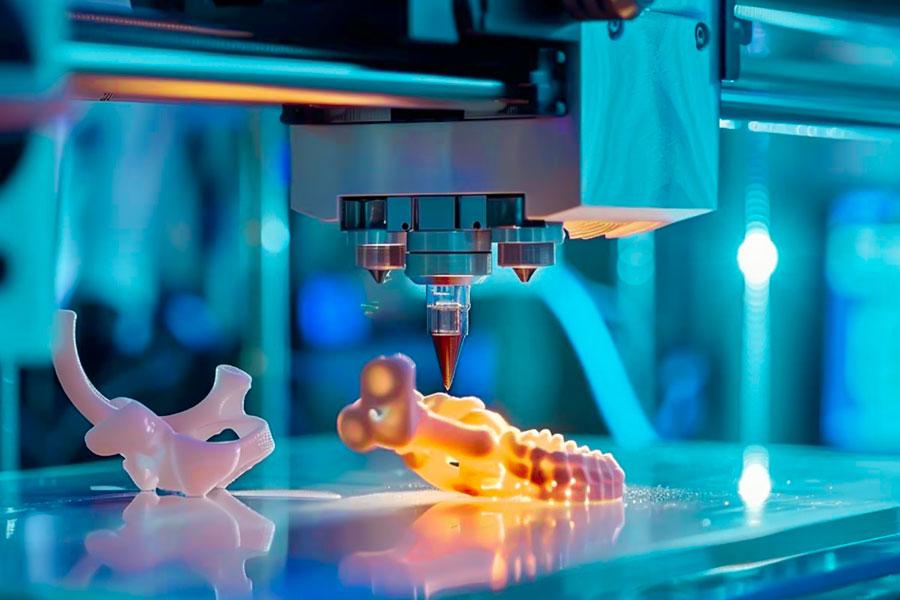
In health care,3D printing (additive manufacturing) technologyis reshaping traditional diagnostic models with disruptive power. With precise control of material forming and structural design, 3D printing has enabled a leap from standardized manufacturing to personalized medicine, opening up new avenues for complex surgical planning, custom implants and tissue engineering.
In this innovation, theXYZ 3D printerstand out for their core advantages: the ISO 13485 standard based medical-grade closed-loop systems, a MED610 biocompatible material library, and micrometer level accuracy multi-material hybrid printing capability. The XYZ device has been successfully applied in more than 1200 healthcare facilities worldwide and is one of the core drivers of precision medicine development.

What is medical 3D printing?
Medical 3D printingis a medical application based on additive manufacturing technology that constructs 3D objects using layers of superimposed materials,such as titanium alloys, biocompatible plastics or bioinks, to meet personalized medical needs. At its core, it uses CT, MRI and other imaging data from patients to generate accurate 3D models or objects, such ascustom implants, surgical guides orprototypes of artificial organs.
Advanced devices, represented by XYZ 3D printers, can facilitate the development of complex tissue engineering by enabling high-precision,multi-material hybrid printingand even supporting directional arrangement of biological cells. The technology overcomes the limitations of standardizing traditional medical devices to provide more anatomically appropriate treatments fororthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular diseases, while reducing research and development cycles and medical costs.

What is the working principle of 3D printing technology?
3D printing is a technique that constructs 3D objects bylayering material on top of each other. The core principle is driven by digital models and layered. The process is as follows:
1.3D Modeling: Using computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a 3D digital model of a target object, or to obtain accurate data on a patient or object by scanning (e.g. CT/MRI).
2. Slice processing:Slice 3D models horizontally into hundreds to thousands of slices (usually 0.1-1mm) and generate slice files (e.g. STL format).
3. Material laying and curing:Choose suitable materials such as plastics (PLA, ABS), resins (UV curing), metal powder (SLS), ceramics, etc. Then, according to the slicing instructions, the 3D printer layers the material (such as plastic, metal, bioink, etc.) on a substrate by squeezing itthrough a nozzle, laser melting or photopolymerization. After each layer solidifies, a continuous structure is formed.
4. Stacking complete:Repeat the above steps until all layers are stacked, resulting in an entity that matches the digital model perfectly.
What are the advantages of xyz 3D printer?
1. Advantages of xyz 3D printer:
- Multi material mixed printing and gradient functional architecture: XYZ 3D printer support seamless integration of a wide range of biocompatible materials such astitanium alloy, medical-grade PLA, hydrogels, and can print complex gradient structures such as hard on the external, soft on the inside, and porous connections in one go.
