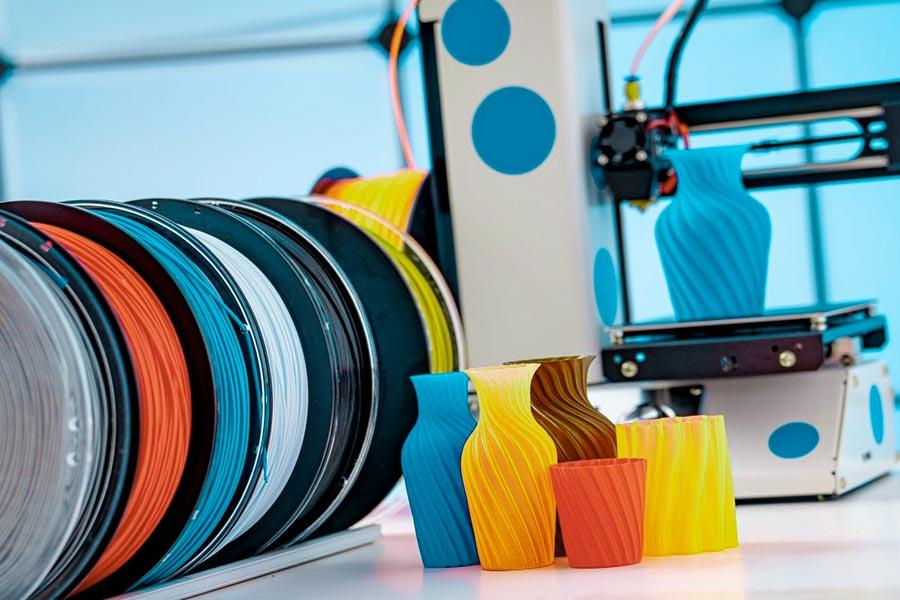
With the penetration of3D printing technologyinto high-end field, the selection of 3D printer filaments has become one of the key factors affecting the quality and efficiency of printing.The pursuit ofstrongest 3D printed filamentshas become a goal for many professional filaments of all types.
These filaments have excellentmechanical strengthto meet complex and changing printing needs, providing a wide range of options for users.In this paper,the types of 3D-printed filamentswill be discussed in depth, the advantages and disadvantages of each type of filaments will be analyzed, to help readers better understand and choose the appropriate filaments, in order to achieve the best printing effect.
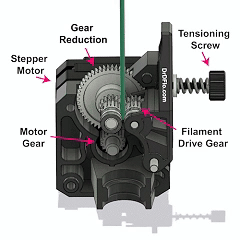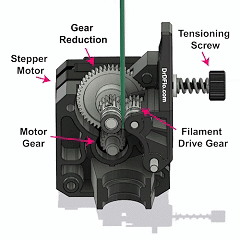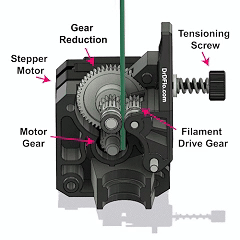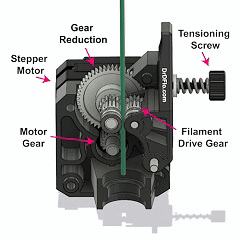
What are the commonly used types of filaments for 3D printers?
1.Thermoplasticity (FDM technology)
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): An environmentally friendly biodegradable material that is easy to print, nontoxic and odorless, with a low melting point (~180 °C) and a smooth finish.
Advantages: convenient processing, low cost, environmental protection.
Weaknesses: high brittleness, high heat resistance (easy deformation above 60 degrees Celsius).
- ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): High strength (tensile strength~50MPa), good abrasion resistance, high temperature resistance. Suitable for printing products with high strength and durability.
Strengths: Good toughness, smooth finish.
Weaknesses: High melting point (~250 °C), risk of release of toxic gases during printing.
- PETG (polyethylene terephthalate 1,4-cyclohexanediol): It is characterized by high strength, flexibility, transparency, high temperature resistance (~ 90 ℃), good printing stability and resistance to warping.
Strengths: Suitable for precision parts and flexible models.
Weaknesses: Small print temperature range (~220-260 °C).
- Carbon fiber reinforced PLA/nylon: Ultra-high strength (tensile strength~420MPa), lightweight, temperature resistance (~280 °C).
Strengths:Industrial-grade strength, suitable for extreme environments.
Weaknesses: Expensive and requires a dedicated printer.
