a key role in the adaptability of the injection molding process and product diversity.
Touch screen: The touch screen is a human-computer interaction interface used to set injection molding parameters, monitor the injection molding process and display fault information. The intuitiveness and ease of use of the touch screen improve the operator’s work efficiency and the intelligence level of the injection molding machine.
Sensor: Sensors are used to monitor the operating status and process parameters of the injection molding machine in real time, such as temperature, pressure, flow, etc. The accuracy and response speed of the sensor have a direct impact on the stability of theinjection molding processand the quality of theinjection moulding products.

Why Use Injection Molding?
Injection moldingexhibits multiple advantages in mass production that make it an integral part of modern manufacturing. The following are the main advantages of injection molding in mass production:
| Advantages | Elaboration |
| Efficient production | Injection moldingis praised for its fast manufacturing cycle, usually between 30 seconds and 1 minute per production cycle. |
| High precision | Through injection molding technology, products with complex shapes and precise dimensions can be manufactured. |
| Complex parts | This method can design complex shapes and structures, especially thin shell parts of various types of equipment. |
| Material versatility | It can handle a variety of mold and thermoset materials including PS, ABS, PA, PP, PE, PVC components. |
| Low waste | The goal of this process is to significantly reduce the loss of material, thus helping to reduce costs and provide benefits to the environment. |
| Mass Production | Once the mold is successfully created and configured, theinjection molding machineis able to manufacture large quantities of parts in a very short time to meet the needs of mass production. |
Your best injection molding services
As a plastic injection molding manufacturer, we are well aware of the importance of selecting the right materials for product quality and customer satisfaction. We have rich experience and professional knowledge to help you make wise decisions in material selection.
Whether you need to produce automotive parts or medical devices, we can provide you with high-quality injection molding solutions. We collaborate with excellent global material suppliers to ensure that you receive the materials that best meet your product needs. We have advanced equipment and technology that can accurately inject and shape products that meet your requirements.
If you need to inquire or order injection molded products, please contact us immediately. Our professional team will work with you to understand your needs and provide you with customized solutions. We are committed to providing you with high-quality products and excellent customer service.
FAQs
1.How does injection molding work step by step?
Injection molding is a process in which adapter plastic is injected into a mold, cooled and solidified to obtain a plastic product of the desired shape and size. The simple steps of injection molding are ① raw material preparation ② adapter plastic ③ injection and filling ④ pressure holding and cooling ⑤ demoulding and removal ⑥ post-processing.
2.What are the 4 stages of injection molding?
The main four stages of injection molding are: ① Starting from injection molding when the mold is closed, until the mold cavity is filled to about 95%. ②After filling is completed, the injection molding machine continues to apply a certain pressure to compact the melt and increase the density of the plastic to compensate for the shrinkage behavior of the plastic. ③ During or after the pressure holding process, the cooling system in the mold starts to work, causing the plastic melt to quickly cool down to below the solidification temperature. ④After the plastic product cools and solidifies, the mold is opened and the product is taken out of the mold through a mechanical arm or manually.
3.What is the working principle of injection molding?
The working principle of injection molding is to feed granular or powdered plastic raw materials into a heated barrel, where they are heated, melted and plasticized into a viscous fluid melt. Under the high pressure of the plunger or screw of the injection machine, the melt is injected into the mold cavity through the nozzle at a very high flow rate. After pressure holding and cooling, the melt is solidified and formed in the mold to obtain plastic products of the required shape and size.
4.What is the science behind injection molding?
The science behind injection molding primarily involves the thermoplasticity and flow properties of plastics. After the plastic is heated to a certain temperature, it becomes a molten state, becomes fluid, and can be injected into the mold. After cooling and solidifying in the mold, the plastic regains its solid-state properties and retains the shape and dimensions imparted by the mold. In addition, injection molding involves scientific principles such as pressure transfer, heat conduction and plastic rheology. By precisely controlling parameters such as temperature, pressure, time and injection speed, high-quality, high-efficiency production of plastic products can be achieved.
Summary
The injection molding process occupies an important position in the field of plastic processing due to its high efficiency, precision and automation. By precisely controlling parameters such as temperature, pressure and time, injection molding can produce plastic products with complex shapes, precise dimensions and excellent performance. These products are widely used in automobiles, electronics, home appliances, medical and other fields, promoting the development and progress of related industries. Injection molding is bound to usher in broader development prospects.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.Longshengdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyer seeking a quote for parts to determine the specific requirements for those parts.Please contact us for more information.
Longsheng Team
This article was written by multiple Longsheng contributors. Longsheng is a leading resource in the manufacturing sector, withCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping, and more.