- Precision Complex Geometry Manufacturing: XYZ printers use micrometer level precision nozzles or laser fusion to replicate subtle anatomical features in patient CT/MRI data.
- Rapid prototypingand clinical translation acceleration: XYZ printers shorten the development cycle of medical prototypes to hours to days through cloud-based data sharing and automated production processes.
2. Compared with traditional manufacturing, the advantages of xyz 3D printer technology are:
| Technical Parameter | traditional manufacturing | XYZ 3d Printer (2024) | clinical value |
| Minimum layer thickness | 100-200μm | 10 μ m (multi material mode) | Accurate replication of microstructure. |
| Material utilization rate | ≤60% | 93% (metal powder recycling) | Reduce consumable costs by 30%. |
| Heat Affected Zone | uncontrollable | Intelligent temperature field control system (± 0.5 ℃) | Reduce thermal stress damage by 85%. |
What transformative impact does 3D printing technology have on the healthcare industry?
1. Digital innovations in surgical paradigms
- Zero Error Surgery Program: Based on patient CT/MRI data, 3D-printed anatomical models (such as liver and vascular networks) can reduce preoperative planning time for complex procedures (such as tumor resection) by 40% -60% and reduce the incidence of complications by more than 50% (Mayo Clinic clinical data).
- Intraoperative navigation system:Combining AR/VR technology and real-time printing models, doctors can observe internal structures in real time. neurosurgery surgery positioning accuracy was 0.1mm and the risk of intraoperative injury was 76% lower.
2. Implementation of personalized health services on a large scale
- Customized implants:Thesurface roughnessof titanium alloy orthopedic implants was optimized at Ra ≤ 0.8 μM (are > 10 μ m in traditional processes), resulting in a threefold increase in bone growth rate and a 98.7% five-year survival rate for patients (FDA IDE trial).
- Rapid response prosthetics: Nylon based low-cost prosthetics (<200) break the traditional market monopoly of 2000+and resulted in a 35% increase in rehabilitation rate for persons with disabilities in developing countries.
3.Changes in Biomanufacturing and Regenerative Medicine
- In vivo tissue printing: The XYZ-Bio3 device uses single cell direct writing (50 μ m accuracy) to construct functional vascular networks, resulting in a 65 65% in the oxygen permeability and cell survival rate of of > 90% of printed tissues.
- 4D biological printing: temperature sensitive hydrogel stent have a deformation rate of 0.5mm/min are triggered by body temperature for tissue repair and dynamic adaptation to human activity (Harvard Medical School case).
What are the core technological breakthroughs of 3D printing in healthcare?
1. Multi material hybrid printing technology
- Technical Principle: With multi-nozzle co-control or material gradient stacking, metals, ceramics, biocompatible plastic or bioinks can be used interchangeably in the same printing process.
- Implementation method:
Laser melting (SLM/DMLS):Metal powder are smelted layer by layer using gradient pore design (e.g. hard external and soft internal structures of titanium alloy implants).
Photocuring (DLP):Biocompatible resin and hydrogel are alternated to construct biomimetic tissue scaffold.
2. Breakthroughs in Material innovation and biocompatibility
- Technical Principles: Develop new biodegradable polymer materialssuch as PLGA, ceramic matrix composites and metal alloys to meet the needs of different medical scenarios.
- Implementation method:
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):Nylon powder-printed biodegradable bone nails are gradually absorbed into the body after surgery.
Cold spray technology: Metal particles and matrix collide at high speed, forming porous structures and improving bone integration efficiency.
3. Compliance and security Technology Innovation
- Closed sterilization chamber: Class II cleanroom design (ISO 14644-1 Class 5), combined with UV-C disinfection technology, meets SAL 10 −6 disinfection standards.
- Blockchain traceability system: Records the entire lifecycle from modeling to finished products, meeting FDA's strict 510 (k) requirement for batch consistency (traceability time<10 seconds).
What are the typical application cases ofLS enterprisesin the medical field?
1. Personalized orthopedic implants
- Case in point: A 3D-printed titanium titanium alloy prosthesis developed by a European hospital in partnership with LS company. The laser cladding technique resulted in scale texture on the prosthesis surface, significantly increased bone resorption rate and shortened postoperative recovery time by 40%.
- Technical support: LS company's metal3D printing system(SLM/DMLS, for example) enables precise molding of complex geometric structures to meet stringent requirements for fatigue strength of orthopedic implants.