2. Photosensitive resin (SLA technology)
- Standard photosensitive resin: Curing by ultraviolet or laser beam irradiation, high precision (micrometer level details), fast curing speed (second level).
Strengths: Smooth surface for complex geometric models.
Weaknesses: high brittleness, require for late cleaning, not heat resistant.
- High strength epoxy resin: Support structures are usually provided during 3D printing with a bending strength of~100MPa and resistance to high temperatures (~80-120 °C).
Strengths: Sturdy, suitable for functional components.
Weaknesses: High shrinkage rate and pungent odor.
3. Thermosetting materials (SLS Technology)
- Nylon (PA12/PA66):High strength (tensile strength~150MPa), wear resistance, good chemical stability.
Strengths: No support structure, suitable for long-term use of components.
Weaknesses: High moisture absorption, easy aging.
- TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane):Ultra-flexible (tensile deformation > 300%), low temperature (-40 °C), wear-resistant, oil resistance, solvent resistance.
Strengths: Good softness, good shock absorption performance.
Weaknesses: Low printing accuracy, easy edge warping.

Which type of filament performs the best in strength?
If the tensile strength of 120-140 MPa is a definite indicator (60% higher than conventional nylon),carbon fiber reinforced nylon(such as PA66/PA12 substrate) is the best option forplastic filaments. This material achieves a balance of strength and toughness through synergistic effects of carbon fiber (usually 15-30% weight) and nylon, as manifested by:
Tensile strength advantage
1. Strength range: 120-140 MPa (about 80-120 MPa for traditional pure nylon), meeting the requirements of high-intensity scenarios.
2. Strength enhancement mechanisms:
- Fiber orientation optimization: Carbon fibers is arranged along the printing direction to form a continuous stress transmission path.
- Interface enhancement: improve the adhesion of fiber to matrix and reduce interface slip by chemical modification such as silane coupling agents.
Key limitations: nozzle material requirements
1. Necessity of quenching steel nozzle: Carbon fiber has extremely high hardness (Mohs hardness~6-7) and rapidly wears down brass nozzles during printing (hardness~2-3), causing pore sizes to enlarge or become blocked, usually within 20 hours.
2. Solution: AHardened steel nozzles(such as H13 or SKD61) must be used, with a surface hardness of HRC58-62.

Which type of filament can withstand the high temperature of a car engine?
In extreme heat conditions, such ascar engines(which typically operating temperatures of 200 to300 degrees Celsius), 3D-printed filaments that can withstand high temperatures must meet requirements for both temperature resistance, mechanical stability and chemical resistance. The selection and technical analysis of eligible materials are as follows:
- Temperature resistance: 343 ° C, thermal deformation 315 ° C, long-term use up to 250-300 ° C.
- Super chemical resistance (to fuel and coolant corrosion resistance), suitable forthe manufacture of oil circuit seals and high temperature pipelines.
- High mechanical strength (tensile strength~140MPa), self-lubrication, reduce friction losses.
2. Carbon fibre-reinforced nylon/ polylactic acid
- Temperature resistance: modified with a benzene ring structure, the maximum temperature resistance is 280 ° C (about 160 ° C for traditional carbon fiber materials). Plasma grafting tripled the antioxidant lifetime of the material at 280 ° C.
- Tensile strength 420MPa, lightweight (density 1.4g/cm3), suitable forengine lightweight componentssuch as piston links. It costs less and has better process compatibility than metals.
How to prevent nylon filament from absorbing moisture?
Sealed storage: scientific protection with vacuum bag and dryers
1. Preparation work
- Cut and wash: Cutnylon filamentinto short segments (to avoid tangling) and place them in a clean, dust-free vacuum bag.
- Desiccant selection:
Long-term storage: Use a 3A molecular sieve desiccant (up 25% your weight in moisture absorption capacity and up to 6 months of service life).
Short-term emergency: Replacement of food grade silicone drying bags (to be replaced monthly).
2. Vacuum packaging
- Vacuum pumping technique: Use a vacuum pump to pull the air out of the bag completely, ensuring the moisture content is below 15% RH (household vacuum pumps can also meet basic needs).
- Dual protection: If conditions permit, wrap an aluminum foil around the vacuum bag to keep out outside moisture infiltration.
3. Storage environment requirements
- Temperature and humidity control: Store in a cool, shady place (ideal temperature 15-25 ° C, humidity<40% RH), away from high-humidity areas such as bathrooms and kitchens.
- Equipment assistance:It is recommended to use a dehumidifier (humidity control accuracy ± 5%) in industrial settings, and air conditioning dehumidification function can be used in the household.