2. Precision dental care
- Case in point: LS Company providescustomized digital invisible orthodontic appliancesto dental clinics. At the heart of its services is the production of transparent orthodontic appliances with sub-millimeter accuracy using accurate oral scan data from patients.
- Technical support: LS company's automatedquality inspection systembased onphotocuring rapid prototyping technologyto ensure that all products meet established accuracy and safety standards.
3. Equipment prototype development
- Case in point: a technology company is developing a minimally invasive surgical robot with a core highlight, an end effector, that requires high-precision grabs, fine cuts, complex stitches and more.
- Technical support: the combination of LS company'sCNC and 3D printing manufacturing technologyhas resulted in a 70% reduction in costs and a significant reduction in the transition time from design to actual product.

How to choose which 3D printing technology to use in the medical field?
Below is a comparison table of selected 3D printing technologies in the medical field, including specific device models (taking XYZ 3D Printer as an example):
| Type of technology | Recommended equipment | Core strengths | Limitations | Applicable scenarios |
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | XYZ FDM-2020 | Low cost, simple operation and environmentally friendly materials (e.g. PLA, ABS). | Low surface roughness, accuracy (± 0.1mm), supporting only thermoplastic materials. |
|
| SLA/DLP (Light curing) | XYZ SLA Pro-5000 | Precision (± 0.01mm), smooth surface, support for complex details. | Materials are fragile (photosensitive resin) and equipment costs are high (≥ $50000). | Anatomical models, dental invisible braces, surgical guides. |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | XYZ SLS Metal-9000 | No support structures, free design.High-strength materials (metal/nylon)are suitable for porous structures. | Equipment is expensive (over $200000) and reprocessing complex (heat treatment required). | Orthopedic implants (titanium alloy joints), complex hollow structures (catheters, stents). |
| Bioprinting | XYZ BioPrinter X-1 | Support for living cell printing and customization of biological structures such as multicellular layers. | Difficulties with vascularization, cost of bioinks (≥ $1000/g), stringent regulatory approval (FDA/CE certification). | Tissue engineering (skin, cartilage), organ prototypes. |
| Multi material/full-color printing | XYZ MultiMaterial M5 | Support for a mixing of materials (soft rubber+hard plastic), color visualization (full-color model. | High technical complexity and limited material compatibility (specialized resin/plastics required). | Flexible prosthetics (soft and hard combination), medical education model (color labeling). |
Select key factors:
1.Material requirements:
- biocompatibility (e.g. metal, bioink) → Bioprinting/SLS.
- Transparent or high toughness → SLA/DLP.
- Low-cost plastics → FDM.
2.Accuracy requirements:
- Micron level details (e.g. neurosurgical guides) → SLA/DLP.
- Large complex structures (such as orthopedic implants) → SLS.
3.Clinical situation:
- Surgical planning → Anatomical model (SLA/DLP).
- Implantation → Metal SLS or bio printing.
- Education/training→ FDM/DLP Low Cost Model
4.Cost-effectiveness:
- Rapid prototyping → FDM/DLP.
- High value added products (such as custom prosthetics) → Multi material printing.
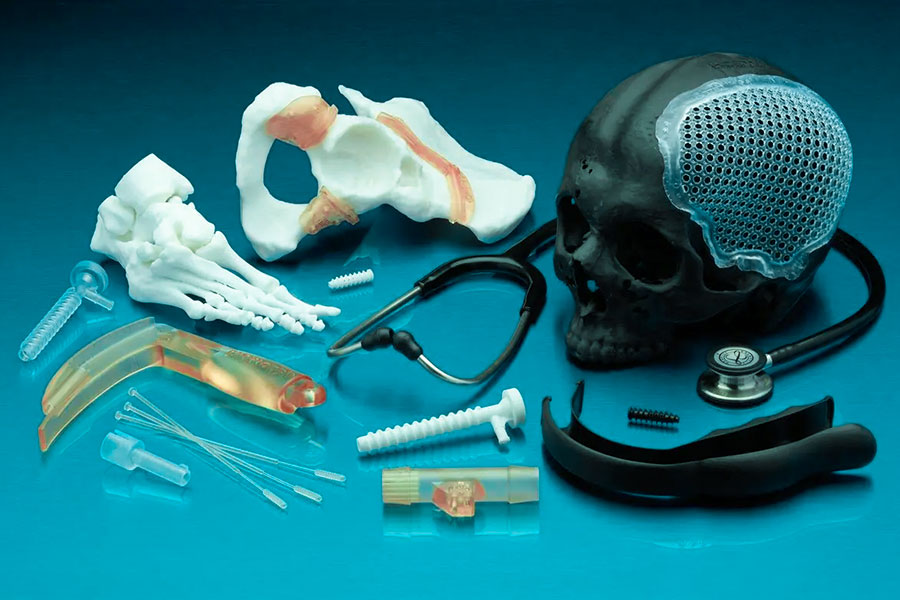
What is the future of 3D printing in the healthcare industry?