-
Different types of nylon storage differences:
Nylon type Moisture absorption rate (50% RH) Sensitivity Suggested sealing cycle PA6 (Nylon 6) 12-15% tall ≤ 3 months PA66 (Nylon 66) 8-10% centre ≤ 6 months PA12 (Nylon 12) 10-12% Lower ≤ 12 months
Emergency dehydration plan: operate the 80°C oven with precision
1. Scenario
Nylon filament are exposed to humidity and need to be quickly restored to their properties.
2. Operational steps
- Pre-treatment: Spread the wet strands evenly on a baking tray (avoid buildup and ensure ventilation).
- Temperature control:
Dedicated oven: Heat the oven to 80° C/ gas 6 and place on a baking tray before preheating.
PA6 restriction: No baking at high temperatures! Switch to a low-temperature air dryer at 40-60 °C (continuous stirring or flipping of filaments is required).
Cooling test: After drying, place room temperature (to avoid stress cracking due to sudden cooling) tocheck that the surface is dry and uniform.
3. Technical principles
- High temperature resistance: Molecular chains contain chlorine atoms, which are chemically stable at high temperatures and are not susceptible to oxidation or yellowing.
- Fragility of PA6: Lack of chlorine element and high temperatures can cause chain breakage and oxidation reactions, leading to yellowing and decreased strength.
4. Preventive measures
- Baking duration: Too much baking time can cause nylon to brittle. Samples are recommended for testing every 2 hours.
- Alternative solution: If there is no oven, use an industrial dehumidifier (humidity<30% RH) to cycle and dry for 12-24 hours.

What is the best PETG for outdoor use?
1. Thethe best PETG filamentin extreme outdoor environments with high temperatures, UV rays, humidity or dust should have the following characteristics:
- Anti-UV aging: Add UV absorbers (such as carbon black or HALS stabilizers) to prevent yellowing and brittleness due to prolonged exposure.
- Wide-range temperature tolerance: ≥ 260 ° C melting point, up to 280 ° C short term, flexibility at low temperature (-30 ° C).
- Chemical corrosion resistance: rain, salt mist, weak acidity and alkalinity (pH 2-12).
- Strength and toughness: tensile strength ≥ 60MPa, impact strength ≥ 5kJ/m (superior to ordinary PETG).
2. Key Performance Comparison (Ordinary vs. outdoor grade PETG)
| Characteristic | Ordinary PETG | Outdoor grade PETG |
| UV resistance | Yellowing cycle<6 months | >2 years |
| Temperature resistance range | Melting point 260 ° C | Melting point 260 ° C + temperature fluctuation resistance |
| Impact resistance | Izod notch impact 5kJ/m ² | ≥8kJ/m² |
| Moisture absorption rate | ≤1.5%(23°C/50%RH) | ≤ 0.8% (under the same conditions) |
3. Notes on Use
- Printing parameter optimization:
Extrusion temperature: 240-260 ° C is recommended (to avoid degradation due to overheating).
Interlayer adhesion: Increased printing speed (≤ 40mm/s) is appropriate to enhance interlayer bonding.
- Post processing:
Surface coating:can be sprayed with polyurethane or acrylic coatings to further enhance weather resistance.
Periodic inspection: material performance should be checked every 6 months for prolonged outdoor use.

What are the main factors determining the fatigue life of components made from Strongest 3D printer film?
The following are the main determinants of fatigue life of components of strongest 3D printer filament (e.g. carbon fibre-reinforced nylon/ polyethylene lactic acid), combined with material properties and process optimization:
Intrinsic properties of materials
1. Fiber orientation: The distribution of carbon fibers along the printing direction (e.g. Z axis direction) cansignificantly increase stress transfer efficiencyand reduce fatigue crack production.
2. Additives and modifiers: Antioxidants are used to slow the degradation of substances caused by high-temperature oxidation and increase fatigue life (at 200 ° C, antioxidants can double their lifespan).
Printing processparameters
1. Extrusion temperature and speed
- High temperature (>270 ° C) leads to matrix degradation, while low temperature (<230 ° C) affects fiber dispersion.
- Interlayer temperature consistency: Printing intervals between layers should be limited to 5-10 seconds to avoid residual stress due to temperature differences (which can reduce fatigue crack rate by 40%).
2. Layer thickness and filling rate
- Thin-layer printing (0.1-0.2mm):improves surface roughnessand reduces stress concentration (increases fatigue life by 25%).
- High filling rate (>30% carbon fiber): Increases material rigidity at the expense of some toughness (requires gradient filling optimization).
3. Support for structural design
Grid support: use honeycomb support structure in suspension area toreduce local stress concentration(can extend fatigue life by 30%).
Geometric Design and Load Conditions Members
1. Optimization of stress concentration points
- Rounded corner design: When R ≥ 0.5mm, the stress concentration factor (Kt) can be reduced to less than 1.5 (3-5 for sharp angle Kt).
- Topology optimization:Eliminating redundant materials by using finite element analysis (FEA) allows load to be evenly distributed (e.g., LS company's space bracket increases fatigue life by 40%).
2. Dynamic Load Type
- Alternating load frequency: High frequency vibration (greater than100Hz) accelerates fatigue failure and requires damping design (e.g. rubber toughening agents).
- Multiaxial stress state: Avoid pure shear stress or alternating tension compression load, and give priority to designing a simple loading path dominated by unidirectional stress.
The fatigue life of the filament assembly of Strongest 3D printer filament depends on three core factors: material fiber orientation, printing process control, geometric design and load matching. By optimizing carbon fiber dispersion, using thin-layer high-frequency printing, and designing a stress-resistant centralized structure, the cycle life of more than 10 weeks can be achieved to meet the needs of high-end scenarios such asaerospaceandautomotive industries.
How does LS company utilize the 5 mainstream filament types?
1. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
- Core Applications:Rapid prototyping,Education Mode, Short-Term Functional Components.
- LS Features: Provides environmental solutions utilizing PLA's biodegradability, supportsmulticolor printing, and is often used in customer rapid prototyping design, such as home appliance shell prototypes.
2. ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer)
- Core applications:High temperature resistant industrial components,automotive interiors,electronic and electrical casings.
- LS Advantages: Byoptimizing printing parametersto solve ABS warping problems, it provides high strength parts suitable for automotive mold testing, tool fixtures, etc., which require high ambient temperature tolerance.
3. PETG (polyethylene terephthalate 1,4-cyclohexanediol ester)
- Core applications: Transparent/ translucent components, food contact grade products.
- LS Innovation: Leveraging PETG's high transparency and impact resistance, weproduce customized componentsto meet our customers' dual aesthetic and practical needs.
4. TPU/(thermoplastic polyurethane)
- Core applications: Flexible seals, shock absorber.
- LS Technology: Adopts a professionalflexible consumables printing processto produce products such as mobile phone cases andmedical protectiveequipment with high rebound requirements. We support ultrathin walls with 0.8mm thickness for greater flexibility.
5.Nylon
- Core applications:Wearable mechanical parts,aerospace components, functional sports equipment.
- LS expertise: Manufactures industrial-grade components such as gears and bearings utilizing nylon's high strength and abrasion resistance, combiningSLS selective laser sintering technologyto achieve lightweight and complex structural components.
Summary
There are various types of 3D-printed filaments,each filament has different printing requirements and application scenarios. Of these,strongest 3D printer filament, such as carbon-fibre-reinforced nylon or PLA, are central to high-end industrial applications because of their superior strength and heat resistance. It can be decorated or partially functional at a lower cost through metal-like composite processes such as stainless steel PLA.
Therefore, when choosing 3D-printed filaments, users should consider the advantages and disadvantages of various filaments according to their specific printing objectives, performance requirements and cost budgets to find the filaments that best suit them.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1.Which filament is safest for food?
PLA is made from corn starch and is naturally non-toxic. PETG contains food grade additives and is heat resistant (melting point 260 °C). These two materials are chemical properties stable at room temperature, do not release harmful substances easily.
2.Why is carbon fiber reinforced PLA called strong 3D printer film?
When carbon fibers is aligned in a directional fashion, the tensile strength can reach 420MPa, far higher than the 60MPa of regular PLA. Through the benzene ring structure, the temperature resistance is increased to 280 ° C (compared to 60 ° C in normal PLA).
3.What are the improvements in PETG filament technology?
Extrusion of the first layer was increased by 20% to compensate for thermal shrinkage (reduction of edge warping) and to achieve -30 °C cold resistance (normal PETG brittleness temperature -50 ° C) by copolymerization modification.
4.How to distinguish between ordinary PLA and imitation metal PLA (such as stainless steel PLA)?
surface coating imitation metal PLA,such as nickel, mimic metallic gloss but do not have no metallic conductivity. True metal density was > 99% titanium alloy 4.4g/cm), while imitation metal PLA was only about 92%. the tensile strength of imitation metal PLA is less than 100MPa, much lower than that of real metal (>900MPa).