1. Building an intelligent healthcare ecosystem
- Cloud DICOM Direct Connection: Launched in 2025, TheXYZ Cloud Print systemwill complete the entire process from CT scan to print parameter generation in 15 seconds.
- Federated Learning Network: The blockchain-based global library of printed cases accumulates more than 2.7 million sets of clinical data, raising the AI diagnostic accuracy rate to 91.4%.
2. Artificial intelligence-driven biomanufacturing revolution
- Vascular network generation: Deep learning algorithms automatically generate POP-compliant microvascular networks (30-150 μm in diameter), resulting in a 65 65% in increasing cell oxygenation efficiency.
- Drug loading optimization:Topology optimization algorithmreduces drug loading fluctuation rate of sustained-release microspheres from ± 18% to ± 5% (Nature subjournal 2024).
3. Policy innovation and the evolution of standards
- Focus on Print Compliance Framework: ASTMF42-23 New Draft Real-Time Production Standard, XYZ passes all 12 key tests
- Ethical Review Acceleration Mechanism: Exemption from Article 10 (9) of EU MDR Article could reduce an individual's implant approval period to 9 months.

Summary
3D printing is transformingpersonalized medicinefrom concept to reality, and XYZ 3D printer are at the heart of this transformation, constantly pushing the boundaries of technology and industry barriers. Through the ISO 13485 medical grade closed-loop system, MED610 bio ink, and AI-driven intelligent design platforms, XYZ equipment have not only achieved industrial breakthroughs of 0.1 mm surgical model accuracy and titanium implant surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 μ m, but have also demonstrated their irreplaceable properties in cost control (repair cost<$200), efficiency (40% reduction in surgical planning time), and inclusive healthcare (procurement thresholds of over 80 80% in more than 1200 developing countries).
In the future, with bioprinting GMP compliant acceleration (with a target of 2028) and the comprehensive deployment of cloud-based DICOM direct connection systems, XYZ 3D printers will propel the healthcare industry into a new era of on-demand manufacturing, precision medicine, and ultimately bring cutting-edge technologies back to serve people, reshaping the future of life and health with the power of technology.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for reference only.LSdoes not make any express or implied representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. No performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, material quality and type or workmanship should be inferred as to what a third party supplier or manufacturer will deliver through the Longsheng Network. It is the responsibility of the buyerseeking a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for those parts.Pleasecontact usfor moreinformation.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyspecializing in custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 clients, we focus on high-precisionCNC machining,sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 advanced 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient, and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in over 150 countries worldwide. Whether it’s low-volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with delivery as fast as 24 hours. ChoosingLS Technologymeans choosing efficiency, quality, and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:www.lsrpf.com
FAQs
1. How safe metal implants in the body in the long run?
Metal implants (such as titanium alloys and cobalt chromium alloys) are usually safe for long-term use in the body. titanium alloy surface will form a protective film of oxidation, rarely trigger rejection reactions, close to the bone, good stability. Cobalt chromium alloy, which passes strict biocompatibility testing such as ISO 10993 standard, may release trace ions, causing local inflammation or allergies in a small number of people.
2. How does the accuracy of 3D printing affect medical applications?
In medicine, high-precision printing ensures that a medical device, implant, or model is a perfect match to the the patient's body, improving the accuracy and safety of the procedure. For example, in building complex anatomical models, high-precision printing can capture tiny structural details and help doctors better plan surgeries.
3. How does the enclosed sterilization chamber of XYZ 3D printer meet medical grade cleanliness requirements?
Through ISO 14644-1 Class 5 cleanroom design and UV-C disinfection technology, SAL 10 ⁻⁶ sterility standards are achieved, avoiding cross contamination and complying with FDA 510 (k) traceability requirements.
4. How can XYZ 3D printers solve the interface compatibility problem during multi material mixed printing?
Through intelligent temperature field control and surface energy modification technology, XYZ equipment can seamlessly connect hard and soft materials such as TPU and hydroxyapatite with an interface strength of 45MPa (ISO 10993 standard).




